From the journals: JLR
Breaking down atherosclerotic plaque. Location matters in liver disease. A lipidomic profile drives liver disease. Read about papers on these topics recently published in the Journal of Lipid Research.
Breaking down atherosclerotic plaque
According to the World Health Organization, cardiovascular disease is the leading cause of death worldwide and causes 17.9 million deaths each year. Most cardiovascular disease is caused by atherosclerosis, which is the thickening of the arteries as a result of plaque buildup.
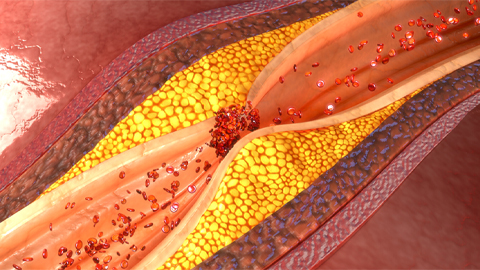
Plaques are usually made up of cholesterol, cellular waste products, calcium and fibrin. In addition, they often contain oxidized polyunsaturated fatty acids, which can be further broken down into cholesteryl hemiesters, or ChEs. However, researchers do not yet completely understand the role of ChEs in plaque buildup and atherosclerosis. In a recent study in the Journal of Lipid Research, Neuza Domingues of NOVA University Lisbon and an international team of researchers used lipidomics and human-obstructed artery samples to learn more.
The team showed that ChEs are found in patients with cardiovascular disease and are localized to blocked arteries. The most common ChE the team identified was cholesteryl hemiazelate, or ChA. When the researchers exposed human monocytes to ChA in a dish, the cells produced proinflammatory cytokines.
The team also examined the role of ChA in zebrafish. After feeding zebrafish larvae a ChA-enriched diet, they accumulated inflammatory immune cells such as monocytes and neutrophils as well as lipids in the vasculature. The inflammatory outcomes were caspase-1 and cathepsin-B. This led the authors to conclude that ChEs such as ChA behave as a damage-associated molecular pattern and promote inflammation and atherosclerosis.
Further analysis of ChA levels in humans may provide a diagnostic or prognostic marker for patients with cardiovascular disease and atherosclerosis.
Location matters in liver disease
Alcoholic-related liver disease is a leading cause of chronic liver disease-related mortality in Western countries, but researchers do not yet completely understand the condition. Excessive alcohol consumption can lead to an imbalance in the biogenesis and breakdown of lipids and to mitochondrial dysfunction. Steroidogenic acute regulatory protein, or StARD1, regulates steroid hormone synthesis and mediates the transport of cholesterol from the outer mitochondrial membrane to the inner mitochondrial membrane. In addition, StARD1 has been shown to promote nonalcoholic fatty liver disease.
In a recent study in the Journal of Lipid Research, Raquel Fucho and Estel Solsona–Vilarrasa of the Institute of Biomedical Research of Barcelona, Spain, and colleagues investigated the role of StARD1 in chronic liver disease and alcohol-induced liver injury. Using mouse models of alcoholic-related liver diseases, the team showed that alcohol feeding induces StARD1 expression in perivenous zone liver hepatocytes. By contrast, animals that were not fed alcohol showed StARD1 expression in the periportal liver hepatocytes. Transmission electron microscope images revealed that alcohol feeding increased lipid droplet accumulation and mitochondrial number in the perivenous zone.
These results demonstrate that the role of StARD1 in hepatocyte mitochondrial metabolism depends on their location within the liver during alcoholic-related liver disease.
A lipidomic profile drives liver disease
Nonalcoholic fatty liver disease, or NAFLD, is the most common chronic liver disorder. Risk factors include conditions such as obesity and diabetes as well as dyslipidemia — the imbalance of lipids such as triglycerides; low-density lipoprotein, or LDL; high-density lipoprotein, or HDL; and apolipoprotein B, or ApoB. Though the roles of cholesterol and triglycerides have been extensively studied in NAFLD, researchers have not yet defined the role of ApoB.
In a recent study published in the Journal of Lipid Research, Yiying Wang and Lijie Kong of Shanghai Jiao Tong University School of Medicine and colleagues followed a group of patients with nonalcoholic fatty liver disease for five years. They assessed whether the lipid phenotype hypertriglyceridemic hyperapoB is associated with the incidence or resolution of NAFLD. This phenotype is characterized by hypertriglyceridemia, increased numbers of small dense LDL particles, low levels of HDL cholesterol and ApoB dyslipoproteinemia, with an increased number of very low-density lipoprotein. The cohort was made up of over 9,000 individuals 40 years or older. The team completed baseline and multiple follow-up lipid measurements while assessing the cohort for NAFLD incidence and recovery.
Results showed that adults with hypertriglyceridemic hyperapoB have a higher risk of NAFLD incidence and a lower likelihood of NAFLD recovery. Therefore, characteristics of hypertriglyceridemic hyperapoB may be a biomarker for future NAFLD prevention and treatment.
Enjoy reading ASBMB Today?
Become a member to receive the print edition four times a year and the digital edition monthly.
Learn moreGet the latest from ASBMB Today
Enter your email address, and we’ll send you a weekly email with recent articles, interviews and more.
Latest in Science
Science highlights or most popular articles

Sizing up cells: How stem cells know when to divide
Stanford University researchers find that stem cells control their size early in cell division across living multicellular systems.

When oncogenes collide in brain development
Researchers at University Medical Center Hamburg, found that elevated oncoprotein levels within the Wnt pathway can disrupt the brain cell extracellular matrix, suggesting a new role for LIN28A in brain development.

The data that did not fit
Brent Stockwell’s perseverance and work on the small molecule erastin led to the identification of ferroptosis, a regulated form of cell death with implications for cancer, neurodegeneration and infection.

Building a career in nutrition across continents
Driven by past women in science, Kazi Sarjana Safain left Bangladesh and pursued a scientific career in the U.S.

Avoiding common figure errors in manuscript submissions
The three figure issues most often flagged during JBC’s data integrity review are background signal errors, image reuse and undeclared splicing errors. Learn how to avoid these and prevent mistakes that could impede publication.

Ragweed compound thwarts aggressive bladder and breast cancers
Scientists from the University of Michigan reveal the mechanism of action of ambrosin, a compound from ragweed, selectively attacks advanced bladder and breast cancer cells in cell-based models, highlighting its potential to treat advanced tumors.

