Researchers identify key metabolic regulators of drug resistance in pancreatic cancer
Researchers from the University at Buffalo School of Pharmacy and Pharmaceutical Sciences recently published an article in the journal Molecular & Cellular Proteomics describing their pursuit of key metabolic regulators involved in cancer cell resistance to gemcitabine, a standard-of-care chemotherapy for pancreatic dual adenocarcinoma, the most lethal type of pancreatic cancer.
Pancreatic adenocarcinoma does not respond well to current treatments or to newer immunotherapies that have worked well in some cancers. Gemcitabine is the mainstay drug for PDAC patients but provides only modest survival benefits.
Gemcitabine resistance can develop clinically during chemotherapy, resulting in poor patient prognosis. Clinically, development of gemcitabine resistance can be rapid and compromises its efficacy. Understanding the molecular mechanisms of gemcitabine resistance has been challenging.
Researchers Robert M. Straubinger and Jun Qu led the study, which included work by researcher William J. Jusko and several of his lab members. Straubinger and Qu collaborated on the application of a cutting-edge comprehensive, quantitative proteomic analysis approach to identify key metabolic regulators of gemcitabine resistance in PDAC. Their team systematically examined PDAC cancer cells and identified several therapeutic vulnerabilities of drug resistance that could be targeted to improve therapeutic outcomes for PDAC patients experiencing gemcitabine resistance.
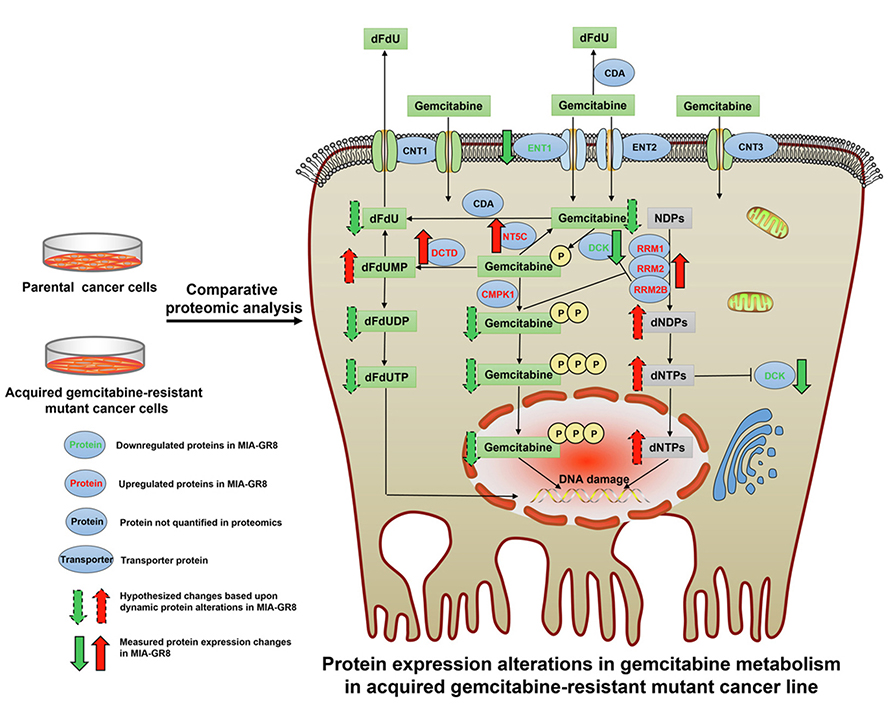
First author Qingxiang (Nick) Lin — who performed much of the work as a graduate student of Straubinger‘s in the Roswell Park Comprehensive Cancer Center Cancer Stress Biology Program and is now a postdoctoral scholar at Massachusetts General Hospital/Harvard Medical School — developed multiple cancer cell lines that acquired a high degree of gemcitabine resistance.
The team then employed the detailed proteomic analyses to test their hypothesis that the very large loss in gemcitabine sensitivity in the cell lines developed would identify multiple protein functional networks that cooperate in PDAC cells to create a highly drug-resistant state.
Overall, the work has developed a more complete understanding of gemcitabine resistance and established a rational basis for the design of effective therapeutic approaches to overcome gemcitabine resistance in PDAC patients.
The key findings indicated that the overall consequence of multiple protein-level changes observed in highly gemcitabine-resistant cells is that alterations in multiple drug response networks work in concert to reduce the intracellular concentrations of gemcitabine and its active metabolites.
The team noted significant elevations in protein expression within cellular gemcitabine transport and metabolism pathways that would prevent PDAC cells from experiencing lethal gemcitabine -induced stress and damage. The team concludes that approaches to modulate these drug metabolism pathways could overcome resistance therapeutically in PDAC patients, and it has been working toward identifying potential "master regulators" that may coordinate the overall drug-resistance response in PDAC cells.
“This research utilizes the cutting-edge global quantitative proteomic analyses to dissect systematically the molecular mechanisms of both acquired and intrinsic drug resistance in pancreatic cancer, and provides systems-level insights that could translate into therapeutic modulations of drug metabolism to overcome the chemo-resistance that frequently develops clinically, and improve the therapy of pancreatic cancer patients,” Lin said.
Straubinger added: “Understanding that there are adaptations within multiple pathways of cancer cells enables us to focus on new drugs that can combat drug resistance. One obvious focus would be to identify possible master regulators that drive drug resistance, because the changes we observed in highly drug resistant PDAC cells appear to be coordinated toward an overall purpose. Finding drugs that reprogram drug resistant cells would be the key to exploiting these findings and reverse clinical drug resistance.”
The team continues its work to develop promising drug combination strategies that can reverse drug resistance in PDAC patient tumors. The ultimate hope is that these approaches could move quickly to clinical investigation, benefitting pancreatic cancer patients fighting this highly aggressive and often lethal cancer.
This article first appeared in the University of Buffalo News Center and was republished with permission. Read the original.
Enjoy reading ASBMB Today?
Become a member to receive the print edition four times a year and the digital edition monthly.
Learn moreGet the latest from ASBMB Today
Enter your email address, and we’ll send you a weekly email with recent articles, interviews and more.
Latest in Science
Science highlights or most popular articles

Sizing up cells: How stem cells know when to divide
Stanford University researchers find that stem cells control their size early in cell division across living multicellular systems.

When oncogenes collide in brain development
Researchers at University Medical Center Hamburg, found that elevated oncoprotein levels within the Wnt pathway can disrupt the brain cell extracellular matrix, suggesting a new role for LIN28A in brain development.

The data that did not fit
Brent Stockwell’s perseverance and work on the small molecule erastin led to the identification of ferroptosis, a regulated form of cell death with implications for cancer, neurodegeneration and infection.

Building a career in nutrition across continents
Driven by past women in science, Kazi Sarjana Safain left Bangladesh and pursued a scientific career in the U.S.

Avoiding common figure errors in manuscript submissions
The three figure issues most often flagged during JBC’s data integrity review are background signal errors, image reuse and undeclared splicing errors. Learn how to avoid these and prevent mistakes that could impede publication.

Ragweed compound thwarts aggressive bladder and breast cancers
Scientists from the University of Michigan reveal the mechanism of action of ambrosin, a compound from ragweed, selectively attacks advanced bladder and breast cancer cells in cell-based models, highlighting its potential to treat advanced tumors.

