Targeting cardiolipin modification in a genetic disorder
Barth syndrome, an X-linked disorder that primarily affects males, is characterized by weak skeletal muscles, cardiomyopathy and low neutrophils (the white blood cells that fight bacteria), among other medical concerns. The symptoms can be treated, but no disease-specific therapies have been approved. This rare and serious lipid metabolism disorder is caused by pathogenic variants in the gene TAFAZZIN.
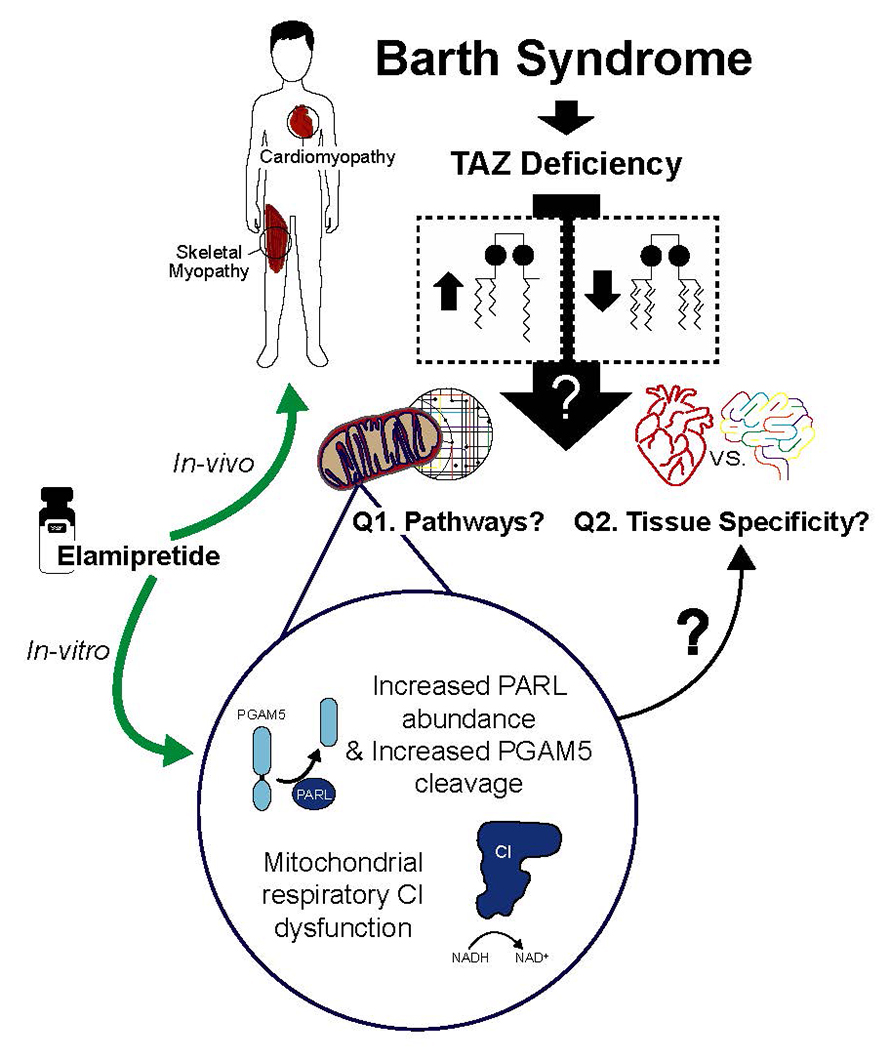
TAFAZZIN encodes for an enzyme involved in the final remodeling step of cardiolipin, a key phospholipid localized to the mitochondrial inner membrane. TAFAZZIN deficiency results in abnormal mitochondrial cardiolipin quantity and composition and subsequent mitochondrial dysfunction. Whereas researchers have known the primary biochemical defect in Barth syndrome for several decades, two important questions have remained unanswered: What molecular pathways are impacted by TAFAZZIN deficiency and contribute to resultant mitochondrial dysfunction? And why does deficiency of an enzyme that affects a molecule present in every cell in the body affect such a specific set of tissues? Answering these questions is key to developing treatments for Barth syndrome.
Combined proteomic, metabolomic and functional studies in a CRISPR-edited TAFAZZIN knockout HEK293 cell model recently have offered insight into these questions. Among the molecular abnormalities that researchers at the Johns Hopkins School of Medicine identified in this cellular model were defects in the expression, assembly and function of complex I of the mitochondrial respiratory chain. The researchers also found increased expression of presenilin-associated rhomboidlike protein, a protease localized to the inner mitochondrial membrane, and abnormal cleavage of its downstream target, phosphoglycerate mutase 5. Thus, TAFAZZIN deficiency affects mitochondrial respiratory chain function and quality control.
The researchers found that both elamipretide, a molecule that binds to cardiolipin, and bromoenol lactone, which inhibits nascent cardiolipin deacylation, partially remediate these mitochondrial defects. Determining if these pathways are differentially impacted in spared versus affected tissues may help researchers understand what causes the pleiotropic effects of TAFAZZIN deficiency and suggest therapeutic approaches.
In addition to demonstrating the effects of cardiolipin targeting in cellular models of TAFAZZIN deficiency in the lab, this approach has shown clinical promise. In a recent study published in the journal Genetics in Medicine, clinical researchers at the Johns Hopkins School of Medicine described results of a placebo-controlled, crossover clinical trial to investigate the role of elamipretide in 12 patients affected by Barth syndrome. The study participants showed improvement in multiple clinical parameters, including muscle strength, exercise tolerance and cardiac stroke volume, after 48 weeks of treatment.
Together, these studies show the translational potential of cellular disease modeling and pathway targeting in lipid metabolism disorders.
Enjoy reading ASBMB Today?
Become a member to receive the print edition four times a year and the digital edition monthly.
Learn moreGet the latest from ASBMB Today
Enter your email address, and we’ll send you a weekly email with recent articles, interviews and more.
Latest in Science
Science highlights or most popular articles

Lipid-lowering therapies could help treat IBD
Genetic evidence shows that drugs that reduce cholesterol or triglyceride levels can either raise or lower inflammatory bowel disease risk by altering gut microbes and immune signaling.

Key regulator of cholesterol protects against Alzheimer’s disease
A new study identifies oxysterol-binding protein-related protein 6 as a central controller of brain cholesterol balance, with protective effects against Alzheimer’s-related neurodegeneration.

From humble beginnings to unlocking lysosomal secrets
Monther Abu–Remaileh will receive the ASBMB’s 2026 Walter A. Shaw Young Investigator Award in Lipid Research at the ASBMB Annual Meeting, March 7-10 in Washington, D.C.

Chemistry meets biology to thwart parasites
Margaret Phillips will receive the Alice and C. C. Wang Award in Molecular Parasitology at the ASBMB Annual Meeting, March 7-10 in Washington, D.C.

ASBMB announces 2026 JBC/Tabor awardees
The seven awardees are first authors of outstanding papers published in 2025 in the Journal of Biological Chemistry.

Missing lipid shrinks heart and lowers exercise capacity
Researchers uncovered the essential role of PLAAT1 in maintaining heart cardiolipin, mitochondrial function and energy metabolism, linking this enzyme to exercise capacity and potential cardiovascular disease pathways.



