There's more to cholesterol than meets the eye
Glaucoma sometimes is called the silent thief in the night, because the eye can be damaged irreversibly before a person experiences any vision loss.
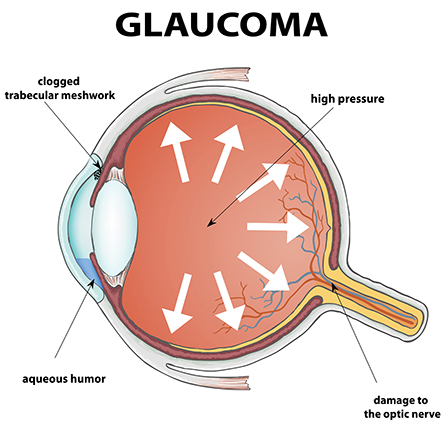
In a healthy eye, tissue called trabecular meshwork controls pressure by draining aqueous humor, the clear fluid filling the space between the cornea and lens. This drainage system clogs up in glaucoma, fluid builds up and the resulting pressure damages the optic nerve that sends visual signals to the brain. In severe cases, the eyes can bulge out.
Understanding how trabecular meshwork cells sense and respond to elevated eye pressure — a type of mechanical stress — is a major goal of researchers in David Križaj’s laboratory at the University of Utah. They study a mechanotransducer, a protein that senses and responds to mechanical stress, called transient receptor potential vanilloid 4, or TRPV4. When activated in trabecular meshwork, TRPV4 promotes aqueous humor drainage.
Previously, the researchers reported that a known risk factor for glaucoma, cholesterol, activates TRPV4 in retinal glia cells, which are at the back of the eye. Now, in a recent article published in the Journal of Lipid Research, Monika Lakk and colleagues report that cholesterol depletion activates TRPV4 in trabecular meshwork cells at the front of the eye — an unexpected result.
“Cholesterol has been public enemy No. 1 in the eye of the public for a long time due to its dysregulation in cardiovascular, neurologic and metabolic disease, and has been shown to subserve multiple types of inherited and acquired vision loss,” Lakk said.
On the other hand, cholesterol plays a crucial role in maintaining homeostasis. The finding that cholesterol regulates TRPV4 in opposite ways depending on its location (front versus back of the eye) demonstrates this complexity. “Clinical solutions may require a thorough understanding of the local biomechanical and cellular context,” Lakk said.
According to the researchers, increased membrane cholesterol in trabecular meshwork cells may dampen the mechanical stress signals caused by high blood pressure and prevent overstimulation of TRPV4 — a protective mechanism that may become dysfunctional in glaucoma.
By just stretching the trabecular meshwork cells — simulating what happens with glaucoma — the researchers were able to deplete membrane cholesterol, which activates TRPV4.
“This study was an exercise in surprise,” Lakk said. “We were completely unprepared for the finding that membrane lipid composition itself is a function of the biomechanical milieu.”
When a person experiences chronic stress due to conditions such as heart disease and glaucoma, she explained, “The cellular remodeling that takes place may involve the entire body and a myriad of processes and mechanisms that may flow under the radar of investigators focusing on immediate targets.”
The researchers have knocked out the TRPV4 gene in multiple eye cell types in mice and are investigating how these cells, which are unable to sense and respond to mechanical stress, affect eye fluid pressure and vision. Since cholesterol can turn TRPV4 on or off in different parts of the eye, their research suggests that glaucoma patients may benefit from carefully balanced diet regimens.
Enjoy reading ASBMB Today?
Become a member to receive the print edition four times a year and the digital edition monthly.
Learn moreGet the latest from ASBMB Today
Enter your email address, and we’ll send you a weekly email with recent articles, interviews and more.
Latest in Science
Science highlights or most popular articles

Sizing up cells: How stem cells know when to divide
Stanford University researchers find that stem cells control their size early in cell division across living multicellular systems.

When oncogenes collide in brain development
Researchers at University Medical Center Hamburg, found that elevated oncoprotein levels within the Wnt pathway can disrupt the brain cell extracellular matrix, suggesting a new role for LIN28A in brain development.

The data that did not fit
Brent Stockwell’s perseverance and work on the small molecule erastin led to the identification of ferroptosis, a regulated form of cell death with implications for cancer, neurodegeneration and infection.

Building a career in nutrition across continents
Driven by past women in science, Kazi Sarjana Safain left Bangladesh and pursued a scientific career in the U.S.

Avoiding common figure errors in manuscript submissions
The three figure issues most often flagged during JBC’s data integrity review are background signal errors, image reuse and undeclared splicing errors. Learn how to avoid these and prevent mistakes that could impede publication.

Ragweed compound thwarts aggressive bladder and breast cancers
Scientists from the University of Michigan reveal the mechanism of action of ambrosin, a compound from ragweed, selectively attacks advanced bladder and breast cancer cells in cell-based models, highlighting its potential to treat advanced tumors.

