Unexpected roles of lipid kinases
Phospholipids are not mere structural components of animal cell membranes. Many of their metabolites are physiologically functional and are pivotal in intracellular signaling. Of those, diacylglycerol, or DAG, is a second messenger activating proteins containing a C1 domain, such as protein kinase C.
Evidence shows that phorbol esters, synthetic functional analogues of DAG, constitutively activate signal transduction pathways that lead to tumor formation. Thus, normal cells must regulate DAG levels within the physiological range. DAG kinases, or DGKs, are the key enzymes that regulate DAG levels. DGK phosphorylates DAG to phosphatidic acid, another lipid messenger molecule. DGKs are thought to be involved in the balanced control of these two lipid messenger signaling systems.
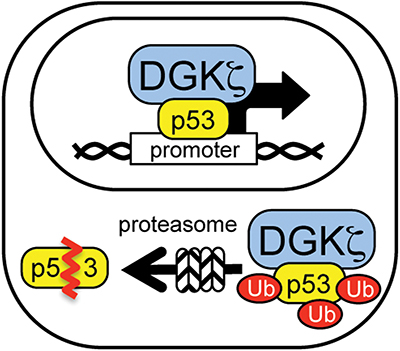 Functional implications of DGK-zeta in p53 regulation: Nuclear DGK-zeta modulates p53 transcriptional activity; cytoplasmic DGK-zeta facilitates p53 protein degradation.Courtesy of Kaoru Goto
Functional implications of DGK-zeta in p53 regulation: Nuclear DGK-zeta modulates p53 transcriptional activity; cytoplasmic DGK-zeta facilitates p53 protein degradation.Courtesy of Kaoru Goto
DGKs differ in their molecular structure, enzymatic activity, subcellular localization and binding partners. One DGK, DGK-zeta, contains both a nuclear localization signal and nuclear export signal (1), suggesting a shuttling between the nucleus and the cytoplasm. Morphological studies on animal tissues report that DGK-zeta predominantly localizes to the nucleus in some cell types, while it exhibits both nuclear and cytoplasmic localization in others. DGK-zeta translocates from the nucleus to the cytoplasm in hippocampal neurons under stress conditions such as transient ischemia and seizures, and appears to be involved in stress responses.
What roles are assigned to DGK-zeta in the nucleus and the cytoplasm? Current data suggest that nucleocytoplasmic shuttling of DGK-zeta in neurons has a dual effect: While decreased levels of nuclear DGK-zeta lead to suppression of p53 transcriptional activity, increased levels of cytoplasmic DGK-zeta facilitate p53 protein degradation. Recent studies reveal that DGK-zeta associates with p53, and DGK-zeta deletion suppresses p53 transcriptional activity under basal and DNA-damage conditions (2). DGK-zeta association with p53 facilitates cytoplasmic degradation of p53 through the ubiquitin proteasome system, or UPS. DGK-zeta deficiency, therefore, results in increased p53 levels. Another study showed that DGK-zeta is degraded after cytoplasmic translocation in neurons, leading to increased levels of p53 protein and aberrant cell cycle reentry. In all, the levels of cytoplasmic DGK-zeta may serve as a supressor for p53 by facilitating its degradation, thus suppressing its cytotoxic effects.
What are the potential effects of DGK-zeta on other transcription factors? Nuclear factor kappa-light-chain-enhancer of activated B cells, or NF-kappaB, for example, is important in numerous biological processes, particularly immune response. A recent study showed that DGK-zeta knockdown enhances the NF-kappaB pathway in response to inflammatory cytokines. DGK-zeta downregulation accelerates phosphorylation of the p65 subunit and its nuclear translocation, increasing NF-kappaB transactivation activity. These reports suggest that DGK-zeta exerts a regulatory effect on p53 and NF-kappaB (3).
A key question is determining the molecular mechanisms exerted by DGK-zeta on p53 and NF-kappaB. We want to know whether DGK-zeta catalytic activity, which alters the balance of DAG and phosphatidic acid in the nucleus and cytoplasm, is essential. How DGK activity modulates transcriptional activities is not known, but it turns out that p53 degradation mediated through cytoplasmic DGK-zeta and UPS is not kinase activity–dependent. We have found unexpected roles of DGK-zeta on transcription factors; there is much to learn about how lipid-metabolizing enzymes impact cellular signaling involved in transcriptional regulation.
References
1. Goto, K. & Kondo, H. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA.93, 11196-11201 (1996).
2. Tanaka, T. et al. J. Cell Sci.126, 2785-2797 (2013).
3. Tanaka, T. et al. Adv. Biol. Regul.60, 15-21 (2016).
Enjoy reading ASBMB Today?
Become a member to receive the print edition four times a year and the digital edition monthly.
Learn moreGet the latest from ASBMB Today
Enter your email address, and we’ll send you a weekly email with recent articles, interviews and more.
Latest in Science
Science highlights or most popular articles

The data that did not fit
Brent Stockwell’s perseverance and work on the small molecule erastin led to the identification of ferroptosis, a regulated form of cell death with implications for cancer, neurodegeneration and infection.

Building a career in nutrition across continents
Driven by past women in science, Kazi Sarjana Safain left Bangladesh and pursued a scientific career in the U.S.

Avoiding common figure errors in manuscript submissions
The three figure issues most often flagged during JBC’s data integrity review are background signal errors, image reuse and undeclared splicing errors. Learn how to avoid these and prevent mistakes that could impede publication.

Ragweed compound thwarts aggressive bladder and breast cancers
Scientists from the University of Michigan reveal the mechanism of action of ambrosin, a compound from ragweed, selectively attacks advanced bladder and breast cancer cells in cell-based models, highlighting its potential to treat advanced tumors.

Lipid-lowering therapies could help treat IBD
Genetic evidence shows that drugs that reduce cholesterol or triglyceride levels can either raise or lower inflammatory bowel disease risk by altering gut microbes and immune signaling.

Key regulator of cholesterol protects against Alzheimer’s disease
A new study identifies oxysterol-binding protein-related protein 6 as a central controller of brain cholesterol balance, with protective effects against Alzheimer’s-related neurodegeneration.


