Adults grow new brain cells
Your brain can still make new neurons when you’re an adult. But how does the rare birth of these new neurons contribute to cognitive function?
Neurons are the cells that govern brain function, and you are born with most of the neurons you will ever have during your lifetime. While the brain undergoes most of its development during early life, specific regions of the brain continue to generate new neurons throughout adulthood, although at a much lower rate. Whether this process of neurogenesis actually happens in adults and what function it serves in the brain is still a subject of debate among scientists.
Past research has shown that people with epilepsy or Alzheimer’s disease and other dementias develop fewer neurons as adults than people without these conditions. However, whether the absence of new neurons contributes to the cognitive challenges patients with these neurological disorders face is unknown.
We are part of a team of stem cell researchers, neuroscientists, neurologists, neurosurgeons and neuropsychologists. Our newly published research reveals that the new neurons that form in adults’ brains are linked to how you learn from listening to other people.
New neurons and learning
Researchers know that new neurons contribute to memory and learning in mice. But in humans, the technical challenges of identifying and analyzing new neurons in adult brains, combined with their rarity, had led scientists to doubt their significance to brain function.
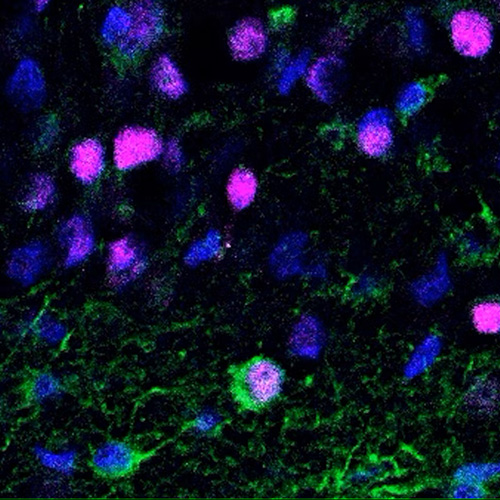
To uncover the relationship between neurogenesis in adults and cognitive function, we studied patients with drug-resistant epilepsy. These patients underwent cognitive assessments prior to and donated brain tissue during surgical procedures to treat their seizures. To see whether how many new neurons a patient had was associated with specific cognitive functions, we looked under the microscope for markers of neurogenesis.
We found that new neurons in the adult brain are linked to reduced cognitive decline – particularly in verbal learning, or learning by listening to others.
This was very surprising to us. In mice, new neurons are known for their role in helping them learn and navigate new spaces through visual exploration. However, we did not observe a similar connection between new neurons and spatial learning in people.
Improving cognition
Talking with others and remembering those conversations is an integral part of day-to-day life for many people. However, this crucial cognitive function declines with age, and the effects are more severe with neurological disorders. As aging populations grow, the burden of cognitive decline on health care systems worldwide will increase.
Our research suggests that the link between newborn neurons and verbal learning may be foundational to developing treatments to restore cognition in people. Enhancing new neuron generation could be a potential strategy to improve brain health and restore cognition in aging and in people with epilepsy or dementia. But for now, these ideas are just goals and any future treatments are a long way off.
Importantly, our finding that new neurons function differently in mice and in humans emphasizes the critical need to study biological functions like neurogenesis in people whenever possible. This will ensure that research conducted in animal models, such as mice, is relevant to people and can translate to the clinic.
Current drugs for epilepsy primarily aim to reduce seizures, with limited focus on addressing the cognitive decline patients experience. To enhance cognitive outcomes for patients, we started a clinical trial focusing on boosting new neuron production and cognition in epilepsy patients through aerobic exercise. We are currently in the early Phase 1 of the clinical trial, which seeks to establish the safety of the study. Thus far, two patients have successfully and safely finished the study. We plan to recruit eight more patients to exercise and complete this phase.
By bringing together basic science in the lab and clinical research in people, a better understanding of brain regeneration could help support brain health throughout the lifespan.
This article is republished from The Conversation. Read the original here.Enjoy reading ASBMB Today?
Become a member to receive the print edition four times a year and the digital edition monthly.
Learn moreGet the latest from ASBMB Today
Enter your email address, and we’ll send you a weekly email with recent articles, interviews and more.
Latest in Science
Science highlights or most popular articles

Sizing up cells: How stem cells know when to divide
Stanford University researchers find that stem cells control their size early in cell division across living multicellular systems.

When oncogenes collide in brain development
Researchers at University Medical Center Hamburg, found that elevated oncoprotein levels within the Wnt pathway can disrupt the brain cell extracellular matrix, suggesting a new role for LIN28A in brain development.

The data that did not fit
Brent Stockwell’s perseverance and work on the small molecule erastin led to the identification of ferroptosis, a regulated form of cell death with implications for cancer, neurodegeneration and infection.

Building a career in nutrition across continents
Driven by past women in science, Kazi Sarjana Safain left Bangladesh and pursued a scientific career in the U.S.

Avoiding common figure errors in manuscript submissions
The three figure issues most often flagged during JBC’s data integrity review are background signal errors, image reuse and undeclared splicing errors. Learn how to avoid these and prevent mistakes that could impede publication.

Ragweed compound thwarts aggressive bladder and breast cancers
Scientists from the University of Michigan reveal the mechanism of action of ambrosin, a compound from ragweed, selectively attacks advanced bladder and breast cancer cells in cell-based models, highlighting its potential to treat advanced tumors.



