Blood Cancer Awareness Month 2021
For some people, the thought of blood is a scary thing and the mere sight of it would make them queasy. As a Type 1 diabetic, I see my blood every day in the form of droplets induced by repeated finger pricks. This makes me quite comfortable with blood, and the information I obtain from this monitoring is essential to my care. A single drop reveals a metric that governs my ability to correctly dose insulin and a means for my endocrinologist to evaluate the effectiveness of my therapy.
If one drop can provide so much knowledge for me, imagine the impact an entire sample can have for medical staff to better understand the illness of a new patient. Many of us have had antibody tests performed to evaluate our adaptive immune response's ability to protect us from COVID-19. Even still exists hundreds of antibody tests to detect the levels of proteins important for diagnosis, prognosis, disease progression and so much more. Moral of the story: Our blood provides us with invaluable data that is key for us to living healthy lives.
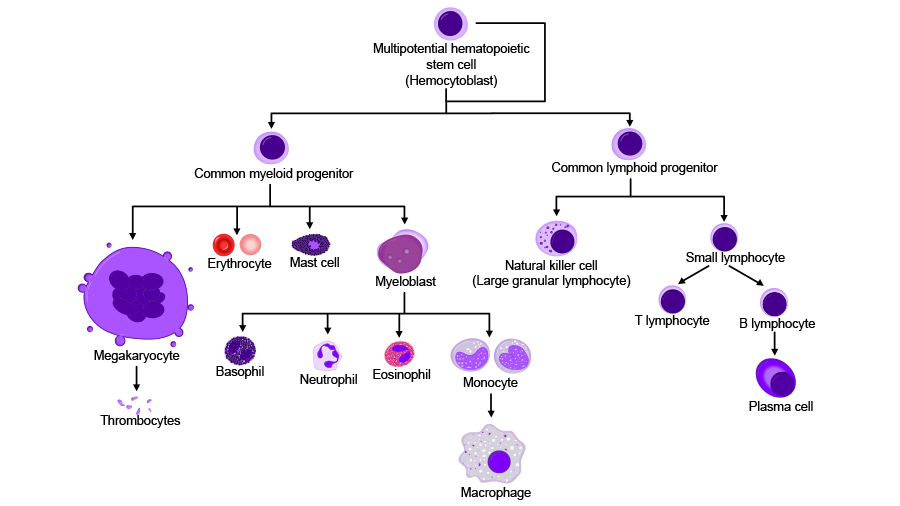
Sometimes, it is the actual blood cells which are being monitored (see image above). These include red blood cells (erythrocytes), white blood cells (leukocytes) and platelets (thrombocytes). Each one of these plays an important role in normal human development and function, and each type is maintained at a level within a specific range. In the case of blood cancer, the levels of these normally functioning blood cells are abnormal (high or low). Mutated blood cells don't do their job very well and will crowd out healthy cells in the bloodstream causing a range of side effects related to the specific role of the healthy cells.
There are three main forms of blood cancer: leukemia, lymphoma and myeloma. Despite the simplicity of that statement, there is incredible diversity and stratification in each one of these forms of blood cancer that create unique and often challenging experiences for oncologists who treat them. An excellent overview of these forms can be found here, with details on the distinct classes of each found in the links above.
In the face of any cancer diagnosis, including blood cancers, it is important to carry an optimistic (or sanguine) attitude. In the past decade, we have advanced not only our understanding of the pathogenesis of blood cancers, but we also have adapted innovative methods for treating patients. These targeted therapies lead to long-term remission in what once were hopeless conditions.
Researchers are working to better understand how blood cancer initiates and what we can do to develop effective therapies and cures. For a glimpse into the many exciting blood cancer-related papers published in the last year in ASBMB journals, check out the links below. As September represents Blood Cancer Awareness Month, take some time to learn more about a cancer that affects someone in the U.S. every three minutes.
Enzyme’s catalytic activity plays important role to prevent lymphoid malignancies
A translational team of researchers from Florida and Nebraska used genetic approaches to understand how mutations in a DNA methyltransferase enzyme impair its tumor suppressor activities. Using mice with germline inactivation as well as catalytically inactive DNMT3b, the team found that this multifunctional enzyme that is important for the regulation of genes for development and generation of blood cells is mutated in various lymphomas as well as lymphocytic leukemia. To learn more about the techniques used and their findings read their Journal of Biological Chemistry manuscript.
Multifaceted transcription factor implicated in hematopoietic differentiation
Scientists at Yale University recently shared a comprehensive review of myocardin-related transcription factor A (MRTFA), a transcriptional coactivator that was first uniquely identified to be involved in a chromosomal translocation event that fused the gene of MRTFA with a gene for an RNA-binding protein. This translocation was unique to a subtype of acute megakaryoblastic leukemia and resulted in the pathophysiology of the disease by allowing the proliferation of abnormal megakaryocytes (platelet precursor cells) and affecting levels of red blood cells in circulation. The work presented in JBC aims to shed light into the mechanisms by which MRTFA functions in malignant hematopoiesis and provide direction for future research efforts for further investigation. Read up this important protein.
Membrane protein expression and interactions are associated with clinical outcomes in leukemia
A multidisciplinary team of researchers from Brazil, Norway and the Netherlands used immunoprecipitation, mass spectrometry and label-free protein quantification to evaluate the gene expression profile of acute myeloid leukemia cells (AML) lacking non-T cell activation linker (NTAL), a lipid raft membrane protein that interacts with a host of binding partners to regulate downstream signaling cascades important for leukemic development. They found that knockdown of this protein in AML decreased the survival of AML cells, that patients with AML express high levels of NTAL, and that several dozen proteins that interact with NTAL can predict overall survival in AML patients. To learn more about their results, read their findings in the journal Molecular & Cellular Proteomics.
Enjoy reading ASBMB Today?
Become a member to receive the print edition four times a year and the digital edition monthly.
Learn moreGet the latest from ASBMB Today
Enter your email address, and we’ll send you a weekly email with recent articles, interviews and more.
Latest in Science
Science highlights or most popular articles

Sizing up cells: How stem cells know when to divide
Stanford University researchers find that stem cells control their size early in cell division across living multicellular systems.

When oncogenes collide in brain development
Researchers at University Medical Center Hamburg, found that elevated oncoprotein levels within the Wnt pathway can disrupt the brain cell extracellular matrix, suggesting a new role for LIN28A in brain development.

The data that did not fit
Brent Stockwell’s perseverance and work on the small molecule erastin led to the identification of ferroptosis, a regulated form of cell death with implications for cancer, neurodegeneration and infection.

Building a career in nutrition across continents
Driven by past women in science, Kazi Sarjana Safain left Bangladesh and pursued a scientific career in the U.S.

Avoiding common figure errors in manuscript submissions
The three figure issues most often flagged during JBC’s data integrity review are background signal errors, image reuse and undeclared splicing errors. Learn how to avoid these and prevent mistakes that could impede publication.

Ragweed compound thwarts aggressive bladder and breast cancers
Scientists from the University of Michigan reveal the mechanism of action of ambrosin, a compound from ragweed, selectively attacks advanced bladder and breast cancer cells in cell-based models, highlighting its potential to treat advanced tumors.