Publication of 2,000 canine genomes provides toolkit for translational research
An international research consortium has generated and analysed 2,000 canine genomes. The resulting advanced genetics toolkit can now be used to answer complex biological questions, spanning dog domestication, genetic differences in breed morphology, behavior and disease susceptibility, as well as the evolution and structure of the genome. The study, published in the journal Genome Biology, describes the toolkit resource package and presents the first set of discoveries.
The publication is the culmination of efforts from the Dog10K consortium — 48 scientists across 25 institutions, contributing samples and resources to the immense analytical effort.
Jennifer Meadows is an Uppsala University research scientist and was a lead co-author of the study. “The goal was to produce a resource the global community could access, and which they could use to speed the translation of their own research, be that in the study of the shared ancestors of dogs and wolves, or the clinical treatment of cancers. All these avenues are exciting, and all can benefit from the Dog10K catalogue,” Meadows said.
The power of the Dog10K analyses lies in the depth of genetic diversity the team was able to capture. Canine samples were drawn from more than 320 of the approximately 400 recognised pedigree dog breeds, as well as niche populations of village dogs, wolves and coyotes.
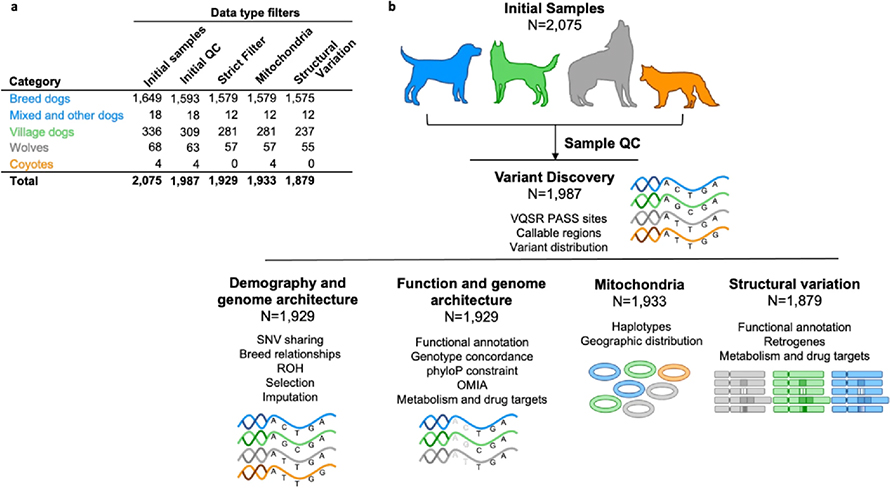
The team developed:
- A comprehensive catalogue of single nucleotide variants, including those which can disrupt protein coding genes and may influence the extremes of dog appearance and physiology. All pedigree dogs in the study were free from disease when sampled, suggesting that some of the variants that cause a loss of protein function do not cause obvious disease in that population.
- A catalogue of structural variants. This category of variants has a minimum size of 50 base pairs, and so impacts more space in the genome than a single nucleotide variant. Some structural variants were found to impact protein coding genes. This could mean that too much, or too little of the protein is made in that individual, but again did not cause obvious disease in the pedigree population.
- For both single nucleotide and structural variants, the Dog10K team illustrated how these variants are distributed within and between pedigree dog breeds, and how these variants may impact the study of potential drug therapies.
- Publicly available data processing pipelines. Combining the results from different studies can be made more difficult when different settings are used to map sequencing data, and then to call variation. The pipeline used by the Dog10K consortium is open to the community so that new or existing data can be processed and easily combined with this set.
- An imputation panel from the single nucleotide variants. Imputation is a process that allows researchers to infer variation at sites that they did not directly measure. The Dog10K team showed that by using the imputation panel, a dataset that contained 170 thousand single nucleotide sites, commonly used in genotyping array studies, can be expanded to up to 8 million sites. This allows researchers to reuse their valuable samples, and to revisit complex questions that need more data.
“We have just scratched the surface of the data’s potential,” Meadows said. “There is yet more genetic diversity left to be found in dogs, wolves and coyotes, but the Dog10K team looks forward to seeing how this first effort is applied by the canine science community.”
This article was first published by Uppsala University. Read the original.
Enjoy reading ASBMB Today?
Become a member to receive the print edition four times a year and the digital edition monthly.
Learn moreGet the latest from ASBMB Today
Enter your email address, and we’ll send you a weekly email with recent articles, interviews and more.
Latest in Science
Science highlights or most popular articles

Avoiding common figure errors in manuscript submissions
The three figure issues most often flagged during JBC’s data integrity review are background signal errors, image reuse and undeclared splicing errors. Learn how to avoid these and prevent mistakes that could impede publication.

Ragweed compound thwarts aggressive bladder and breast cancers
Scientists from the University of Michigan reveal the mechanism of action of ambrosin, a compound from ragweed, selectively attacks advanced bladder and breast cancer cells in cell-based models, highlighting its potential to treat advanced tumors.

Lipid-lowering therapies could help treat IBD
Genetic evidence shows that drugs that reduce cholesterol or triglyceride levels can either raise or lower inflammatory bowel disease risk by altering gut microbes and immune signaling.

Key regulator of cholesterol protects against Alzheimer’s disease
A new study identifies oxysterol-binding protein-related protein 6 as a central controller of brain cholesterol balance, with protective effects against Alzheimer’s-related neurodegeneration.

From humble beginnings to unlocking lysosomal secrets
Monther Abu–Remaileh will receive the ASBMB’s 2026 Walter A. Shaw Young Investigator Award in Lipid Research at the ASBMB Annual Meeting, March 7-10 in Washington, D.C.

Chemistry meets biology to thwart parasites
Margaret Phillips will receive the Alice and C. C. Wang Award in Molecular Parasitology at the ASBMB Annual Meeting, March 7-10 in Washington, D.C.

