Hippocampal lipids linked to brain disorders
The hippocampus is a fundamental brain region for memory processes, and its function is impaired early in the onset of neurodegenerative disorders such as Alzheimer’s disease, or AD.
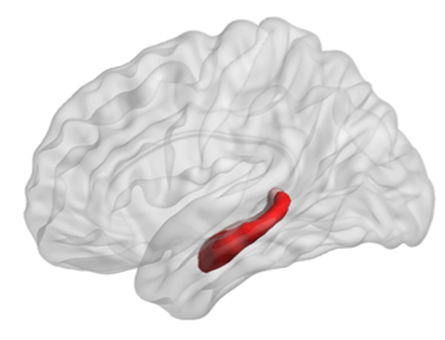
Most studies addressing the hippocampus have considered it as a whole structure, but it also can be divided into subregions along its longitudinal axis, segregating dorsal and ventral poles. For instance, the dorsal hippocampus, or DH, contributes differentially to specific dimensions of spatial memory, while the ventral hippocampus, or VH, is proposed to be implicated predominantly in behaviors linked to emotions.
Lipids are major brain constituents, so we performed mass spectrometry lipidomic analysis of hippocampal subregions along the longitudinal axis. Within the lipidomic signatures we uncovered, we observed that the DH presents increased levels of phosphatidic acid and decreased levels of phosphatidylcholine compared to the VH, potentially implicating the phospholipase D, or PLD, pathway in DH–VH axis regulation.
Although six PLDs are found in mammals, only PLD1 and PLD2 have reported canonical PLD activity, which is based on the hydrolysis of phosphatidylcholine in the presence of water to free choline and phosphatidic acid, a known second messenger signaling lipid. Using mice that were genetically altered to lack Pld1 and Pld2 genes, we gathered data to support the hypothesis that PLD1 and PLD2 are the only contributors to PLD activity in the mouse forebrain.
PLD1 ablation significantly decreased the hippocampal levels of phosphatidic acid, affecting predominantly the DH lipidome, but upon PLD2 ablation, only minor lipid changes occurred, including increased PLD products suggesting PLD1 upregulation.
Since PLD1 was the main PLD activity source, we then focused predominantly on characterizing the effects of PLD1 ablation and showed that the mice lacking Pld1 presented specific deficits in novel object recognition and social interaction, disruption in dendritic arborization, and altered synaptic plasticity in the DH. Overall, we determined that PLD1 ablation impairs hippocampal functioning, predominantly affecting the DH, which, due to its allocated functions, is predicted to be particularly affected in Alzheimer’s disease.
We previously had observed that PLD2 ablation is protective in mice genetically altered to have Alzheimer’s. Future studies should address cross-regulation mechanisms between PLD1 and PLD2 and how these can be used to develop therapeutic strategies to treat or prevent hippocampal dysfunction and memory deficits.
Want more lipid research news?
Check out Lipid Trends, a curated collection of hot picks from the world of lipid research, brought to you by LIPID MAPS.
Enjoy reading ASBMB Today?
Become a member to receive the print edition four times a year and the digital edition monthly.
Learn moreGet the latest from ASBMB Today
Enter your email address, and we’ll send you a weekly email with recent articles, interviews and more.
Latest in Science
Science highlights or most popular articles

Building a career in nutrition across continents
Driven by past women in science, Kazi Sarjana Safain left Bangladesh and pursued a scientific career in the U.S.

Avoiding common figure errors in manuscript submissions
The three figure issues most often flagged during JBC’s data integrity review are background signal errors, image reuse and undeclared splicing errors. Learn how to avoid these and prevent mistakes that could impede publication.

Ragweed compound thwarts aggressive bladder and breast cancers
Scientists from the University of Michigan reveal the mechanism of action of ambrosin, a compound from ragweed, selectively attacks advanced bladder and breast cancer cells in cell-based models, highlighting its potential to treat advanced tumors.

Lipid-lowering therapies could help treat IBD
Genetic evidence shows that drugs that reduce cholesterol or triglyceride levels can either raise or lower inflammatory bowel disease risk by altering gut microbes and immune signaling.

Key regulator of cholesterol protects against Alzheimer’s disease
A new study identifies oxysterol-binding protein-related protein 6 as a central controller of brain cholesterol balance, with protective effects against Alzheimer’s-related neurodegeneration.

From humble beginnings to unlocking lysosomal secrets
Monther Abu–Remaileh will receive the ASBMB’s 2026 Walter A. Shaw Young Investigator Award in Lipid Research at the ASBMB Annual Meeting, March 7-10 in Washington, D.C.


