Arginine tango
As a means to evade the host immune response, S. aureus uses an enzyme called oleate hydratase, or OhyA, to inactivate antimicrobial unsaturated fatty acids in the membrane that would otherwise inhibit bacterial growth. Research scientists at St. Jude Children’s Research Hospital reported today the structure and catalytic mechanism of OhyA.
Christopher Radka of St. Jude’s Department of Infectious Diseases describes the research during a presentation Tuesday at 2 p.m. EDT at the 2021 ASBMB Annual Meeting, held in conjunction with the Experimental Biology conference.
Radka and colleagues used X-ray crystallography to determine the structure of OhyA. Solving and evaluating multiple OhyA crystal structures highlighted a coordinated dance that occurs between key arginine residues and the unsaturated fatty acid substrate in the active site of the enzyme, a process facilitated by the nucleotide cofactor FAD.
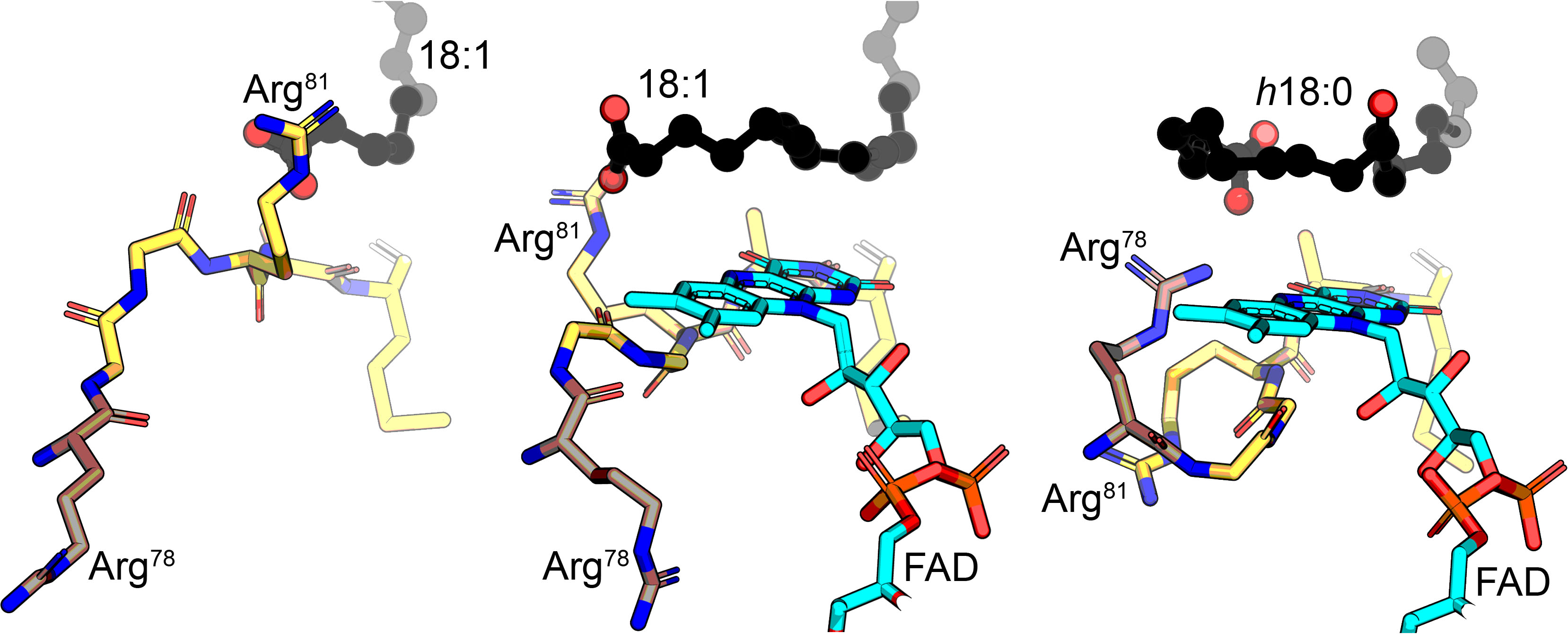
In this dance, the substrate is first guided into the binding tunnel by the oleate carbonyl of OhyA, then encounters its first arginine dance partner (Arg81) at the entrance of the active site. FAD binding then triggers the rotation of Arg81 that guides the fatty acid as it curls into the active site. After catalysis, a second arginine (Arg78) rotates behind the fatty acid carboxyl to release the hydroxylated product from the active site.
“What’s novel about the (active site) is how these conserved arginines guide the substrate through the donut-shaped active site,” Radka said. “Here, the arginines dance like two partners in a tango.”
This highly choreographed dance controls how the fatty acid substrate moves into and out of the active site. “In this coordinated tango at the active site, the FAD is the dramatic third character whose role is to come in and advance the dance so the chemistry can occur,” Radka said.
In this reaction, FAD remains oxidized and unconsumed. This quality is advantageous for industrial biotechnology research looking to use OhyA; FAD-dependent reactions often consume FADH2 and require continued starting product, which can be costly.
Future goals for this research include determining the structural elements required for S. aureus OhyA to remove antimicrobial fatty acids from the membrane.
Enjoy reading ASBMB Today?
Become a member to receive the print edition four times a year and the digital edition monthly.
Learn moreGet the latest from ASBMB Today
Enter your email address, and we’ll send you a weekly email with recent articles, interviews and more.
Latest in Science
Science highlights or most popular articles

When oncogenes collide in brain development
Researchers at University Medical Center Hamburg, found that elevated oncoprotein levels within the Wnt pathway can disrupt the brain cell extracellular matrix, suggesting a new role for LIN28A in brain development.

The data that did not fit
Brent Stockwell’s perseverance and work on the small molecule erastin led to the identification of ferroptosis, a regulated form of cell death with implications for cancer, neurodegeneration and infection.

Building a career in nutrition across continents
Driven by past women in science, Kazi Sarjana Safain left Bangladesh and pursued a scientific career in the U.S.

Avoiding common figure errors in manuscript submissions
The three figure issues most often flagged during JBC’s data integrity review are background signal errors, image reuse and undeclared splicing errors. Learn how to avoid these and prevent mistakes that could impede publication.

Ragweed compound thwarts aggressive bladder and breast cancers
Scientists from the University of Michigan reveal the mechanism of action of ambrosin, a compound from ragweed, selectively attacks advanced bladder and breast cancer cells in cell-based models, highlighting its potential to treat advanced tumors.

Lipid-lowering therapies could help treat IBD
Genetic evidence shows that drugs that reduce cholesterol or triglyceride levels can either raise or lower inflammatory bowel disease risk by altering gut microbes and immune signaling.

