Starved for oxygen, T cells flag in cancer fight
Cytotoxic T cells exist to kill cells subverted by infection or mutation. That makes them the focus of a lot of immuno-oncology research. Although cancers must slip past immune recognition to become established in the first place, immunotherapies such as checkpoint inhibitor antibodies or T cells with modified receptors can retrain the immune system to focus on cancer cells.
So far, this has worked best for blood cancers with many cells spread throughout the body. Solid tumors have been harder to treat. The inside of a tumor differs from normal tissue in complex ways that add up to make it a very immunosuppressive environment.
In a preliminary study published in Molecular & Cellular Proteomics, postdoc James Byrnes and colleagues in Jim Wells’ lab at the University of California, San Francisco, report on their research into how the proteins on the surface of a cytotoxic T cell respond to various stimuli they might encounter in a tumor.
Using primary cells removed from human blood, the team focused on the surface proteome of cytotoxic CD8+ T cells. They investigated how interactions with T regulatory cells, which dampen T cells’ response and help end an immune reaction, and oxygen limitation, a feature of many tumors, changed the cytotoxic T cell surface.
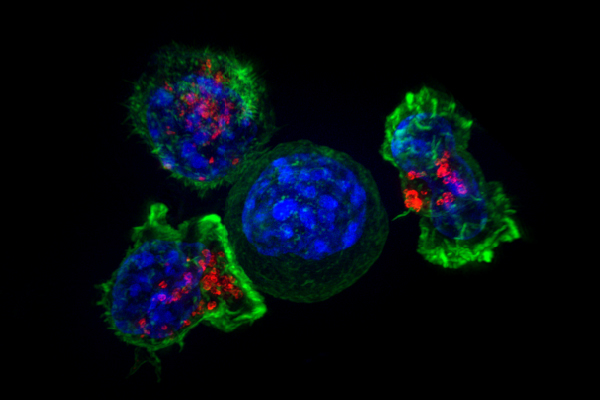
with a target cell, the killer cell attaches and spreads over the target, then uses special chemicals housed
in vesicles(red) to deliver the killing blow. The killer T cells then move on to find the next target.
T regulatory cells are abundant in some solid tumors, and the team expected them to have dramatic effects. They were surprised to find that hypoxia had a much greater effect.
“The prevailing thought is that T regulatory cells are this super-potent immunosuppressive factor,” Byrnes said. But growing CD8+ T cells with T regulatory cells changed only a targeted subset of proteins, mostly the ones that increase in abundance after activation and are involved in signaling and proliferation.
“The T-regs are reversing the activation phenotype,” Byrnes said. “Hypoxia is a little more of a sledgehammer.”
Oxygen starvation shifted cytotoxic T cell expression of many surface proteins: The cells reduced immune signaling receptors and increased metabolic proteins, apparently in an effort to survive using glycolysis. Other studies have shown that hypoxia can make T cells more prone to kill but also slower to multiply; on balance, they may become less effective.
The Wells lab is focused primarily on antibody engineering, Byrnes said, and these results have given them interesting leads to follow as they consider new ways to mobilize the immune cells within a tumor. “We’re hoping … (to) gain biological insight into what some of these proteins are doing, as well as identify handles that we can use to therapeutically engage hypoxic T cells.”
Enjoy reading ASBMB Today?
Become a member to receive the print edition four times a year and the digital edition monthly.
Learn moreGet the latest from ASBMB Today
Enter your email address, and we’ll send you a weekly email with recent articles, interviews and more.
Latest in Science
Science highlights or most popular articles

From humble beginnings to unlocking lysosomal secrets
Monther Abu–Remaileh will receive the ASBMB’s 2026 Walter A. Shaw Young Investigator Award in Lipid Research at the ASBMB Annual Meeting, March 7-10 in Washington, D.C.

Chemistry meets biology to thwart parasites
Margaret Phillips will receive the Alice and C. C. Wang Award in Molecular Parasitology at the ASBMB Annual Meeting, March 7-10 in Washington, D.C.

ASBMB announces 2026 JBC/Tabor awardees
The seven awardees are first authors of outstanding papers published in 2025 in the Journal of Biological Chemistry.

Missing lipid shrinks heart and lowers exercise capacity
Researchers uncovered the essential role of PLAAT1 in maintaining heart cardiolipin, mitochondrial function and energy metabolism, linking this enzyme to exercise capacity and potential cardiovascular disease pathways.

Decoding how bacteria flip host’s molecular switches
Kim Orth will receive the Earl and Thressa Stadtman Distinguished Scientists Award at the ASBMB Annual Meeting, March 7–10, just outside of Washington, D.C.

Defining JNKs: Targets for drug discovery
Roger Davis will receive the Bert and Natalie Vallee Award in Biomedical Science at the ASBMB Annual Meeting, March 7–10, just outside of Washington, D.C.

