C. elegans studies uncover roles for eicosanoids in development and stress
Eicosanoids are powerful, short-range signaling molecules derived by oxygenation of 20-carbon polyunsaturated fatty acids, or PUFAs. These effectors, including prostaglandins, leukotrienes and thromboxanes, are produced in mammals by cyclooxygenase and lipoxygenase enzymes and act as regulators of pain, inflammation, immunity, blood pressure and reproduction. Two recent studies indicate that eicosanoids generated by cyclooxygenase-independent pathways mediate reproductive and behavioral functions in the roundworm Caenorhabditis elegans.
Prostaglandins and other eicosanoids are produced in many invertebrates, although their precise functions in physiology are not well understood. There is no evidence for cyclooxygenase or lipoxygenase enzyme activities in C. elegans, even though these nematodes synthesize a wide range of 20-carbon PUFAs, including arachidonic acid and eicosapentaenoic acid (See Tanaka et al, andWatts et al, 2002). Synthesis of PUFAs is important, because C. elegans mutants that lack the ability to insert double bonds in fatty acids display a range of developmental and neurological defects (See Watts et al, 2002, Kahn-Kirby et al, Watts et al, 2003 and Lesa et al). The new studies describe crucial functions for specific eicosanoids derived from PUFAs.
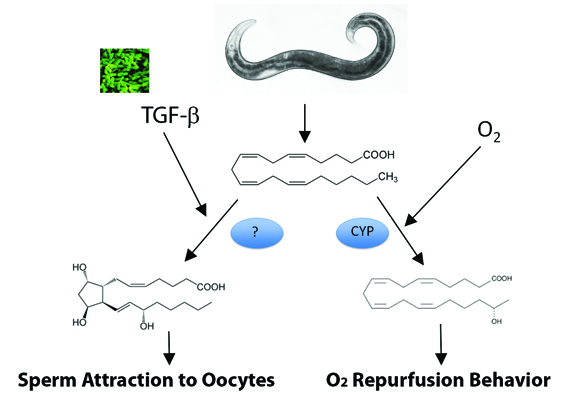
Sperm must locate an oocyte for successful reproduction. In C. elegans, sperm attraction to oocytes requires PUFAs, which are precursors for F-class prostaglandins synthesized independently of cyclooxygenase activity (See Edmonds et al, Hoang et al, 2013 and Kubagawa et al 2006). Recently, Michael Miller’s group at the University of Alabama showed that pheromone-sensing neurons in the C. elegans nose secrete a TGF-β ligand that stimulates the cyclooxygenase-independent synthesis of PGF1α and PGF2α in the germ line during favorable growth conditions. When food is limited and nematode crowding occurs, secreted ascaroside pheromones reduce TGF-β production. TGF-β levels in neurons signal through conserved pathways to regulate R-Smad activity in developing oocytes, which inhibits the conversion of PUFAs into F-class prostaglandins. When fewer prostaglandins are produced by oocytes, sperm are less efficient at locating the fertilization site, leading to reduced fertilization rate. Thus, environmental conditions sensed by females ultimately affect sperm function.
The C. elegans genome also encodes several PUFA-metabolizing cytochrome P450 enzymes, or CYPs, which convert eicosapentaenoic acid and arachidonic acid to epoxide and hydroxyl derivatives (See Kulas et al, and Kosel et al). A recent study from H. Robert Horvitz’s lab at the Massachusetts Institute of Technology used an unbiased genetic screen to discover a role for polyunsaturated fatty acids and CYP-13A12 in an eicosanoid-mediated response to a movement behavior that occurs after oxygen deprivation followed by reoxygenation. In mammals, oxygen deprivation followed by reoxygenation causes reperfusion injury due to inflammation and oxidative damage. In C. elegans, this damage can be modeled by examining movement increases that occur after the transfer of worms from no oxygen to 20 percent oxygen. The EGL-9 protein uses molecular oxygen to hydroxylate the hypoxia-inducing factor, or HIF, inhibiting HIF transcriptional activity. Pre-exposure to low oxygen concentrations or inhibition of EGL-9 activity protects mammals from reperfusion injury and blocks the C. elegans movement response. The Horvitz study showed that in the presence of oxygen, CYP-13A12 produces eicosanoids that drive the reperfusion response.
Thus, C. elegans provides a means to dissect phenotypes and pathways employing cyclooxygenase-independent synthesis of eicosanoids. Importantly, cyclooxygenase-independent synthesis of F-class prostaglandins also has been observed in mammals. Furthermore, CYP-generated eicosanoids likely are involved in more diverse physiological responses than previously appreciated.
Enjoy reading ASBMB Today?
Become a member to receive the print edition four times a year and the digital edition monthly.
Learn moreGet the latest from ASBMB Today
Enter your email address, and we’ll send you a weekly email with recent articles, interviews and more.
Latest in Science
Science highlights or most popular articles

Lipid-lowering therapies could help treat IBD
Genetic evidence shows that drugs that reduce cholesterol or triglyceride levels can either raise or lower inflammatory bowel disease risk by altering gut microbes and immune signaling.

Key regulator of cholesterol protects against Alzheimer’s disease
A new study identifies oxysterol-binding protein-related protein 6 as a central controller of brain cholesterol balance, with protective effects against Alzheimer’s-related neurodegeneration.

From humble beginnings to unlocking lysosomal secrets
Monther Abu–Remaileh will receive the ASBMB’s 2026 Walter A. Shaw Young Investigator Award in Lipid Research at the ASBMB Annual Meeting, March 7-10 in Washington, D.C.

Chemistry meets biology to thwart parasites
Margaret Phillips will receive the Alice and C. C. Wang Award in Molecular Parasitology at the ASBMB Annual Meeting, March 7-10 in Washington, D.C.

ASBMB announces 2026 JBC/Tabor awardees
The seven awardees are first authors of outstanding papers published in 2025 in the Journal of Biological Chemistry.

Missing lipid shrinks heart and lowers exercise capacity
Researchers uncovered the essential role of PLAAT1 in maintaining heart cardiolipin, mitochondrial function and energy metabolism, linking this enzyme to exercise capacity and potential cardiovascular disease pathways.

