A molecular determinant of membrane protein targeting
Specific membrane lipids serve not only as constituents of membrane architecture but also as modulators of membrane-interacting proteins during diverse cellular processes such as cell signalling, receptor-mediated endocytosis, apoptosis, mitochondrial fusion and maintenance of mitochondrial potential. Primarily due to their varying acyl side chains, these lipids assume various shapes including cylinders and cones.
Most proteins residing in or on membrane bilayers are targeted to their destination co-translationally, whereas specific proteins involved in membrane remodeling — such as clathrin, caveolin, BAR-domain carrying proteins, Arfs, epsin, flotillin and dynamins — are recruited to their sites of action post-translationally. The latter proteins are known to interact with their target membranes by electrostatic interaction or by inserting their hydrophobic domains or amphipathic helices into the membrane bilayer.
Dynamin superfamily proteins are large GTPases that rely on their ability to form uniformly organised self-assembled structures to generate a scaffold to remodel their underlying membranes. These proteins facilitate the generation of membrane curvature required for membrane fission or fusion. Targeting of dynamins to their target membranes depends on the recognition and clustering of specific lipids. For example, dyanmin1 recognizes PI(4,5)P2 in binding to endocytic vesicles on the plasma membrane, while OPA1 recognises cardiolipin on the opposing inner mitochondrial membranes to cause membrane fusion.
These processes require a dedicated stretch of membrane-binding residues. Binding of classical dynamins to the membrane is mediated by a conventional membrane-binding domain called a pleckstrin homology, or PH, domain. However, a subclass of dynamin family members known as dynamin-related proteins lacks a PH domain and instead contains a B-insert for membrane recognition.
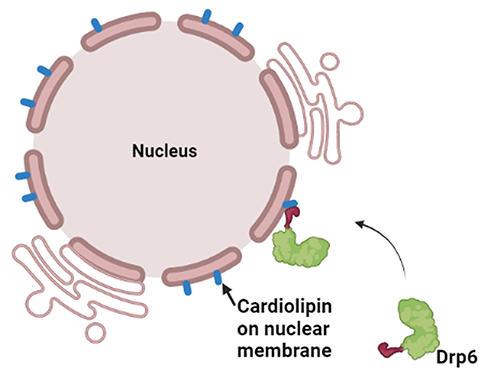
In a recent study, the nuclear envelope–localized dynamin-related protein Drp6 in Tetrahymena has been shown to depend on cardiolipin for the translocation to its target membrane. Though Drp6 interacts with three distinct phospholipids (phosphatidic acid, phosphatidylserine and cardiolipin), mutation of a critical isoleucine residue (Ile553) in the membrane-binding domain of Drp6 inhibits its interaction specifically with cardiolipin and abrogates nuclear membrane recruitment. This study establishes a role for a single amino acid residue in determining target membrane specificity through interaction with a specific lipid. Though the membrane-binding domain (PH domain or B-insert) and interacting lipid of several dynamin family proteins have been identified, researchers do not yet know the mechanism by which these proteins determine target membrane specificity.
Partitioning of proteins to different compartments is emerging as a robust mechanism for spatiotemporal regulation of protein function. Although a large number of studies demonstrate the importance of hydrophobic and electrostatic interactions in determining target membrane binding, researchers have not yet determined how proteins discriminate different phospholipids. Detailed structural analysis of protein–lipid complexes using techniques such as high-resolution cryo-electron microscopy or X-ray crystallography is likely to shed light on the precise mechanism of membrane protein targeting.
Enjoy reading ASBMB Today?
Become a member to receive the print edition four times a year and the digital edition monthly.
Learn moreGet the latest from ASBMB Today
Enter your email address, and we’ll send you a weekly email with recent articles, interviews and more.
Latest in Science
Science highlights or most popular articles

From humble beginnings to unlocking lysosomal secrets
Monther Abu–Remaileh will receive the ASBMB’s 2026 Walter A. Shaw Young Investigator Award in Lipid Research at the ASBMB Annual Meeting, March 7-10 in Washington, D.C.

Chemistry meets biology to thwart parasites
Margaret Phillips will receive the Alice and C. C. Wang Award in Molecular Parasitology at the ASBMB Annual Meeting, March 7-10 in Washington, D.C.

ASBMB announces 2026 JBC/Tabor awardees
The seven awardees are first authors of outstanding papers published in 2025 in the Journal of Biological Chemistry.

Missing lipid shrinks heart and lowers exercise capacity
Researchers uncovered the essential role of PLAAT1 in maintaining heart cardiolipin, mitochondrial function and energy metabolism, linking this enzyme to exercise capacity and potential cardiovascular disease pathways.

Decoding how bacteria flip host’s molecular switches
Kim Orth will receive the Earl and Thressa Stadtman Distinguished Scientists Award at the ASBMB Annual Meeting, March 7–10, just outside of Washington, D.C.

Defining JNKs: Targets for drug discovery
Roger Davis will receive the Bert and Natalie Vallee Award in Biomedical Science at the ASBMB Annual Meeting, March 7–10, just outside of Washington, D.C.


