We put the titles of JBC’s most-read articles into an AI art generator
In the past week or two, you may have noticed a spate of whimsical images with scientific captions proliferating on social media like some kind of unannounced journal cover contest. Perhaps you’ve posted one yourself.
Researchers from many disciplines are putting the titles of their work –abstract phrases dense with academic jargon – into an AI art generator, and sharing the results. The trend is powered by an app called Dream from Canadian software developer Wombo, which also publishes a deepfake video app that makes photos appear to lip-synch.
Dream solicits text inputs, and using the free-associating power of artificial intelligence - plus the conventions of an art style the user chooses – custom-generates an image. Usually strange but appealing, the images tend to contain at least a few elements that you can trace back to the elements in the prompt. Wombo isn't saying much about what powers the software, but machine learning experts have speculated publicly that it may use a neural network technique called VQGAN + CLIP. The technique uses two neural networks, one to conjure images based on a text input, and the second to assess and tweak the outputs. (You can read an explanation of how it works here.)
Since it launched in late November, Dream has seen a wave of interest, partly on the strength of its sheer weirdness. ASBMB Today staff wondered how it would handle molecular biology and biochemistry. Here are AI-generated artworks based on four of JBC’s top papers of the year.
Rapid kinetics reveal surprising flavin chemistry in bifurcating electron transfer flavoprotein
We think: The festive style plays nicely with the weird blend of ball-and-stick and protein backbone model the algorithm cooked up. We think “chemistry,” “electron” and “flavoprotein” all helped set the tone.
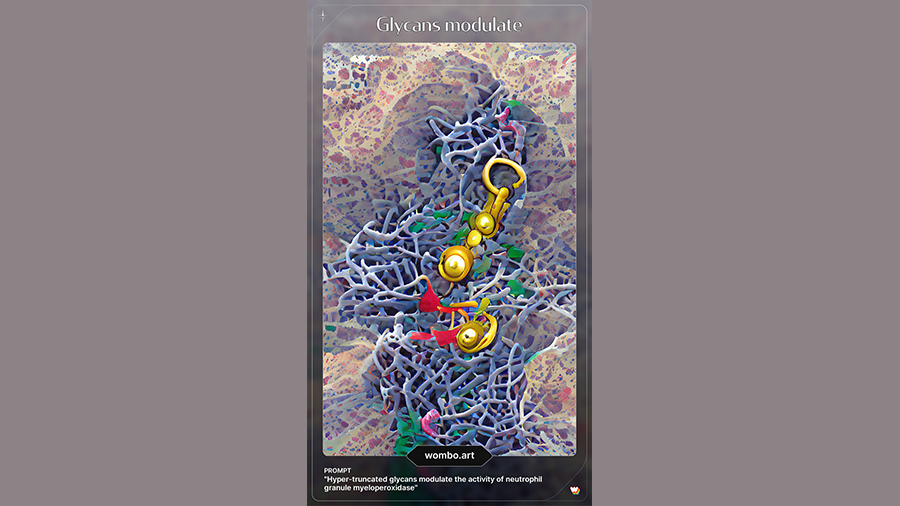
Hyper-truncated glycans modulate the activity of neutrophil granule myeloperoxidase
We think: The branch-like structures and webbing evoke both glycan tree images, and neutrophil extracellular traps. We decided to spare the AI the difficulty of rendering “Asn-355.”
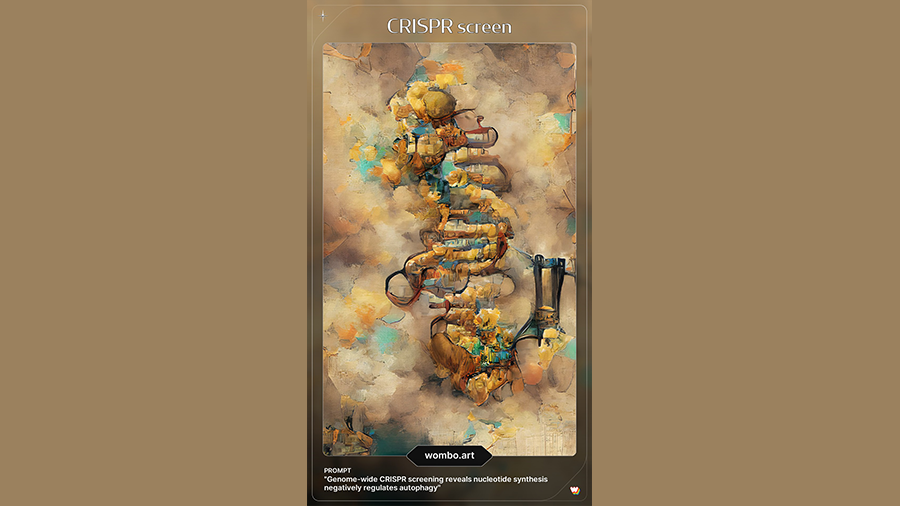
Genomewide CRISPR screening reveals nucleotide synthesis negatively regulates autophagy
We think: Genomewide CRISPR screens. Artwork generated by computers. Is there any doubt we live in the future? This piece used a steampunk style, and we love the cloud-double helix hybrid the algorithm came up with.
The extensive and functionally uncharacterized mitochondrial phosphoproteome
We think: This was a tough one with a lot of abstract words! We suggested the mystical art style, thinking it would help with the numinous vocabulary. The AI thought about it for quite a while, but it never returned an image output. Eventually, we felt bad about our carbon emissions and stopped the app.
Enjoy reading ASBMB Today?
Become a member to receive the print edition four times a year and the digital edition monthly.
Learn moreGet the latest from ASBMB Today
Enter your email address, and we’ll send you a weekly email with recent articles, interviews and more.
Latest in Science
Science highlights or most popular articles

From humble beginnings to unlocking lysosomal secrets
Monther Abu–Remaileh will receive the ASBMB’s 2026 Walter A. Shaw Young Investigator Award in Lipid Research at the ASBMB Annual Meeting, March 7-10 in Washington, D.C.

Chemistry meets biology to thwart parasites
Margaret Phillips will receive the Alice and C. C. Wang Award in Molecular Parasitology at the ASBMB Annual Meeting, March 7-10 in Washington, D.C.

ASBMB announces 2026 JBC/Tabor awardees
The seven awardees are first authors of outstanding papers published in 2025 in the Journal of Biological Chemistry.

Missing lipid shrinks heart and lowers exercise capacity
Researchers uncovered the essential role of PLAAT1 in maintaining heart cardiolipin, mitochondrial function and energy metabolism, linking this enzyme to exercise capacity and potential cardiovascular disease pathways.

Decoding how bacteria flip host’s molecular switches
Kim Orth will receive the Earl and Thressa Stadtman Distinguished Scientists Award at the ASBMB Annual Meeting, March 7–10, just outside of Washington, D.C.

Defining JNKs: Targets for drug discovery
Roger Davis will receive the Bert and Natalie Vallee Award in Biomedical Science at the ASBMB Annual Meeting, March 7–10, just outside of Washington, D.C.