High-fat diet ‘turns up the thermostat’ on atherosclerosis
In a recent study, researchers determined that derivatives of natural emulsifiers such as phospholipids found in high-fat, high-cholesterol diets can promote atherosclerosis via gut bacteria interactions with the immune system. This study could pave the way for targeted interventions for individuals who are at risk for developing heart disease.
Obesity and a high-cholesterol, high-fat diet are both well-established risk factors for atherosclerosis. In fact, obese individuals are two and a half times more likely to develop heart disease. However, the mechanistic link between obesity and atherosclerosis eludes scientists. The researchers behind this new study believe the link may be in how specific derivatives of natural emulsifiers in a Western diet alter the way that cells that line the intestines interact with gut-resident bacteria. The team published their results in the Journal of Lipid Research.
“The gut is the dietary window to the body,” said Srinivasa Reddy, professor of medicine at the University of California Los Angeles and corresponding author on the study.
Atherosclerosis, sometimes called “hardening of the arteries,” is caused by plaque buildup in blood vessels and can interfere with blood flow to critical organs, which can result in heart attack or stroke. These plaques consist of cholesterol, phospholipids and other fats; immune cells; and fibrous components.
“We study natural emulsifiers in the diet called phospholipids,” Alan Fogelman, a professor of medicine at UCLA and project supervisor, said. “For example, if you look at salad dressing and shake it up, it is the phospholipids, or emulsifiers, that keeps the oil in globules. Those emulsifiers can get modified by specific enzymes in the intestinal cells into very potent pro-inflammatory molecules in the body.”
To study the intricate connection between diet and atherosclerosis, the researchers used a mouse model that not only recapitulates the high levels of low-density lipoprotein, or “bad cholesterol,” seen in atherosclerosis patients but also lack the specific enzyme involved in the generation of pro-inflammatory derivatives of natural emulsifiers in the intestinal lining cells. Using this model, the researchers found that on a high-fat high-cholesterol diet, the cells that line the small intestine churn out reactive phospholipids that makes the intestinal lining more susceptible to invasion by the bacteria that live in the gut.
“The normal defenses for intestinal lining cells to keep bacteria in the lumen of the intestine are reduced when they take up large amounts of cholesterol and fat,” Fogelman said. “This also results in bacteria being able to come in direct contact with the cells lining your intestines called enterocytes. Without those defenses, this results in more bacterial products, like bacterial cell membranes that contain a toxin called endotoxin, getting into the bloodstream to cause inflammation.”
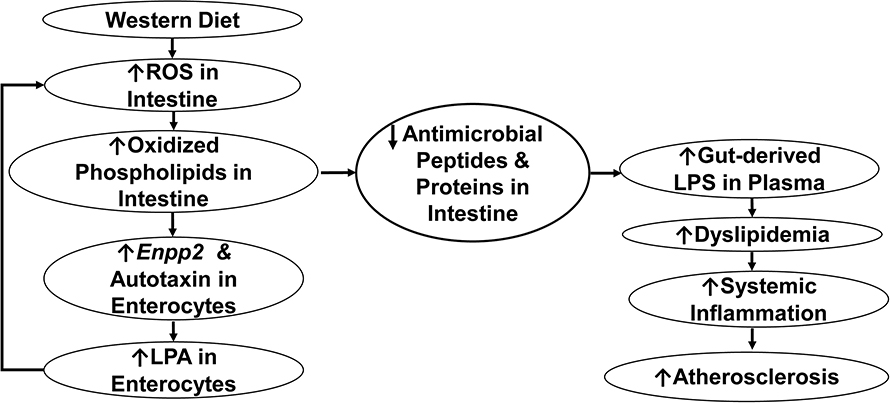
Release of bacterial products from the gut into the blood stream sounds an alarm in the immune system, which deploys immune cells into the blood to eliminate the potential threat.
“People who are obese and people eating high-fat, high-cholesterol diets have higher levels of endotoxin in their blood,” Fogelman said. “It's not at the level of causing sepsis, but it causes a low level of inflammation. When the cholesterol and fat come into the mix, the endotoxin kind of turns up the thermostat on inflammation and that accelerates atherosclerosis and leads to increased heart attacks and strokes.”
The team is looking for ways to reduce the phospholipid derivatives that cause endotoxin to enter the blood stream. One method they have explored previously is using a mimetic of high-density lipoprotein, sometimes called “good cholesterol.”
“We created transgenic tomatoes in our lab that mimic the good cholesterol, high-density lipoprotein,” Arnab Chattopadhyay, project scientist at UCLA and lead author of the study, said. “These tomatoes, when added to a high-fat, high-cholesterol diet, help lower cholesterol and triglycerides and also lower the inflammatory derivatives of the phospholipids.”
The team said that this method of lowering cholesterol levels and triglycerides could be beneficial to obese individuals at risk for inflammatory diseases such as atherosclerosis, arthritis, lupus, multiple sclerosis and more.
Enjoy reading ASBMB Today?
Become a member to receive the print edition four times a year and the digital edition monthly.
Learn moreGet the latest from ASBMB Today
Enter your email address, and we’ll send you a weekly email with recent articles, interviews and more.
Latest in Science
Science highlights or most popular articles

The data that did not fit
Brent Stockwell’s perseverance and work on the small molecule erastin led to the identification of ferroptosis, a regulated form of cell death with implications for cancer, neurodegeneration and infection.

Building a career in nutrition across continents
Driven by past women in science, Kazi Sarjana Safain left Bangladesh and pursued a scientific career in the U.S.

Avoiding common figure errors in manuscript submissions
The three figure issues most often flagged during JBC’s data integrity review are background signal errors, image reuse and undeclared splicing errors. Learn how to avoid these and prevent mistakes that could impede publication.

Ragweed compound thwarts aggressive bladder and breast cancers
Scientists from the University of Michigan reveal the mechanism of action of ambrosin, a compound from ragweed, selectively attacks advanced bladder and breast cancer cells in cell-based models, highlighting its potential to treat advanced tumors.

Lipid-lowering therapies could help treat IBD
Genetic evidence shows that drugs that reduce cholesterol or triglyceride levels can either raise or lower inflammatory bowel disease risk by altering gut microbes and immune signaling.

Key regulator of cholesterol protects against Alzheimer’s disease
A new study identifies oxysterol-binding protein-related protein 6 as a central controller of brain cholesterol balance, with protective effects against Alzheimer’s-related neurodegeneration.

