Calcium channel linked to cancer drug resistance
Chemotherapy tumor resistance develops after long-term regimens of the platinum-containing anticancer drug carboplatin. Scientists have observed an enlarged cell morphology and involvement of T-type calcium channels in resistant ovarian cancer cells. Sooyun Kim and researchers at Seoul National University wanted to find out if these characteristics also relate to carboplatin resistance seen in retinoblastoma, an aggressive childhood cancer. They published their findings in a recent Journal of Biological Chemistry article.
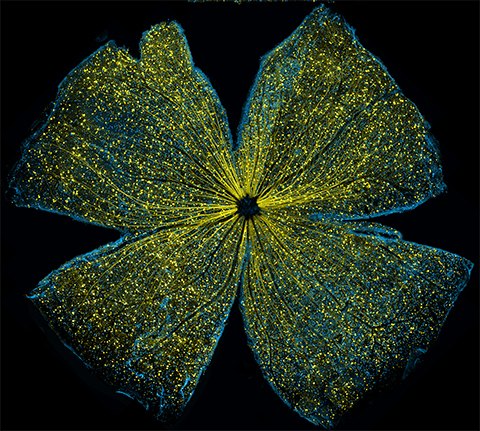
Immunofluorescence staining and pharmacological inhibition experiments identified the Cav3.3 channel as the overexpressed calcium channel subtype that contributes to the sustained currents. The authors further showed that messenger RNA expression levels only for Cav3.3 increased after carboplatin exposure, while the levels for the other Cav3.1 and Cav3.2 subtypes slightly decreased in the resistant cells relative to the original retinoblastoma strain.
Finally, the researchers determined that treating the resistant retinoblastoma giant cells with a Cav3.3 inhibitor increased their sensitivity to carboplatin. They only observed this increase in carboplatin sensitivity in the resistant cells and not in the original retinoblastoma strain, indicating that Cav3.3 plays a specific role in drug resistance.
Cav3.3 could potentially be a target for the treatment of carboplatin-resistant retinoblastoma. Future experiments will help identify additional proteins and pathways that may connect Cav3.3 to chemotherapeutic resistance in retinoblastoma and whether the involvement of Cav3.3 over the other channel subtypes is observed in other cancers.
Enjoy reading ASBMB Today?
Become a member to receive the print edition four times a year and the digital edition monthly.
Learn moreGet the latest from ASBMB Today
Enter your email address, and we’ll send you a weekly email with recent articles, interviews and more.
Latest in Science
Science highlights or most popular articles

The data that did not fit
Brent Stockwell’s perseverance and work on the small molecule erastin led to the identification of ferroptosis, a regulated form of cell death with implications for cancer, neurodegeneration and infection.

Building a career in nutrition across continents
Driven by past women in science, Kazi Sarjana Safain left Bangladesh and pursued a scientific career in the U.S.

Avoiding common figure errors in manuscript submissions
The three figure issues most often flagged during JBC’s data integrity review are background signal errors, image reuse and undeclared splicing errors. Learn how to avoid these and prevent mistakes that could impede publication.

Ragweed compound thwarts aggressive bladder and breast cancers
Scientists from the University of Michigan reveal the mechanism of action of ambrosin, a compound from ragweed, selectively attacks advanced bladder and breast cancer cells in cell-based models, highlighting its potential to treat advanced tumors.

Lipid-lowering therapies could help treat IBD
Genetic evidence shows that drugs that reduce cholesterol or triglyceride levels can either raise or lower inflammatory bowel disease risk by altering gut microbes and immune signaling.

Key regulator of cholesterol protects against Alzheimer’s disease
A new study identifies oxysterol-binding protein-related protein 6 as a central controller of brain cholesterol balance, with protective effects against Alzheimer’s-related neurodegeneration.

