Crystal building blocks of triglycerides
Francis Crick once said, “If you want to understand function, study structure.” Do you agree? I certainly do, and I would argue that most lipid biologists do too. Just consider the effort to define chemical structures for the many thousands of lipids that exist and the hypotheses about individual lipid function that this structural information has generated.
What has lagged behind is the characterization of the structures of the proteins that modify, transport or interact with these lipids, but times are changing. For example, when I started my postdoc in Yusuf Hannun’s lab, only a handful of sphingolipid-metabolizing enzymes had been structurally characterized, and these were mainly from bacteria. While many questions remain open (hey, ceramide synthase — we can’t wait to see what you look like!), work from several labs has defined the structures and mechanisms for many human enzymes in sphingolipid metabolism.
A similar revolution appears to be happening with triglycerides. As most of you know, triglycerides serve as a reservoir for energy storage, but when they accumulate excessively, they can cause health problems, including obesity, diabetes and heart disease. Three new structures in particular have caught my attention.
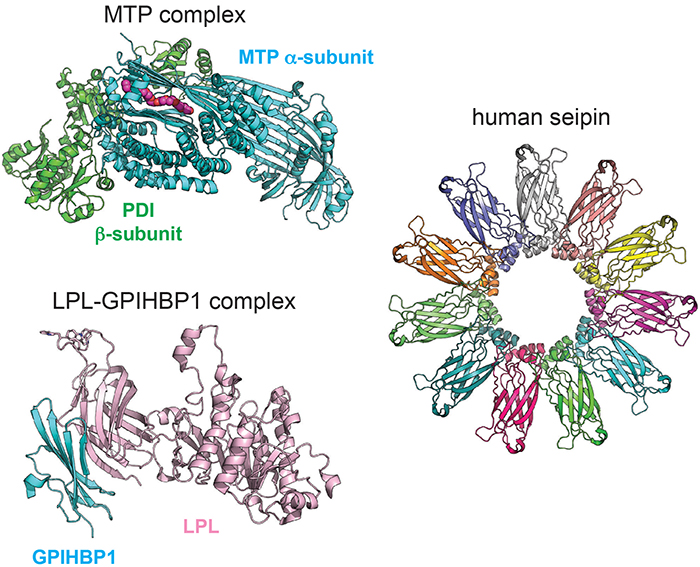 Beautiful structures of proteins involved in triglyceride metabolism and storage.Michael AirolaThe most recent is a crystal structure of microsomal triglyceride transfer protein complex, which transfers neutral lipids into apolipoprotein B-containing lipoproteins. The arduous crystallography required to conduct this work is impressive. The researchers revealed an unexpected lipid-binding cavity and provided insight into disease mutations as well as pharmacological inhibition of this therapeutic target.
Beautiful structures of proteins involved in triglyceride metabolism and storage.Michael AirolaThe most recent is a crystal structure of microsomal triglyceride transfer protein complex, which transfers neutral lipids into apolipoprotein B-containing lipoproteins. The arduous crystallography required to conduct this work is impressive. The researchers revealed an unexpected lipid-binding cavity and provided insight into disease mutations as well as pharmacological inhibition of this therapeutic target.
The second is the crystal structure of lipoprotein lipase, or LPL, the major lipase that clears triglycerides in the blood. Gabriel Birrane and colleagues and Risha Arora and colleagues separately determined the LPL structures, overcoming the relative instability of LPL by complexing it with its binding partner glycosylphosphatidylinositol-anchored high-density lipoprotein-binding protein 1. These structures, along with other biochemical data, suggest LPL is active as a monomer, challenging the long-standing paradigm that LPL was only active as a dimer.
The last notable structure is that of seipin, a homo-oligomeric integral membrane protein that is a key player in the formation of cytoplasmic lipid droplets. Two groups (Renhong Yan and colleagues and Xuewu Sui and colleagues), using cryo-electron microscopy, found that 11 or 12 seipin molecules (dependent on the species) come together to form a ring that spans the endoplasmic reticulum membrane, can bind phosphatidic acid and may stabilize the formation of nascent lipid droplets.
What’s next? Who knows, but I’m darn sure we’re all gonna love it.
Enjoy reading ASBMB Today?
Become a member to receive the print edition four times a year and the digital edition monthly.
Learn moreGet the latest from ASBMB Today
Enter your email address, and we’ll send you a weekly email with recent articles, interviews and more.
Latest in Science
Science highlights or most popular articles

When oncogenes collide in brain development
Researchers at University Medical Center Hamburg, found that elevated oncoprotein levels within the Wnt pathway can disrupt the brain cell extracellular matrix, suggesting a new role for LIN28A in brain development.

The data that did not fit
Brent Stockwell’s perseverance and work on the small molecule erastin led to the identification of ferroptosis, a regulated form of cell death with implications for cancer, neurodegeneration and infection.

Building a career in nutrition across continents
Driven by past women in science, Kazi Sarjana Safain left Bangladesh and pursued a scientific career in the U.S.

Avoiding common figure errors in manuscript submissions
The three figure issues most often flagged during JBC’s data integrity review are background signal errors, image reuse and undeclared splicing errors. Learn how to avoid these and prevent mistakes that could impede publication.

Ragweed compound thwarts aggressive bladder and breast cancers
Scientists from the University of Michigan reveal the mechanism of action of ambrosin, a compound from ragweed, selectively attacks advanced bladder and breast cancer cells in cell-based models, highlighting its potential to treat advanced tumors.

Lipid-lowering therapies could help treat IBD
Genetic evidence shows that drugs that reduce cholesterol or triglyceride levels can either raise or lower inflammatory bowel disease risk by altering gut microbes and immune signaling.

