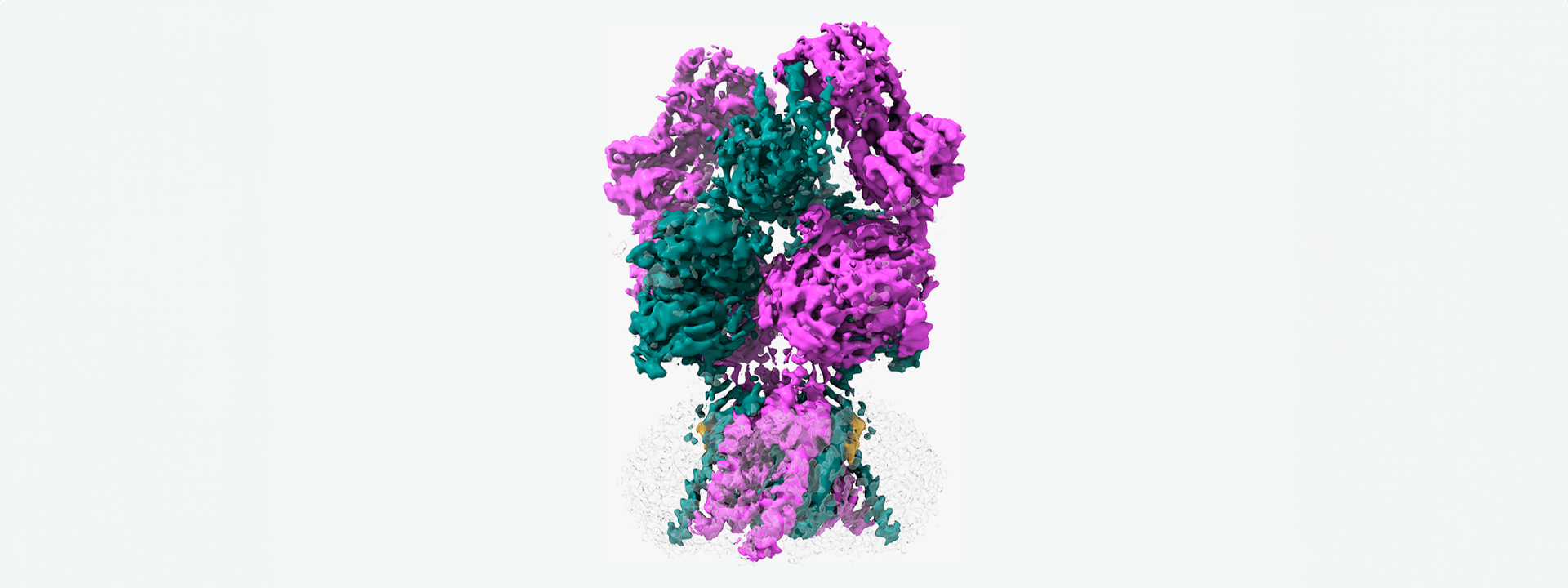
This protein does “The Twist”
Proteins are constantly performing a kind of dance. They move and contort their bodies to fulfill specific functions inside our bodies. The NMDAR protein executes an especially hard dance routine in our brains. One wrong step can lead to a range of neurological disorders. NMDAR binds to the neurotransmitter, glutamate, and another compound, glycine. These bindings control NMDAR’s dance steps. When their routine is over, the NMDAR opens. This open ion channel generates electrical signals critical for cognitive functions like memory.
The problem is that scientists couldn’t figure out the last step in NMDAR’s routine—until now. Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Professor Hiro Furukawa and his team have deciphered the critical dance move in which NMDAR rotates into an open formation. In other words, they’ve learned the NMDAR “Twist.”
To capture this key step, Furukawa and his team used a technique called electron cryo-microscopy (cryo-EM), which freezes and visualizes proteins in action. First, the team had to find a way to keep a type of NMDAR called GluN1-2B in its open pose long enough to image it. So, Furukawa teamed up with Professors Stephen Traynelis and Dennis Liotta at Emory University. Together, they discovered a molecule that favors NMDAR in an open position.
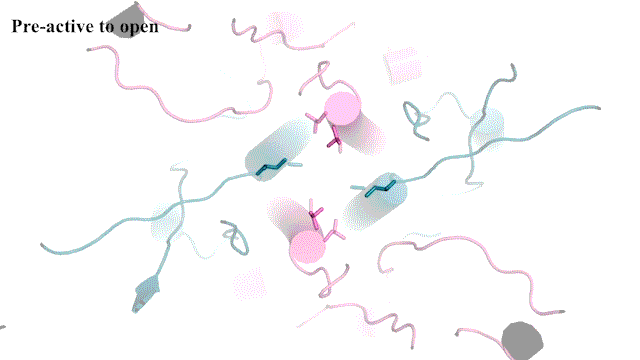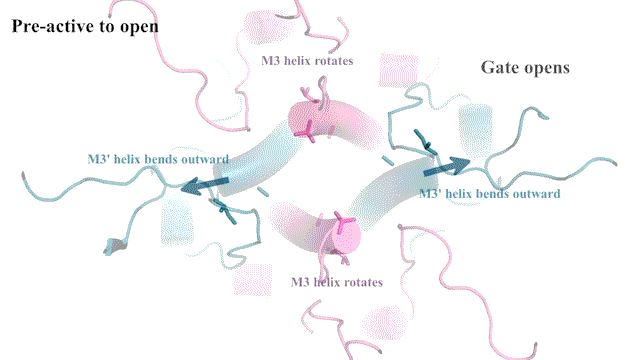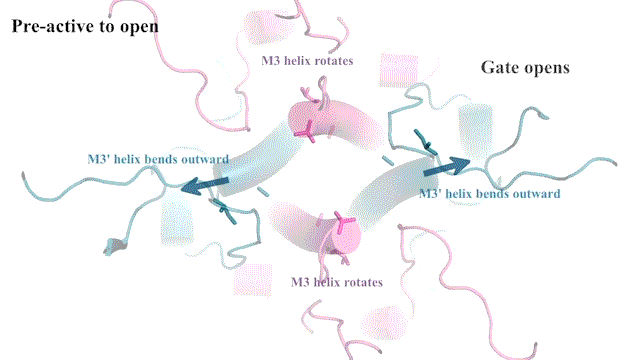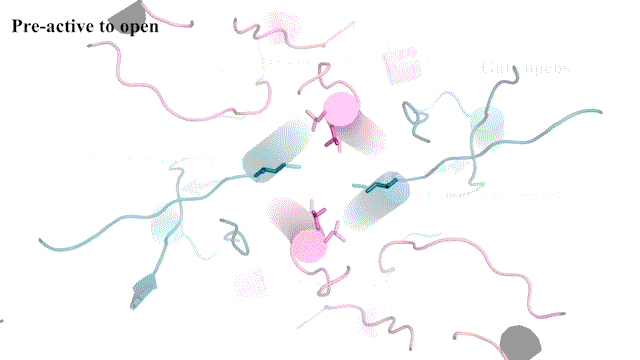
“It’s not the most stable conformation,” Furukawa explains. “There are many pieces dancing independently in NMDAR. They have to coordinate with each other. Everything has to go perfectly to open the ion channel. We need a precise amount of electrical signals at the right time for proper behaviors and cognitions.”
The cryo-EM images allow researchers to see precisely how the NMDAR’s atoms move during its “Twist.” This may one day lead to drug compounds that can teach the correct moves to NMDARs that have lost a step. Better drugs that target NMDARs might have applications for neurological disorders like Alzheimer’s and depression. Furukawa explains:
“Compounds bind to pockets within proteins and are imperfect, initially. This will allow us and chemists to find a way to fill those pockets more perfectly. That would improve the potency of the drug. Also, the shape of the pocket is unique. But there could be something similarly shaped in other proteins. That would cause side effects. So, specificity is key.”
Indeed, there are many types of NMDARs in the brain. Another recent study from Furukawa’s lab offers the first view of the GluN1-3A NMDAR. Surprisingly, its dance moves are completely different. This routine results in unusual patterns of electrical signals.
In other words, we’re mastering the Twist.
Enjoy reading ASBMB Today?
Become a member to receive the print edition four times a year and the digital edition monthly.
Learn moreGet the latest from ASBMB Today
Enter your email address, and we’ll send you a weekly email with recent articles, interviews and more.
Latest in Science
Science highlights or most popular articles

Sizing up cells: How stem cells know when to divide
Stanford University researchers find that stem cells control their size early in cell division across living multicellular systems.

When oncogenes collide in brain development
Researchers at University Medical Center Hamburg, found that elevated oncoprotein levels within the Wnt pathway can disrupt the brain cell extracellular matrix, suggesting a new role for LIN28A in brain development.

The data that did not fit
Brent Stockwell’s perseverance and work on the small molecule erastin led to the identification of ferroptosis, a regulated form of cell death with implications for cancer, neurodegeneration and infection.

Building a career in nutrition across continents
Driven by past women in science, Kazi Sarjana Safain left Bangladesh and pursued a scientific career in the U.S.

Avoiding common figure errors in manuscript submissions
The three figure issues most often flagged during JBC’s data integrity review are background signal errors, image reuse and undeclared splicing errors. Learn how to avoid these and prevent mistakes that could impede publication.

Ragweed compound thwarts aggressive bladder and breast cancers
Scientists from the University of Michigan reveal the mechanism of action of ambrosin, a compound from ragweed, selectively attacks advanced bladder and breast cancer cells in cell-based models, highlighting its potential to treat advanced tumors.

