Progression of ALS linked to a membrane and an enzyme
Researchers at Nagoya University in Japan have discovered a relationship between the progression of amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS), also known as Lou Gehrig's disease, and the disruption of mitochondria-associated membranes (MAM), the contact point between the mitochondria and the endoplasmic reticulum (ER) of the cell. This discovery, published in the Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, provides important information about the mechanisms behind this neurodegenerative condition.
ALS is a complex disease that affects motor neurons. Previous studies have found that mitochondria, the energy-generating cells of the body, and the ER, a complex membrane network that serves protein synthesis, metabolism, and calcium storage, are involved. The MAM is where the ER interfaces with mitochondria. Although both mitochondria and ER abnormality, especially at the MAM, play a role in the progression of the disease, it is not clear how.
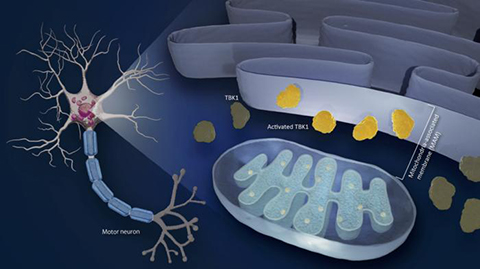
One possible agent is TANK-binding kinase 1 (TBK1), an enzyme that plays a crucial role in various biological processes, including inflammation and clearing damaged proteins from cells. Its disruption is important in the development of many diseases. Although mutations in the TBK1 gene cause ALS, it is not clear how TBK1 malfunctions lead to its development.
A team led by Koji Yamanaka at Nagoya University’s Research Institute of Environmental Medicine, in collaboration with Masahisa Katsuno of the Graduate School of Medicine discovered that brain and spinal cord tissues in ALS patients as well as mice with a disrupted MAM showed decreased activation of TBK1.
Seiji Watanabe, the first author of the study, explained: "TBK1 is crucial for stress response in motor neurons. If we reduce its activity, it will result in reduced tolerance to stressors, leading to neurotoxicity and eventual motor neuron death. This finding is particularly significant because abnormal protein accumulation and the resulting stress cause ALS and other neurodegenerative diseases."
When MAM is disrupted in ALS, TBK1 activity decreases. When the researchers administered arsenite, an agent that lowers TBK1 activity and disrupts MAM, to mice, they found that the mice exhibited motor problems similar to ALS.
Yamanaka added, "Our study strongly suggests that MAM significantly influences the stress response of motor neurons through TBK1 activation. Our study is consistent with human genetic studies that reported that TBK1 mutations cause ALS. Restoring TBK1 activity emerges as a potential therapeutic strategy to counter ALS, marking a promising direction for future research endeavors."
By focusing on the TBK1 pathway, the researchers have found a critical foundation for developing new ways to treat ALS and possibly other brain disorders. “We expect these results to lead to the development of new therapeutic strategies for ALS in the future,” said Yamanaka. “In future projects, restoring the TBK1 activity (or function) may be a therapeutic strategy to treat ALS.”
This article was originally published on the Nagoya University NU Research Information page. Read the original here.
Enjoy reading ASBMB Today?
Become a member to receive the print edition four times a year and the digital edition monthly.
Learn moreGet the latest from ASBMB Today
Enter your email address, and we’ll send you a weekly email with recent articles, interviews and more.
Latest in Science
Science highlights or most popular articles

Sizing up cells: How stem cells know when to divide
Stanford University researchers find that stem cells control their size early in cell division across living multicellular systems.

When oncogenes collide in brain development
Researchers at University Medical Center Hamburg, found that elevated oncoprotein levels within the Wnt pathway can disrupt the brain cell extracellular matrix, suggesting a new role for LIN28A in brain development.

The data that did not fit
Brent Stockwell’s perseverance and work on the small molecule erastin led to the identification of ferroptosis, a regulated form of cell death with implications for cancer, neurodegeneration and infection.

Building a career in nutrition across continents
Driven by past women in science, Kazi Sarjana Safain left Bangladesh and pursued a scientific career in the U.S.

Avoiding common figure errors in manuscript submissions
The three figure issues most often flagged during JBC’s data integrity review are background signal errors, image reuse and undeclared splicing errors. Learn how to avoid these and prevent mistakes that could impede publication.

Ragweed compound thwarts aggressive bladder and breast cancers
Scientists from the University of Michigan reveal the mechanism of action of ambrosin, a compound from ragweed, selectively attacks advanced bladder and breast cancer cells in cell-based models, highlighting its potential to treat advanced tumors.

