Acylcarnitines, a warning signal for Type 2 diabetes
Type 2 diabetes, or T2D, is a chronic disease characterized by insulin resistance that impacts 34.2 million people in the United States. Another 88 million adults are prediabetic, meaning they likely will develop diabetes if they do not receive preventative care. Risk factors for T2D include aging, genetics and obesity. An estimated 89% of adults diagnosed with T2D between 2013 and 2016 were obese.
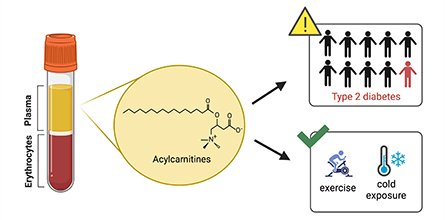
Irregular lipid metabolism associated with obesity and T2D is termed diabetic dyslipidemia, which includes increased plasma triglycerides and low-density lipoprotein cholesterol. This dyslipidemia occurs in 70% of T2D cases and is associated with higher rates of secondary conditions such as cardiovascular disease. Using mass spectrometry, researchers have found that dyslipidemia is associated with increases in more than 300 lipid species in the plasma, and there is mounting evidence that lipids contribute to T2D as signaling molecules.
Acylcarnitines, one of the lipid classes elevated in plasma with diabetic dyslipidemia, function in transport and signaling. In cells, acylcarnitines are made when a fatty acid is bound to carnitine on the outer mitochondria membrane by the enzyme carnitine palmitoyltransferase 1, or CPT1. Then acylcarnitines are transported into the mitochondria matrix, where they are converted back to free carnitines and fatty acid to be broken down by beta-oxidation for energy production. Acylcarnitines also can evade mitochondrial entry and are exported to the blood plasma.
Plasma acylcarnitines contribute to insulin resistance in obesity and T2D. Mice with genetic loss of CPT1 have lower plasma acylcarnitines and greater insulin sensitivity, while mice with a more active form of CPT1 have higher levels of acylcarnitines and insulin resistance. When Mary-Ellen Harper’s lab at the University of Ottawa treated isolated skeletal muscle cells with acylcarnitines, insulin resistance rapidly developed.
So, why would acylcarnitines signal for insulin resistance?
Plasma acylcarnitines increase in diabetes but also with normal stress such as exercise and cold exposure. Deborah Muoio’s lab at Duke University showed that loss of acylcarnitine processing in muscles leads to exercise intolerance, and work from our lab established that mice with a loss of CPT1 are intolerant to cold. A variant of CPT1 is abundant in Inuit populations of Greenland, Alaska and Canada. Work from our laboratory at the University of Wisconsin–Madison describes how this CPT1 variant is constitutively active, leading to higher acylcarnitine levels, which would be beneficial in response to the cold environment inhabited by the Inuit.
Exertion and cold cause organisms to switch fuel sources rapidly from glucose to lipids. Since insulin stimulates glucose uptake, insulin resistance might be advantageous for the switch to lipids. Acylcarnitine signaling could potentiate insulin resistance to facilitate the fuel transition, but the question is how.
As prediabetes and diabetes prevalence increases, we must identify early warning signs and understand the underlying pathobiology. Acylcarnitines are a piece of the puzzle; questions still loom about their transport and regulation in T2D. Understanding how acylcarnitines signal for insulin resistance and their functional role in normal physiology such as cold stress can hold the key to therapeutic intervention for T2D.
Want more lipid research news?
Check out Lipid Trends, a curated collection of hot picks from the world of lipid research, brought to you by LIPID MAPS.
Enjoy reading ASBMB Today?
Become a member to receive the print edition four times a year and the digital edition monthly.
Learn moreGet the latest from ASBMB Today
Enter your email address, and we’ll send you a weekly email with recent articles, interviews and more.
Latest in Science
Science highlights or most popular articles

The data that did not fit
Brent Stockwell’s perseverance and work on the small molecule erastin led to the identification of ferroptosis, a regulated form of cell death with implications for cancer, neurodegeneration and infection.

Building a career in nutrition across continents
Driven by past women in science, Kazi Sarjana Safain left Bangladesh and pursued a scientific career in the U.S.

Avoiding common figure errors in manuscript submissions
The three figure issues most often flagged during JBC’s data integrity review are background signal errors, image reuse and undeclared splicing errors. Learn how to avoid these and prevent mistakes that could impede publication.

Ragweed compound thwarts aggressive bladder and breast cancers
Scientists from the University of Michigan reveal the mechanism of action of ambrosin, a compound from ragweed, selectively attacks advanced bladder and breast cancer cells in cell-based models, highlighting its potential to treat advanced tumors.

Lipid-lowering therapies could help treat IBD
Genetic evidence shows that drugs that reduce cholesterol or triglyceride levels can either raise or lower inflammatory bowel disease risk by altering gut microbes and immune signaling.

Key regulator of cholesterol protects against Alzheimer’s disease
A new study identifies oxysterol-binding protein-related protein 6 as a central controller of brain cholesterol balance, with protective effects against Alzheimer’s-related neurodegeneration.


