Scientists identify cancer biomarkers in breast milk
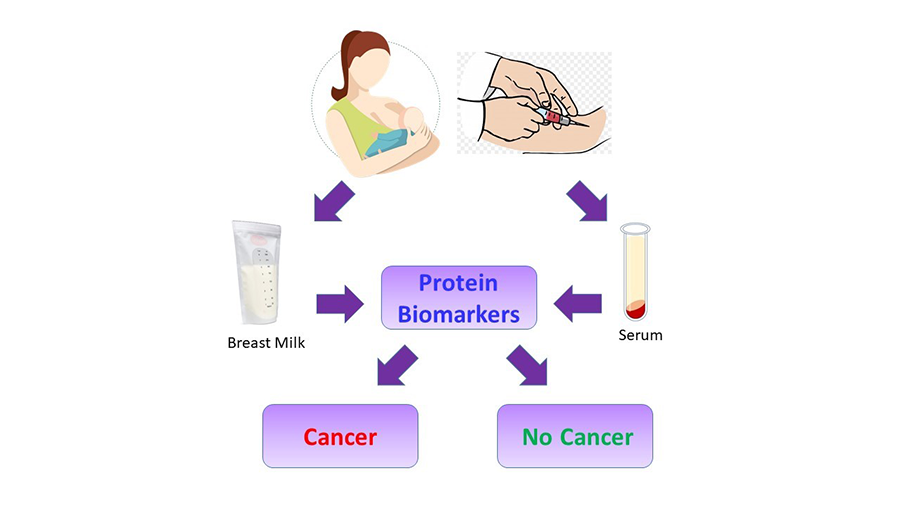
A simple blood test for women of all ages and risk levels could one day be possible thanks to a new set of protein biomarkers that researchers identified using breast milk.
“Although mammograms are a useful tool for catching breast cancer early, they aren’t typically recommended for low-risk women under 40,” said Danielle Whitham, a doctoral candidate at Clarkson University in New York. “Because the biomarkers we found in breast milk are also detectable in blood serum, screening could potentially be done in women of any age using blood or breast milk.”
The newly identified biomarkers are for a specific type of cancer called invasive ductal carcinoma (IDC), one of the most common types of breast cancers. However, the researchers say that their approach could be used to identify biomarkers for other types of breast cancer.
“If our future studies are successful, it could change how women are monitored for breast cancer and aid in earlier diagnosis,” said Whitham. “This could even lead to a higher survival rate in women.”
Whitham will present the research at the American Society for Biochemistry and Molecular Biology annual meeting during the Experimental Biology (EB) 2022 meeting, to be held April 2–5 in Philadelphia.
“We used breast milk because it contains proteins, epithelial cells and immune cells, all of which provide a great deal of information about what is happening in a woman’s body during a crucial time in breast development,” said Whitham.
For the study, breast milk samples were obtained from three women diagnosed with breast cancer and three women without cancer. Using liquid chromatography with tandem mass spectrometry, the researchers compared the relative levels of certain proteins between the two groups to identify differences in the women with cancer. The analysis revealed 23 proteins that were dysregulated. All the proteins that showed differences were previously shown to play a role in cancer or tumor development.
Now that the researchers have identified a biomarker set, they plan to confirm it with a larger group of women. Then, they will test the protein biomarkers’ applicability in blood serum. If those tests are successful, a blood test could be developed to be used on women of any age to monitor protein changes for detection of breast cancer.
Research collaborators on this team include Costel Darie and Sumona Mondal of Clarkson University, Kathleen Arcaro and Brian Pentecost of the University of Massachusetts, Amherst and David Fenyo of New York University School of Medicine.
Women interested in helping with this research by donating breast milk samples can visit http://breastmilkresearch.org.
Danielle Whitham will present this research from 12:30–1:45 p.m. Monday, April 4, in Exhibit/Poster Hall A-B, Pennsylvania Convention Center (Poster Board Number A248) (abstract).
Enjoy reading ASBMB Today?
Become a member to receive the print edition four times a year and the digital edition monthly.
Learn moreGet the latest from ASBMB Today
Enter your email address, and we’ll send you a weekly email with recent articles, interviews and more.
Latest in Science
Science highlights or most popular articles

Avoiding common figure errors in manuscript submissions
The three figure issues most often flagged during JBC’s data integrity review are background signal errors, image reuse and undeclared splicing errors. Learn how to avoid these and prevent mistakes that could impede publication.

Ragweed compound thwarts aggressive bladder and breast cancers
Scientists from the University of Michigan reveal the mechanism of action of ambrosin, a compound from ragweed, selectively attacks advanced bladder and breast cancer cells in cell-based models, highlighting its potential to treat advanced tumors.

Lipid-lowering therapies could help treat IBD
Genetic evidence shows that drugs that reduce cholesterol or triglyceride levels can either raise or lower inflammatory bowel disease risk by altering gut microbes and immune signaling.

Key regulator of cholesterol protects against Alzheimer’s disease
A new study identifies oxysterol-binding protein-related protein 6 as a central controller of brain cholesterol balance, with protective effects against Alzheimer’s-related neurodegeneration.

From humble beginnings to unlocking lysosomal secrets
Monther Abu–Remaileh will receive the ASBMB’s 2026 Walter A. Shaw Young Investigator Award in Lipid Research at the ASBMB Annual Meeting, March 7-10 in Washington, D.C.

Chemistry meets biology to thwart parasites
Margaret Phillips will receive the Alice and C. C. Wang Award in Molecular Parasitology at the ASBMB Annual Meeting, March 7-10 in Washington, D.C.

