Sphingolipid secrets of wound healing
We need the right kinds of sphingolipids in our bodies.
Sphingolipids are a class of lipids containing sphingosine, a long hydrocarbon chain attached to a head group derived from an amino acid — humble molecules that researchers are finding have many roles in the cell.
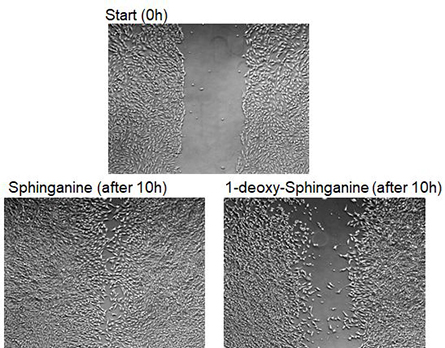
hours later (bottom). On bottom left, cells were exposed to canonical sphingolipids;
on bottom right, cells were exposed to 1-deoxy-sphingolipids.
An example of the havoc incorrect sphingolipid metabolism can wreak is the rare disease hereditary sensory neuropathy type 1, or HSAN1, which is caused by altered sphingolipid synthesis. People with HSAN1 experience severe peripheral neuropathy, a progressive loss of sensation in the extremities.
Thorsten Hornemann at the University Hospital Zurich has been studying sphingolipids in the context of such diseases for more than a decade. Hornemann and colleagues discovered that people with HSAN1 have a mutation in the enzyme that catalyzes the first step of sphingolipid synthesis, greatly overproducing an atypical type of sphingolipid called 1-deoxy-sphingolipid, or 1-deoxy-SL, that uses glycine or alanine in its synthesis instead of the canonical serine. This work showed that 1-deoxy-SLs are neurotoxic, potentially explaining the mechanism of HSAN1 neuropathy.
HSAN1 is estimated to affect only about two in every million people, but Type 2 diabetes, which has been diagnosed in about half a billion people worldwide, can cause almost identical symptoms.
A missing puzzle piece of this coincidence slid into place when Hornemann’s lab discovered that people with diabetes also have increased 1-deoxy-SLs, like HSAN1 patients. They then showed that lowering the levels of 1-deoxy-SLs improves neuropathy in diabetic rats.
There’s more than neuropathy though.
“HSAN1 patients frequently develop recurring and bad-healing wounds and ulcers,” Hornemann wrote in an email. “Since the patients also have no feeling for pain, they often don’t have proper wound protection or care, which makes the injuries progressively worse.”
The most severe injuries sometimes require amputation, and the same thing can happen in diabetes.
Hornemann’s group had observed that 1-deoxy-SLs alter the cytoskeleton, which gave them a new hypothesis: “We realized that (the cytoskeleton) might not only be important for neurons to maintain their structural integrity, but also for the wound healing process itself,” he explained. “The healing of a skin wound requires a highly coordinated migration of cells.”
This depends on the cytoskeleton and could be altered directly by 1-deoxy-SLs.
In their recent work published in the Journal of Lipid Research, Hornemann’s lab investigated this hypothesis by modeling wound healing in cell culture. The team grew plates of cells and then scratched the surface of the cell-covered plate, leaving a gap where cells were scratched away. They then measured how well cells migrated over the gap and filled it back in. Cells that were exposed to a higher level of 1-deoxy-SLs had a harder time migrating and filling in the gap, providing an explanation for the wound healing defect seen in HSAN1 and diabetes.
The lab’s work highlights two possible routes for treatment. In the current paper, it turned out that blocking the enzyme that interconverts different species of 1-deoxy-SL prevented the wound-healing defect. They also had shown previously that HSAN1 symptoms can be relieved by supplementation with serine, which pushes the cellular equilibrium away from 1-deoxy-SL toward canonical sphingolipids.
Since it appears that the same mechanism is behind the wound healing and neuropathy in diabetes, Hornemann suggests, “the same approach might also suppress 1-deoxySL formation in patients with diabetes and could be a therapeutic option.”
Enjoy reading ASBMB Today?
Become a member to receive the print edition four times a year and the digital edition monthly.
Learn moreGet the latest from ASBMB Today
Enter your email address, and we’ll send you a weekly email with recent articles, interviews and more.
Latest in Science
Science highlights or most popular articles

Avoiding common figure errors in manuscript submissions
The three figure issues most often flagged during JBC’s data integrity review are background signal errors, image reuse and undeclared splicing errors. Learn how to avoid these and prevent mistakes that could impede publication.

Ragweed compound thwarts aggressive bladder and breast cancers
Scientists from the University of Michigan reveal the mechanism of action of ambrosin, a compound from ragweed, selectively attacks advanced bladder and breast cancer cells in cell-based models, highlighting its potential to treat advanced tumors.

Lipid-lowering therapies could help treat IBD
Genetic evidence shows that drugs that reduce cholesterol or triglyceride levels can either raise or lower inflammatory bowel disease risk by altering gut microbes and immune signaling.

Key regulator of cholesterol protects against Alzheimer’s disease
A new study identifies oxysterol-binding protein-related protein 6 as a central controller of brain cholesterol balance, with protective effects against Alzheimer’s-related neurodegeneration.

From humble beginnings to unlocking lysosomal secrets
Monther Abu–Remaileh will receive the ASBMB’s 2026 Walter A. Shaw Young Investigator Award in Lipid Research at the ASBMB Annual Meeting, March 7-10 in Washington, D.C.

Chemistry meets biology to thwart parasites
Margaret Phillips will receive the Alice and C. C. Wang Award in Molecular Parasitology at the ASBMB Annual Meeting, March 7-10 in Washington, D.C.

