Cracking cancer’s code through functional connections
Among cancer researchers, their computers, servers and databanks store thousands of terabytes of omics data, enabling novel discoveries about genetic and proteomic relationships. However, making meaningful connections can be computationally challenging. What if there were a way to harness the power of machine learning to help interpret this data and identify unrecognized patterns that advance therapeutic strategies?
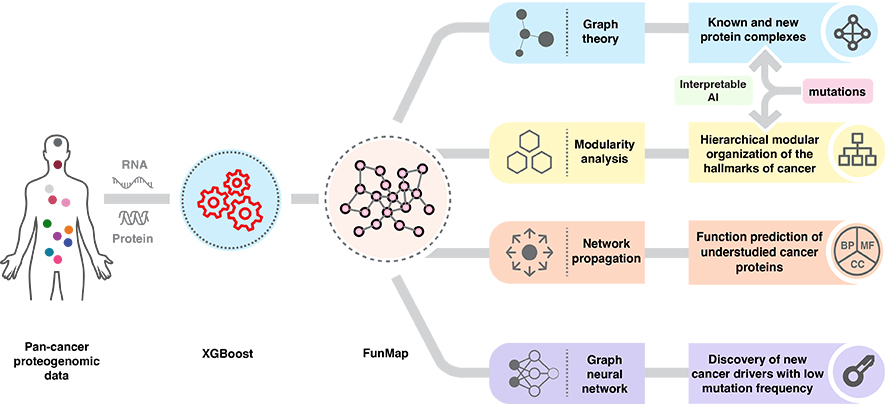
A recent paper in Nature Cancer introduces a new tool for decoding and uncovering functional connections within cancer biology. FunMap, a machine-learning-driven platform, allows researchers to understand how genes and proteins work together in cancer, even when they aren’t directly connected. Bing Zhang, a professor of molecular and human genetics at Baylor College of Medicine, and his lab aim to bridge the gap between large-scale cancer omics data and functional interpretation using machine learning.
The team used large-scale proteogenomic data, or integrated information about genes, RNA and proteins, across 11 cancer types to chart a functional network of more than 10,000 genes. Unlike traditional protein–protein interaction networks, which focus on physical contacts between proteins, FunMap assesses “cofunctionality,” the concept that genes or proteins can participate in the same biological process even if they do not physically interact.
“Think of a complex research lab,” Zhiao Shi, lead programmer in the lab and first author of the paper, explained the computational tool. “A computational biologist and a wet lab scientist may never perform experiments together, but the computational analysis is crucial for guiding the wet lab experiments and interpreting results. Though they do not interact directly, their roles are tightly coordinated to achieve scientific breakthroughs — this is cofunction.”
With the ability to incorporate graph-neural-network-based deep learning, a type of model that learns from data structured as networks of connected elements, FunMap can identify cancer driver mutations with low frequencies. This expands the understanding of cancer pathogenesis beyond high-frequency mutations and may potentiate new discoveries in cancer diagnostics and treatment.
FunMap also advances functional genomics by shedding light on understudied cancer genes, such as RBM34 and MAB21L4, also known as dark genes. These understudied genes and their protein counterparts have not been studied in the context of cancer but are significantly over or under expressed in tumors. Shi explained that their approach “enables a more systematic and data-driven assignment of functions to poorly characterized cancer-associated genes, aiding in the discovery of novel cancer biology.”
The platform is available to the public at funmap.linkedomics.org, where scientists can explore the network and apply it to their own studies. The Zhang lab plans to expand its tool with additional data types, such as epigenomics and protein modification.
“By identifying key cancer-associated proteins and functional pathways, our findings can help prioritize therapeutic targets, ultimately contributing to the development of more effective treatments,” Shi said. “In the long run, this research could lead to improved cancer diagnostics and therapies, benefiting patients by making precision medicine more actionable and impactful.”
Enjoy reading ASBMB Today?
Become a member to receive the print edition four times a year and the digital edition monthly.
Learn moreGet the latest from ASBMB Today
Enter your email address, and we’ll send you a weekly email with recent articles, interviews and more.
Latest in Science
Science highlights or most popular articles

Avoiding common figure errors in manuscript submissions
The three figure issues most often flagged during JBC’s data integrity review are background signal errors, image reuse and undeclared splicing errors. Learn how to avoid these and prevent mistakes that could impede publication.

Ragweed compound thwarts aggressive bladder and breast cancers
Scientists from the University of Michigan reveal the mechanism of action of ambrosin, a compound from ragweed, selectively attacks advanced bladder and breast cancer cells in cell-based models, highlighting its potential to treat advanced tumors.

Lipid-lowering therapies could help treat IBD
Genetic evidence shows that drugs that reduce cholesterol or triglyceride levels can either raise or lower inflammatory bowel disease risk by altering gut microbes and immune signaling.

Key regulator of cholesterol protects against Alzheimer’s disease
A new study identifies oxysterol-binding protein-related protein 6 as a central controller of brain cholesterol balance, with protective effects against Alzheimer’s-related neurodegeneration.

From humble beginnings to unlocking lysosomal secrets
Monther Abu–Remaileh will receive the ASBMB’s 2026 Walter A. Shaw Young Investigator Award in Lipid Research at the ASBMB Annual Meeting, March 7-10 in Washington, D.C.

Chemistry meets biology to thwart parasites
Margaret Phillips will receive the Alice and C. C. Wang Award in Molecular Parasitology at the ASBMB Annual Meeting, March 7-10 in Washington, D.C.

