cAMP: Mapping a second messenger
Cyclic adenosine 3,5-monophosphate, known as cAMP, acts as what the Nobel prize–winning neuroscientist Paul Greengard called a “second messenger” in regulating cellular functions such as growth and specialization, protein expression, and gene transcription by relaying extracellular signals to the cell’s interior.
In disease, intracellular pathways control cytokine secretion, resistance to toxins and pathological events by balancing the activity of enzymes, which adjust intracellular cAMP levels. Researchers recently have recognized that receptors can regulate cAMP production not only from the cell surface but also from intracellular membranes.
cAMP can diffuse rapidly, but under normal conditions, its concentration varies from place to place within a cell. It can cause highly localized downstream effects, suggesting that cellular compartmentalization underlines selective cellular responses. To investigate the impact of cAMP production when initiated from endocytic vesicles, a team led by Nikoleta Tsvetanova of Duke University and Mark von Zastrow of the University of California, San Francisco, used localized optical stimulation of cAMP synthesis and quantitative mass spectrometry to determine how compartmentalized cAMP production impacts downstream responses assessed through protein phosphorylation. Their study was published in the Journal of Biological Chemistry.
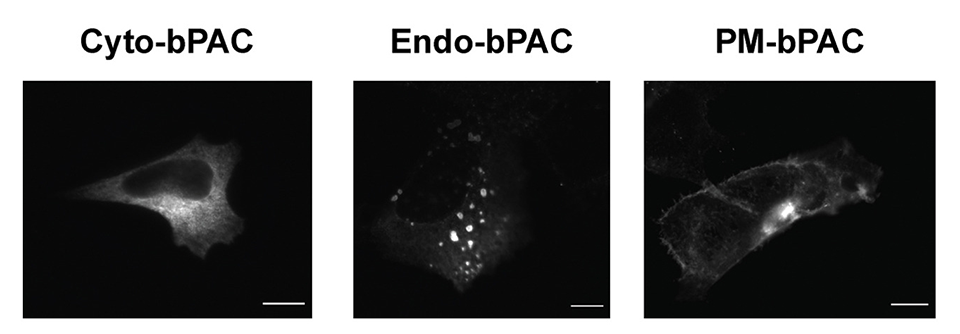
“We sought to determine the overall functional significance of generating cAMP from internal membranes relative to the plasma membrane,” von Zastrow said.
The researchers seek to delineate the fundamental principles by which cells and tissues mount physiologically appropriate responses to a range of external and internal chemical inputs. They also are investigating the cellular basis of receptor-mediated drug action to identify paths for improving therapeutic efficacy.
“The first main takeaway is that generating cAMP from endosomes has widespread downstream effects,” von Zastrow said. “We initially thought we’d see only a small number of differences, but we identified many changes in the cellular phosphoproteome that result from endosome-generated cAMP relative to cAMP generated from the plasma membrane.”
The authors shed light on a less understood cellular signaling aspect: Location-encoded signaling is not restricted to increased protein phosphorylation or to effects mediated by the activity of a cAMP-dependent protein kinase such as protein kinase A, or PKA, in the nucleus. cAMP binds with and activates PKA, which then phosphorylates the protein to elicit cellular reactions.
The study also identified proteins that are dephosphorylated selectively in response to endosome-localized cAMP production and in sequences that do not correspond to PKA consensus sites. “Broadly speaking, our results show that producing cAMP from endosomes has potential to fundamentally ‘re-wire’ downstream cellular signaling by phosphorylation,” von Zastrow said.
The researchers were fascinated to see how multiple proteins are phosphorylated preferentially in response to cAMP produced from endosomes and to see proteins that are dephosphorylated selectively on distinct sites relative to those phosphorylated by PKA. Their cell culture model had tightly controlled variables, so the team cautions against directly extending their results to physiological systems or therapeutics. However, there are potentially profound biomedical implications for future studies.
This collaborative project involved researchers with various backgrounds, and each had different expectations, von Zastrow said. “Dr. Tsvetanova and I would frequently place bets on what results would be obtained. The data was so rich and clear that each one of us was surprised — to the degree that we generally forgot what the original bets were in the first place.”
Enjoy reading ASBMB Today?
Become a member to receive the print edition four times a year and the digital edition monthly.
Learn moreGet the latest from ASBMB Today
Enter your email address, and we’ll send you a weekly email with recent articles, interviews and more.
Latest in Science
Science highlights or most popular articles

The data that did not fit
Brent Stockwell’s perseverance and work on the small molecule erastin led to the identification of ferroptosis, a regulated form of cell death with implications for cancer, neurodegeneration and infection.

Building a career in nutrition across continents
Driven by past women in science, Kazi Sarjana Safain left Bangladesh and pursued a scientific career in the U.S.

Avoiding common figure errors in manuscript submissions
The three figure issues most often flagged during JBC’s data integrity review are background signal errors, image reuse and undeclared splicing errors. Learn how to avoid these and prevent mistakes that could impede publication.

Ragweed compound thwarts aggressive bladder and breast cancers
Scientists from the University of Michigan reveal the mechanism of action of ambrosin, a compound from ragweed, selectively attacks advanced bladder and breast cancer cells in cell-based models, highlighting its potential to treat advanced tumors.

Lipid-lowering therapies could help treat IBD
Genetic evidence shows that drugs that reduce cholesterol or triglyceride levels can either raise or lower inflammatory bowel disease risk by altering gut microbes and immune signaling.

Key regulator of cholesterol protects against Alzheimer’s disease
A new study identifies oxysterol-binding protein-related protein 6 as a central controller of brain cholesterol balance, with protective effects against Alzheimer’s-related neurodegeneration.

