How HCMV hijacks host cells — and beyond
Over 200 viruses infect humans, and all rely on living host cells to survive. In doing so, they induce striking changes to the cell and its environment. Scientists like Ileana Cristea are investigating these changes to better understand the complex virus–host relationship.

Cristea recently shared her research on the American Society for Biochemistry and Molecular Biology webinar Breakthroughs, a series highlighting research from ASBMB journals. A professor of molecular biology and director of graduate studies at Princeton University, she also serves as editor-in-chief of Molecular & Cellular Proteomics. During her talk, sponsored by MCP, Cristea discussed how viral infections reshape organelles and cellular metabolism and how these changes relate to broader disease biology.
One key intracellular change during viral infection, Cristea said, is organelle remodeling. Organelles — such as mitochondria, which drive energy production, and the endoplasmic reticulum, or ER, which synthesizes proteins and lipids — are often disrupted by viruses.
“Diverse viruses that infect so many different types of cells (and) have different replication strategies, different genomes, they're united by this need to induce organelle remodeling,” she said.
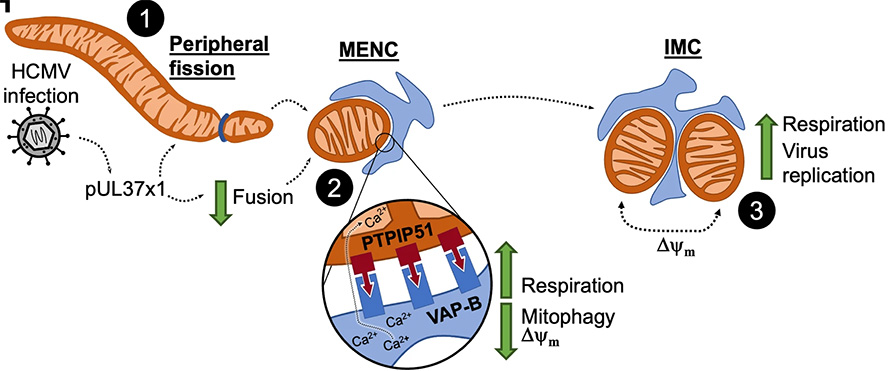
Cristea and colleagues observed that cells infected with human cytomegalovirus, or HCMV, a double-stranded DNA virus, exhibited mitochondrial fragmentation; but, in HCMV-infected cells, it surprisingly increased cellular respiration. The team turned to mass spectrometry-based proteomics and microscopy to investigate.
They discovered a novel organelle–organelle interaction: small mitochondrial fragments induced by HCMV infection became encased in ER pockets. They named these new structures mitochondria–ER encapsulations, or MENCs. Studies across various HCMV strains and cell types confirmed MENCs as a consistent feature of late-stage infection.
Additional work revealed that MENCs helped sustain high cellular respiration, ultimately benefiting the virus. Similar patterns of elevated metabolism despite mitochondrial fragmentation had been seen in other diseases.
“When we thought about this, we immediately thought about cancer, because HCMV is known to be also an oncomodulatory virus, and in cancer, we see mitochondrial fragmentation,” Cristea said.
In metastatic melanoma cells, the team observed the same phenomenon: fragmented mitochondria encapsulated in MENCs with high bioenergetic activity — and MENC formation correlated with greater cancer severity.
In addition to organelle remodeling, viral infection disrupts metabolism, notably increasing levels of the byproduct lactate. While lactate is known to dampen immunity in cancer, its role in viral infection was unclear.
In a recent study, Cristea’s team found that treating cells with lactate enhanced viral replication. Proteomics analysis of cells infected with HCMV, or the herpes simplex 1 virus, called HSV-1, showed lactate-modified host defense proteins. This lactylation, occurring in intrinsically disordered regions, inhibited immune signaling and promoted infection.
Cristea’s research also explores how viruses influence the space outside infected cells. Her team found that viruses can alter the surrounding microenvironment to promote infection. Using a fluorescence-based assay, they observed that infection in one cell disrupted cell division and weakened immune responses in neighboring cells. This priming helped HCMV, HSV-1 and influenza viruses spread more easily.
“We thought initially that (the neighboring cells should) be ready for defense because this cell is becoming infected, but actually they have dampened immunity,” she said.
While much of Cristea’s work has largely focused on viral infections, her lab is now exploring whether the same cellular mechanisms underlie other diseases, including cancer.
In case you missed it, here's the full Breakthroughs webinar.
Enjoy reading ASBMB Today?
Become a member to receive the print edition four times a year and the digital edition monthly.
Learn moreGet the latest from ASBMB Today
Enter your email address, and we’ll send you a weekly email with recent articles, interviews and more.
Latest in Science
Science highlights or most popular articles

The data that did not fit
Brent Stockwell’s perseverance and work on the small molecule erastin led to the identification of ferroptosis, a regulated form of cell death with implications for cancer, neurodegeneration and infection.

Building a career in nutrition across continents
Driven by past women in science, Kazi Sarjana Safain left Bangladesh and pursued a scientific career in the U.S.

Avoiding common figure errors in manuscript submissions
The three figure issues most often flagged during JBC’s data integrity review are background signal errors, image reuse and undeclared splicing errors. Learn how to avoid these and prevent mistakes that could impede publication.

Ragweed compound thwarts aggressive bladder and breast cancers
Scientists from the University of Michigan reveal the mechanism of action of ambrosin, a compound from ragweed, selectively attacks advanced bladder and breast cancer cells in cell-based models, highlighting its potential to treat advanced tumors.

Lipid-lowering therapies could help treat IBD
Genetic evidence shows that drugs that reduce cholesterol or triglyceride levels can either raise or lower inflammatory bowel disease risk by altering gut microbes and immune signaling.

Key regulator of cholesterol protects against Alzheimer’s disease
A new study identifies oxysterol-binding protein-related protein 6 as a central controller of brain cholesterol balance, with protective effects against Alzheimer’s-related neurodegeneration.