Thicker glycocalyx barrier helps cancer evade immune system
One of the ways that cancer cells hide from the body’s immune system is by forming a thin surface barrier called the glycocalyx. In a new study, researchers examined the material properties of this barrier with unprecedented resolution, revealing information that could help improve current cell-based cancer immunotherapies.
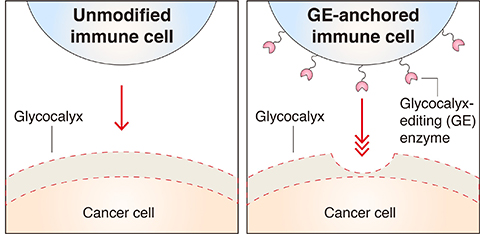
Cancer cells often form the glycocalyx with high levels of cell-surface mucins, which are thought to help protect the cancer cell from immune cell attack. However, a physical understanding of this barrier has remained limited, especially as it relates to cell-based cancer immunotherapies, which involve removing immune cells from a patient, modifying them to seek and destroy cancer, and then putting them back into the patient’s body.
“We found that changes in the thickness of the barrier that were as small as 10 nanometers could affect the antitumor activity of our immune cells or the engineered cells used for immunotherapy,” said Sangwoo Park, a graduate student in Matthew Paszek’s Lab at Cornell University in Ithaca, New York. “We used this information to engineer immune cells that can get through the glycocalyx, and we hope this approach could be used to enhance current cell-based immunotherapies.”
Park will present the findings at Discover BMB, the annual meeting of the American Society for Biochemistry and Molecular Biology, March 25–28 in Seattle.
“Our lab has advanced a powerful strategy called scanning angle interference microscopy (SAIM) for measuring the nanoscale dimensions of the cancer cell glycocalyx,” said Park. “This imaging technique allows us to understand the structural relationship of cancer-associated mucins to the biophysical properties of the glycocalyx.”
The researchers generated a cellular model to precisely control the cell-surface mucin expression to mimic the cancer cell glycocalyx. They then combined SAIM with genetic approaches to study how the surface density, glycosylation and crosslinking of cancer-associated mucins affect the thickness of the barrier at the nanoscale. They also analyzed how the glycocalyx thickness affected a cell’s resistance to attack by immune cells.
The study revealed that the thickness of cancer cells' glycocalyx is one of the major parameters determining immune cell evasion and that engineered immune cells worked better if the glycocalyx was thinner.
Based on this knowledge, the researchers engineered immune cells with special enzymes on their surface to allow them to attach to and interact with the glycocalyx. Experiments performed at the cellular level showed that these immune cells were able to overcome the glycocalyx armor of cancer cells.
Next, the researchers plan to determine whether these findings can be replicated in the laboratory and, eventually, in clinical trials.
Sangwoo Park will present this research during the Regulatory Glycosylation Spotlight Session from 2–3 p.m. PDT on Sunday, March 26, in Room 608 of the Seattle Convention Center (abstract). Contact the media team for more information or to obtain a free press pass to attend the meeting.
Enjoy reading ASBMB Today?
Become a member to receive the print edition four times a year and the digital edition monthly.
Learn moreGet the latest from ASBMB Today
Enter your email address, and we’ll send you a weekly email with recent articles, interviews and more.
Latest in Science
Science highlights or most popular articles

Building a career in nutrition across continents
Driven by past women in science, Kazi Sarjana Safain left Bangladesh and pursued a scientific career in the U.S.

Avoiding common figure errors in manuscript submissions
The three figure issues most often flagged during JBC’s data integrity review are background signal errors, image reuse and undeclared splicing errors. Learn how to avoid these and prevent mistakes that could impede publication.

Ragweed compound thwarts aggressive bladder and breast cancers
Scientists from the University of Michigan reveal the mechanism of action of ambrosin, a compound from ragweed, selectively attacks advanced bladder and breast cancer cells in cell-based models, highlighting its potential to treat advanced tumors.

Lipid-lowering therapies could help treat IBD
Genetic evidence shows that drugs that reduce cholesterol or triglyceride levels can either raise or lower inflammatory bowel disease risk by altering gut microbes and immune signaling.

Key regulator of cholesterol protects against Alzheimer’s disease
A new study identifies oxysterol-binding protein-related protein 6 as a central controller of brain cholesterol balance, with protective effects against Alzheimer’s-related neurodegeneration.

From humble beginnings to unlocking lysosomal secrets
Monther Abu–Remaileh will receive the ASBMB’s 2026 Walter A. Shaw Young Investigator Award in Lipid Research at the ASBMB Annual Meeting, March 7-10 in Washington, D.C.

