From the journals: JLR
Targeting protein folding to combat Niemann–Pick type C1. Pinpointing substrate specificity for phospholipase A2S. A high-throughput assay of lipase activity. Read about articles on these topics recently published in the Journal of Lipid Research.
Targeting protein folding to combat Niemann–Pick type C1
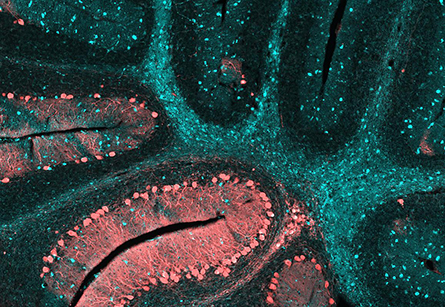
and Human Development, National Institutes of Health
The dense lipid pockets shown in blue are due to reduced cholesterol transport.
The glycoprotein Niemann–Pick type C1, or NPC1, functions in intracellular cholesterol transport. Mutation of this protein hinders its folding and trafficking between organelles, which leads to reduced cholesterol transporting and subsequent accumulation. This disorder can have early- or late-onset consequences ranging from death in infancy to adult neurodegeneration. No treatment exists for NPC1 disorder; trials of intrathecal therapies only slow disease progression.
Previous research showed that histone deacetylase, or HDAc, inhibitors offered some correction for the NPC1 mutant in cells. Researchers believed this was caused by changes in molecular chaperone activity, in particular HSP70 and HSP90, in the presence of HDAc inhibitors. In a recent publication in the Journal of Lipid Research, Nina Pipalia of Weill Cornell Medical College and a multi-institutional team investigated the effects of HSP90 inhibition on NPC1 mutant fibroblasts.
The investigators confirmed that inhibitors of HSP90 showed potent dose-dependent effects, with one in particular, AUY922, counteracting the NPC1 mutation phenotype after 48 hours at subnanomolar concentrations. This was due to the NPC1 mutant’s increased ability to exit the endoplasmic reticulum after folding — hinderance of which is the main phenotype of the disorder. This was coupled with increased ability to localize within late endosomes and lysosomes and perform its function — transport of cholesterol.
But why would chaperone inhibition increase protein folding and trafficking ability? HSP90 inhibition actually resulted in overexpression of HSP70 and HSP40, both of which were shown to play a role in counteracting NPC1 mutant phenotypes. While mouse models will provide the real litmus test, the authors state that “the promising effect of HSP90 inhibition and HSP70 over expression provides a basis for further investigations of protein chaperones in the treatment of NPC1 disease.”
Pinpointing substrate specificity for phospholipase A2s
The phospholipase A2s, or PLA2, superfamily catalyzes the hydrolysis of the sn-2 ester bond with an elegant simplicity that requires extreme specificity. The products of this reaction play vital downstream roles. Free arachidonic acid, for example, is the precursor in the synthesis of the proinflammatory prostaglandins and the leukotrienes. To ensure this specificity is met, expression levels and localization of each PLA2 group are finely tuned. So too is the substrate specificity.
In a recent publication in the Journal of Lipid Research, Daiki Hayashi and a team at the University of California, San Diego, describe their effort to catalog the selectivity of each PLA2 for omega-3 and omega-6 fatty acids. Using a combination of mass spectrometry and molecular dynamics simulations, the researchers presented in detail the substrate specificity for each PLA2 toward arachidonic acid and the fish oil containing omega-3 fatty acids eicosapentaenoic acid and docosahexaenoic acid. The MD simulations demonstrated this specificity to be rooted in the geometry of the hydrophobic active site, with encoded selectivity toward chain length and double-bond position.
As the authors state, “This illustrates the enormous power of a hydrophobic site cavity to show the unexpected, exquisite specificity and sensitivity generally attributed to charged and polar sites in proteins.”
High-throughput assay of lipase activity
Measuring the activity of lipases in a research setting often involves cumbersome multistep protocols using radiolabeled substrates and separation of substrates from products. This time-consuming process has hindered thorough investigation of inhibitors of lipases, leading to a lack of clinically approved lipase-targeting drugs with potency and specificity. This is of significant concern because lipases have relevance in numerous metabolic diseases.
In a recent paper in the Journal of Lipid Research, Sujith Rajan and colleagues at New York University Long Island School of Medicine describe how they developed a more streamlined method to determine rates of hydrolysis of triacylglycerols, or TAGs, by lipases. This was validated by testing a panel of lipase inhibitors.
The researchers incorporated a fluorescent nitrobenzoxadiazole moiety onto the TAG substrate to form an NBD-TAG substrate, which they incorporated into liposomes, thus developing a rapid, fluorescence-based assay. This was partnered with the use of Cos-7 cells for enzyme overexpression, due to their low levels of naturally occurring lipases. Finally, incorporation of the phosphatidylinositol into NBD-TAG substrate vesicles was found to greatly increase enzyme activity. This negated the cumbersome step of separating substrate from product to accurately measure activity. Combined, this presents a promising route for future lipase inhibitor discovery studies and opens such studies up to the promise of high-throughput screening.
Enjoy reading ASBMB Today?
Become a member to receive the print edition four times a year and the digital edition monthly.
Learn moreGet the latest from ASBMB Today
Enter your email address, and we’ll send you a weekly email with recent articles, interviews and more.
Latest in Science
Science highlights or most popular articles

When oncogenes collide in brain development
Researchers at University Medical Center Hamburg, found that elevated oncoprotein levels within the Wnt pathway can disrupt the brain cell extracellular matrix, suggesting a new role for LIN28A in brain development.

The data that did not fit
Brent Stockwell’s perseverance and work on the small molecule erastin led to the identification of ferroptosis, a regulated form of cell death with implications for cancer, neurodegeneration and infection.

Building a career in nutrition across continents
Driven by past women in science, Kazi Sarjana Safain left Bangladesh and pursued a scientific career in the U.S.

Avoiding common figure errors in manuscript submissions
The three figure issues most often flagged during JBC’s data integrity review are background signal errors, image reuse and undeclared splicing errors. Learn how to avoid these and prevent mistakes that could impede publication.

Ragweed compound thwarts aggressive bladder and breast cancers
Scientists from the University of Michigan reveal the mechanism of action of ambrosin, a compound from ragweed, selectively attacks advanced bladder and breast cancer cells in cell-based models, highlighting its potential to treat advanced tumors.

Lipid-lowering therapies could help treat IBD
Genetic evidence shows that drugs that reduce cholesterol or triglyceride levels can either raise or lower inflammatory bowel disease risk by altering gut microbes and immune signaling.

