From the journals: JLR
A safer combination therapy for liver disease. A mechanistic pathway of the pathophysiology of NASH. A novel therapeutic target for heart failure. Read about papers on these topics recently published in the Journal of Lipid Research.
A safer combination therapy for liver disease
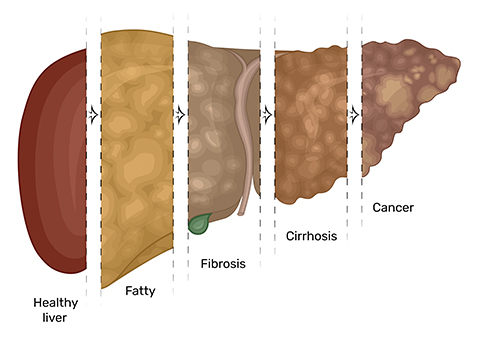
Over 90 million Americans suffer from nonalcoholic fatty liver disease, or NAFLD, which can progress to the inflammatory condition nonalcoholic steatohepatitis, or NASH. The enzyme acetyl CoA carboxylase, or ACC, catalyzes lipogenesis and regulates fatty acid oxidation, so inhibiting ACC is an attractive therapeutic target for these disorders. However, treating NASH with ACC inhibitors can alter the levels of lipoproteins such as apoB-low density lipoprotein, or LDL, and triglyceride, or TG, content in plasma.
Mohamad Dandan and a team from the University of California, Berkeley, and Gilead Sciences USA conducted a safety and efficacy trial in adults aged 18–75 to study how certain drugs affect lipid metabolism on NASH. The researchers investigated the effects of an ACC inhibitor drug called firsocostat on production rates of plasma LDL-apoB in NASH and described their findings in a recent paper in the Journal of Lipid Research.
The team performed metabolic labeling with water containing deuterium in place of hydrogen and analyzed lipoprotein complex enrichments in NASH patients for 12 weeks. In patients treated with firsocostat, the plasma TG levels and lipoprotein clearance kinetics increased without a significant increase in apoB concentrations. The rise in plasma TG and apoB-containing lipoprotein levels was only seen in NASH patients with cirrhotic conditions.
The researchers looked at whether a lipid-lowering drug, fenofibrate, could mitigate these side effects of firsocostat. They treated 29 NASH patients with both fenofibrate and firsocostat. After 12 weeks, it appeared that fenofibrate could prevent changes in the lipid turnover and apoB-LDL kinetics associated with firsocostat.
Altered TG levels and lipoprotein metabolism correlate with a higher risk of atherogenesis and cardiovascular diseases, so these results suggest that combining firsocostat and fenofibrate for NASH treatment could lessen undesirable consequences and risks. Further studies and clinical trials are needed to substantiate these results.
A mechanistic pathway of the pathophysiology of NASH
Oxidized cholesterol metabolites known as oxysterols are involved in various biological processes including hepatic cholesterol metabolism and bile acid synthesis. Hydroxylation of oxysterols by the enzyme CYP7B1 facilitates their conversion to bile acids in hepatocytes. Babies born without enough CYP7B1 activity often develop liver failure. Previous reports have associated the accumulation of free cholesterol and its metabolites with mitochondrial dysfunction and hepatocyte apoptosis often seen in nonalcoholic steatohepatitis, or NASH, but researchers do not yet fully understand the underlying mechanism.
Kei Minowa of Virginia Commonwealth University and Juntendo University, Japan, and a research team studied the role of mitochondrial cholesterol metabolism in the pathophysiology of NASH and published their findings in the Journal of Lipid Research.
The researchers fed three kinds of diet — normal, Western and high cholesterol — to mice genetically altered to lack CYP7B1. They analyzed the mice’s levels of serum and liver cholesterol metabolites and hepatic gene expressions. The researchers saw the development of insulin resistance and accumulation of oxysterols in mice on the Western diet but not in mice on the normal or high cholesterol diet. This study indicates that an insulin resistance–mediated pathway mediates the accumulation of toxic cholesterol metabolites in hepatocyte mitochondria, driving hepatocellular damage in nonalcoholic fatty liver diseases.
A novel therapeutic target for heart failure
A patient with heart failure with preserved ejection fraction, or HFpEF, shows symptoms of heart failure but 50% or more of the blood in the left ventricle is still pushed out with each heartbeat. Many HFpEF patients have comorbidities associated with metabolic syndrome or MetS. Scientists have proposed that inflammation associated with MetS promotes ventricular tissue remodeling, leading to heart failure.
Researchers have reported that a receptor for fatty acids, free fatty acid receptor 4, or Ffar4, reduces metabolic dysfunction and resolves inflammation. In a recent paper in the Journal of Lipid Research, Naixin Zhang of the University of Minnesota and a team from UMN and Penn State proposed that Ffar4 could reduce ventricular remodelling associated with HFpEF.
The researchers fed a high-fat/high-sucrose diet to mice genetically altered to lack Ffar4, or Ffar4KO mice, to induce an HFpEF–MetS phenotype. This diet worsened diastolic function in male Ffar4KO mice, but the Ffar4KO females became obese with no ventricular remodeling compared to unaltered mice. Ffar4KO male mice showed an altered balance of inflammatory mediators called oxylipins with a lower level of an anti-inflammatory oxylipin and a higher proinflammatory oxylipin than unaltered mice.
This suggests that preventing HFpEF remodeling by modulating oxylipin levels and consequent attenuation of inflammation might underlie Ffar4’s cardioprotective role. The authors suggest that Ffar4 agonists could be used to treat cardiometabolic diseases such as HFpEF.
Enjoy reading ASBMB Today?
Become a member to receive the print edition four times a year and the digital edition monthly.
Learn moreGet the latest from ASBMB Today
Enter your email address, and we’ll send you a weekly email with recent articles, interviews and more.
Latest in Science
Science highlights or most popular articles

Avoiding common figure errors in manuscript submissions
The three figure issues most often flagged during JBC’s data integrity review are background signal errors, image reuse and undeclared splicing errors. Learn how to avoid these and prevent mistakes that could impede publication.

Ragweed compound thwarts aggressive bladder and breast cancers
Scientists from the University of Michigan reveal the mechanism of action of ambrosin, a compound from ragweed, selectively attacks advanced bladder and breast cancer cells in cell-based models, highlighting its potential to treat advanced tumors.

Lipid-lowering therapies could help treat IBD
Genetic evidence shows that drugs that reduce cholesterol or triglyceride levels can either raise or lower inflammatory bowel disease risk by altering gut microbes and immune signaling.

Key regulator of cholesterol protects against Alzheimer’s disease
A new study identifies oxysterol-binding protein-related protein 6 as a central controller of brain cholesterol balance, with protective effects against Alzheimer’s-related neurodegeneration.

From humble beginnings to unlocking lysosomal secrets
Monther Abu–Remaileh will receive the ASBMB’s 2026 Walter A. Shaw Young Investigator Award in Lipid Research at the ASBMB Annual Meeting, March 7-10 in Washington, D.C.

Chemistry meets biology to thwart parasites
Margaret Phillips will receive the Alice and C. C. Wang Award in Molecular Parasitology at the ASBMB Annual Meeting, March 7-10 in Washington, D.C.

