Scavenger protein receptor aids the transport of lipoproteins
Lipoproteins are spherical molecules made up of fat and proteins that play a crucial role in transporting lipids, such as cholesterol and triglycerides, from the liver to other tissues in the body. Anton Potapenko of the University of Zurich, and a team in Switzerland recently published a study in the Journal of Lipid Research detailing structural characteristics of the scavenger receptor B1, or SCARB1, a protein that mediates lipid exchange between many cell types and facilitates uptake of high density lipoproteins, or HDL, and low density lipoproteins, or LDL, in some cell types. The gene encoding SCARB1 produces two major splice variants that share structural similarities but differ in their carboxy-terminal domains. Researchers wanted to understand if these splice variants play different roles in the cellular uptake of LDL and HDL by endothelial cells.
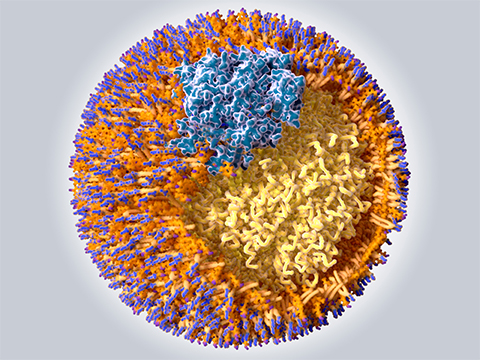
The researchers examined cultured endothelial cells to understand how expression of the two SCARB1 variants affected the binding, uptake and trafficking of lipoproteins. They found that variants 1 and 2 localized to the cell surface, and endosomes and lysosomes, respectively. Overexpression of variant 1 increased both HDL and LDL binding and uptake. However, overexpression of variant 2 also increased the uptake of either lipoprotein, but not via surface binding. Therefore, the researchers concluded that variant 2 facilitates lipoprotein uptake indirectly by regulatory and indirect mechanisms.
The study suggests that the two major splice variants of SCARB1 facilitate transendothelial transport of HDL and LDL by different mechanisms, either dependent or independent of the adapter proteins. Because of the limitations of overexpression, it will be important to examine how eliminating each SCARB1 splice variant affects cellular lipid metabolism and lipoprotein trafficking.
Enjoy reading ASBMB Today?
Become a member to receive the print edition four times a year and the digital edition monthly.
Learn moreGet the latest from ASBMB Today
Enter your email address, and we’ll send you a weekly email with recent articles, interviews and more.
Latest in Science
Science highlights or most popular articles

The data that did not fit
Brent Stockwell’s perseverance and work on the small molecule erastin led to the identification of ferroptosis, a regulated form of cell death with implications for cancer, neurodegeneration and infection.

Building a career in nutrition across continents
Driven by past women in science, Kazi Sarjana Safain left Bangladesh and pursued a scientific career in the U.S.

Avoiding common figure errors in manuscript submissions
The three figure issues most often flagged during JBC’s data integrity review are background signal errors, image reuse and undeclared splicing errors. Learn how to avoid these and prevent mistakes that could impede publication.

Ragweed compound thwarts aggressive bladder and breast cancers
Scientists from the University of Michigan reveal the mechanism of action of ambrosin, a compound from ragweed, selectively attacks advanced bladder and breast cancer cells in cell-based models, highlighting its potential to treat advanced tumors.

Lipid-lowering therapies could help treat IBD
Genetic evidence shows that drugs that reduce cholesterol or triglyceride levels can either raise or lower inflammatory bowel disease risk by altering gut microbes and immune signaling.

Key regulator of cholesterol protects against Alzheimer’s disease
A new study identifies oxysterol-binding protein-related protein 6 as a central controller of brain cholesterol balance, with protective effects against Alzheimer’s-related neurodegeneration.

