New diagnostic finds intact sperm in infertile men
In a recent study, researchers created a diagnostic test to identify functional sperm in infertile men that could change the treatment of male infertility and assisted reproductive technology.
“Male infertility is a recognized issue and deserves scientific and clinical attention,” said Andrei Drabovich, an assistant professor of laboratory medicine and pathology at the University of Alberta and corresponding author of the Molecular & Cellular Proteomics study.
One in every six couples trying to conceive experience infertility issues. In fact, about 10% of men in the United States are infertile. The most common cause of severe male infertility is a condition known as nonobstructive azoospermia, which results in the absence of sperm in the ejaculate due to poor sperm, or spermatozoa, development.
While assisted reproductive technology has improved exponentially over the past 50 years, according to Drabovich, extracting sperm from men with NOA can take up to 10 hours in the operating room and has varying rates of success.
“Sometimes surgeons can only extract a few intact spermatozoa during a surgery that takes many hours,” Drabovich said.
That’s why he set out to develop a noninvasive method to diagnose NOA and figure out if these men contain intact sperm that could fertilize an egg.
“Tests that show the presence or absence of intact spermatozoa in semen can give a good clue of the total numbers of spermatozoa in the patient,” Drabovich said. “If there are intact spermatozoa in the ejaculate that is a green light for urologist and the surgeon to go ahead with the surgery. However, it is an extreme challenge to find intact spermatozoa in a field of debris.”
Drabovich performed mass spectrometry on semen from men with normal fertility as well as infertile men with biopsy-confirmed obstructive azoospermia or NOA.
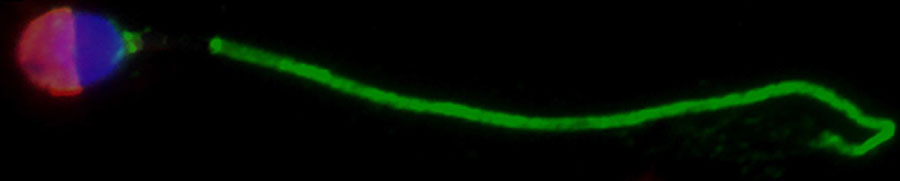
After analysis, his team identified two proteins, AKAP4 and ASPX, that are found in intact sperm in men with NOA. They showed that ASPX is located in the head of sperm while AKAPA4 is found in the tail using a method called imaging flow cytometry. During imaging flow cytometry, a machine takes images of individual cells. After running these samples, computational algorithms help the researchers mine the millions of images of cell debris and underdeveloped sperm to identify a few intact sperm cells.
Since the roles of AKAP4 and ASPX are not fully understood, Drabovich plans to investigate how they contribute to sperm function.
He also said that his work may lead to male birth control drugs in the future.
“We want to see if we can flip the story and try to work on male contraceptives,” Drabovich said. “If we know the function of the protein, we may be able to inhibit it to create a nonhormonal male contraceptive, which is a much desired type of drug at the moment.”
Enjoy reading ASBMB Today?
Become a member to receive the print edition four times a year and the digital edition monthly.
Learn moreGet the latest from ASBMB Today
Enter your email address, and we’ll send you a weekly email with recent articles, interviews and more.
Latest in Science
Science highlights or most popular articles

The data that did not fit
Brent Stockwell’s perseverance and work on the small molecule erastin led to the identification of ferroptosis, a regulated form of cell death with implications for cancer, neurodegeneration and infection.

Building a career in nutrition across continents
Driven by past women in science, Kazi Sarjana Safain left Bangladesh and pursued a scientific career in the U.S.

Avoiding common figure errors in manuscript submissions
The three figure issues most often flagged during JBC’s data integrity review are background signal errors, image reuse and undeclared splicing errors. Learn how to avoid these and prevent mistakes that could impede publication.

Ragweed compound thwarts aggressive bladder and breast cancers
Scientists from the University of Michigan reveal the mechanism of action of ambrosin, a compound from ragweed, selectively attacks advanced bladder and breast cancer cells in cell-based models, highlighting its potential to treat advanced tumors.

Lipid-lowering therapies could help treat IBD
Genetic evidence shows that drugs that reduce cholesterol or triglyceride levels can either raise or lower inflammatory bowel disease risk by altering gut microbes and immune signaling.

Key regulator of cholesterol protects against Alzheimer’s disease
A new study identifies oxysterol-binding protein-related protein 6 as a central controller of brain cholesterol balance, with protective effects against Alzheimer’s-related neurodegeneration.

