Phospholipids and innate immunity
The innate immune system is an ancient evolutionary arm of defense that responds to acute trauma by generating a barrier that prevents pathogen invasion and arrests bleeding. It also patrols healthy epithelial tissues, monitoring and responding to foreign antigens and supporting development of adaptive immunity.
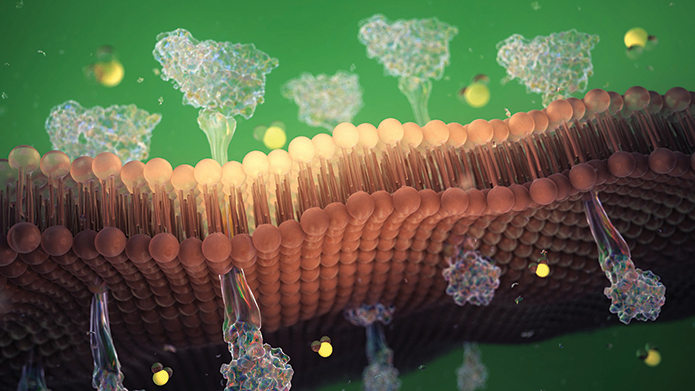 This representation of a phospholipid bilayer shows integral membrane proteins protruding throughout.
This representation of a phospholipid bilayer shows integral membrane proteins protruding throughout.
Healthy functioning of the innate immune system relies on communication among diverse cell types, both from the bloodstream and based in stromal tissues such as epithelia and fibroblasts. Here, phospholipid signaling takes center stage in diverse ways, many of which we are only beginning to understand.
Phospholipids, or PLs, provide the membranes that hold our cells together. Researchers increasingly appreciate how these unique and diverse lipids also play essential roles in communicating within the immune system and how this is required for human health and disease. Indeed, PLs and their metabolic products are central players in vascular inflammation, hemostasis, immunity, cancer, infection and cardiovascular disease.
Here is some of what we know about PL biology in mammals so far:
Prostaglandin and eicosanoid precursors: Researchers long have known that PL hydrolysis provides polyunsaturated fatty acid substrates for generation of eicosanoids and prostaglandins by cyclooxygenases and lipoxygenases. This involves large families of phospholipases expressed in a cell-specific manner. Prostaglandins signal by activating well-characterized G protein-coupled receptors, or GPCRs, after they are secreted from immune and stromal cells during inflammation.
Phosphoinositides: The phosphorylation of inositol headgroups of phosphatidylinositol at up to three sites leads to a multitude of PL products that are potently bioactive and highly transient. These lipids form short-lived membrane anchors for kinases that regulate GPCRs, apoptosis and endocytosis.
Platelet activating factor: This extremely transient lipid contains a choline headgroup, and an alkyl bond at sn1. According to IUPAC nomenclature, it is a plasmanylcholine, with an acetyl group at sn2. The chain at sn1 is generally a 16:0 ether, but variants of other length also show bioactivity towards platelets.
Phospholipase C and phospholipase D: Families of enzymes called PLCs cleave PLs to form diacylglycerol and release the phosphorylated headgroup. Diacylglycerols are potent activators of the protein kinase C pathway, while the PL headgroup mobilizes calcium. PLD metabolizes phosphatidylcholine to form phosphatidic acid, an intracellular molecule that regulates proteins involved in Ras and Rac1 signaling.
Enzymatically oxidized PL: Researchers long have known that PLs oxidize in atherosclerosis and inflammation via nonenzymatic processes. Now, they are finding that a cell-specific group of related lipids, generated by enzymatic oxidation, is formed in innate immune cells in the bloodstream. These lipids allow the interaction of coagulation factors with cell membranes, an event required for blood clotting. A deficiency of enzymatically oxidized PLs, or eoxPLs, leads to too much bleeding, and studies suggest eoxPLs are involved in vascular inflammatory diseases such as aneurysms. In some situations, eoxPLs and their nonenzymatically generated analogs may be regulators of ferroptosis, an iron-dependent cell-death process relevant for cancer and organ failure.
Phospholipid innate immune recognition: Both self- and pathogen-derived PLs can act as ligands for a family of MHC class I-like antigen-presenting molecules called CD1. Lipid reactive T cells such as natural killer T cells then recognize the lipid-CD1 complexes. This type of antigen recognition shows significant molecular diversity in terms of PL species implicated, and a role is emerging for CD1-lipid presentation in human allergies, including to dust mites, pollen and bee sting.
Our lab recently published a review covering these aspects of PL signaling in the innate immune system in the Journal of Clinical Investigation.
(Terminology in the section of this article on platelet activating factor was corrected by the author on Nov. 14, 2019.)
Enjoy reading ASBMB Today?
Become a member to receive the print edition four times a year and the digital edition monthly.
Learn moreGet the latest from ASBMB Today
Enter your email address, and we’ll send you a weekly email with recent articles, interviews and more.
Latest in Science
Science highlights or most popular articles

The data that did not fit
Brent Stockwell’s perseverance and work on the small molecule erastin led to the identification of ferroptosis, a regulated form of cell death with implications for cancer, neurodegeneration and infection.

Building a career in nutrition across continents
Driven by past women in science, Kazi Sarjana Safain left Bangladesh and pursued a scientific career in the U.S.

Avoiding common figure errors in manuscript submissions
The three figure issues most often flagged during JBC’s data integrity review are background signal errors, image reuse and undeclared splicing errors. Learn how to avoid these and prevent mistakes that could impede publication.

Ragweed compound thwarts aggressive bladder and breast cancers
Scientists from the University of Michigan reveal the mechanism of action of ambrosin, a compound from ragweed, selectively attacks advanced bladder and breast cancer cells in cell-based models, highlighting its potential to treat advanced tumors.

Lipid-lowering therapies could help treat IBD
Genetic evidence shows that drugs that reduce cholesterol or triglyceride levels can either raise or lower inflammatory bowel disease risk by altering gut microbes and immune signaling.

Key regulator of cholesterol protects against Alzheimer’s disease
A new study identifies oxysterol-binding protein-related protein 6 as a central controller of brain cholesterol balance, with protective effects against Alzheimer’s-related neurodegeneration.

