Exploring lipid metabolism: A journey through time and innovation
Year after year, groundbreaking research in lipid metabolism fuels new discoveries, transforming our understanding of cellular function and unlocking potential treatments for metabolic disorders and neurodegenerative diseases. At the American Society for Biochemistry and Molecular Biology annual meetings, scientists come together to share the latest breakthroughs — each study building on the last — to push the boundaries of what’s possible in basic research and clinical innovation.
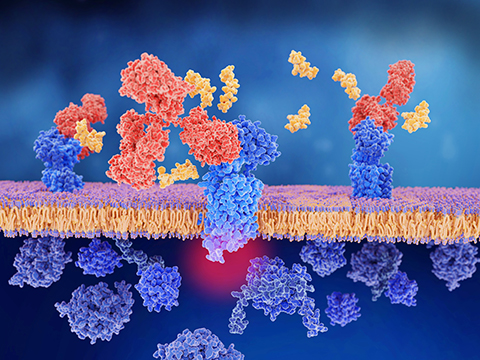
Membrane dynamics and lipid–protein interactions
Lipid–protein interactions are central to maintaining cell membrane integrity, signaling, and protein activity. Disruptions in these interactions have been linked to diseases like Alzheimer's, cardiovascular disorders and autoimmune diseases, making them crucial targets for therapeutic research.
One notable 2022 abstract used cryogenic electron microscopy to explore ABHD5, a regulator of lipid homeostasis. This research revealed how ABHD5 interacts with lipids and regulates adipose triglyceride lipase activity, which is essential for lipid breakdown and energy balance. Mutations in ABHD5 can lead to nonalcoholic fatty liver disease, or NAFLD. Therefore, this research lays a foundation for potential NAFLD gene therapies.
In the same year, an abstract on NAFLD investigated oxidized phospholipids that are recognized by an antibody. The researchers used a viral vector to express the antibody in the liver, which protected mice from liver damage and fibrosis. This suggests that oxidized phospholipids could serve as biomarkers for NAFLD and offers new therapeutic possibilities targeting lipid abnormalities.
Building on foundational phospholipid research from previous years, a 2024 abstract examined how extracellular crowding agents affect the membrane binding of antimicrobial peptides like Buforin II. This discovery informs researchers on how to design more effective peptides to combat pathogens.
Another 2024 abstract explored lipid rafts — specialized membrane regions — and their impact on the human follicle-stimulating hormone receptor, or hFSHR, crucial for fertility. Mutations in the receptor motif that binds the membrane protein caveolin disrupted signaling, impairing spermatogenesis. These findings emphasize the importance of lipid–protein interactions in cellular function and health.
These studies advance lipid science by examining how lipids and proteins interact to influence cellular function and disease progression. Lipidomics research highlights the diagnostic potential of specific lipid species, while studies on caveolae — lipid-rich membrane domains — demonstrate how membrane structure regulates signaling pathways. Furthermore, research on oxidized phospholipids connects these molecules to oxidative stress in NAFLD, while investigations into the membrane protein caveolin reveal its role in controlling stress-related signaling.
By targeting these lipid–protein interactions, researchers may unlock new therapeutic strategies for NAFLD, reproductive disorders and endothelial dysfunction.
Future of lipid science
Lipid metabolism research is evolving quickly, with breakthroughs reshaping our understanding of cellular function, disease progression and treatment options. Whether you're a researcher, clinician or science enthusiast, ASBMB meetings provide a unique opportunity to engage with the latest advancements in lipid science.
Stay up to date with the field and join us in shaping the future of lipid metabolism research. Register for the ASBMB annual meeting and be part of this exciting journey.
For lipid-focused sessions at #ASBMB25, check out the symposium on lipids and membranes, organized by Gerry Hammond of the University of Pittsburgh and Judith Simcox of the University of Wisconsin–Madison.
Enjoy reading ASBMB Today?
Become a member to receive the print edition four times a year and the digital edition monthly.
Learn moreFeatured jobs
from the ASBMB career center
Get the latest from ASBMB Today
Enter your email address, and we’ll send you a weekly email with recent articles, interviews and more.
Latest in Science
Science highlights or most popular articles

Building a career in nutrition across continents
Driven by past women in science, Kazi Sarjana Safain left Bangladesh and pursued a scientific career in the U.S.

Avoiding common figure errors in manuscript submissions
The three figure issues most often flagged during JBC’s data integrity review are background signal errors, image reuse and undeclared splicing errors. Learn how to avoid these and prevent mistakes that could impede publication.

Ragweed compound thwarts aggressive bladder and breast cancers
Scientists from the University of Michigan reveal the mechanism of action of ambrosin, a compound from ragweed, selectively attacks advanced bladder and breast cancer cells in cell-based models, highlighting its potential to treat advanced tumors.

Lipid-lowering therapies could help treat IBD
Genetic evidence shows that drugs that reduce cholesterol or triglyceride levels can either raise or lower inflammatory bowel disease risk by altering gut microbes and immune signaling.

Key regulator of cholesterol protects against Alzheimer’s disease
A new study identifies oxysterol-binding protein-related protein 6 as a central controller of brain cholesterol balance, with protective effects against Alzheimer’s-related neurodegeneration.

From humble beginnings to unlocking lysosomal secrets
Monther Abu–Remaileh will receive the ASBMB’s 2026 Walter A. Shaw Young Investigator Award in Lipid Research at the ASBMB Annual Meeting, March 7-10 in Washington, D.C.


