SUMO and stem cells
Stem cells are like master cells — they can divide to create more stem cells and be triggered by signals within and outside of themselves to give rise to virtually any cell type in the body. In order to exist as precursors, in what is called the pluripotent state, stem cells must be tightly controlled by internal signals but also highly responsive to developmental cues. Researchers do not yet understand this balance completely.
A team from the University of Dundee in Scotland led by Barbara Mojsa recently investigated how stem cells are influenced by SUMOylation, a post-translational modification in which a small ubiquitinlike modifier called SUMO is attached to a lysine residue on target proteins. Their work recently was published in the journal Molecular & Cellular Proteomics.
The SUMOylation and deSUMOylation processes are reversible and dynamic and can affect cell fate by altering protein function, interactions or stability. The group previously was studying SUMOylation in cancer cells but decided they may not be the best model system due to the numerous mutations they contain.
“Stem cells are much more dynamic, require tighter control of all cellular processes and undergo dramatic changes during differentiation,” Mojsa said, “making them ideal to study the biological role of SUMOylation.”
The researchers started using human induced pluripotent stem cells instead. These hiPSCs are derived from terminally differentiated somatic cells such as blood or skin cells that have been reprogrammed back into a pluripotent state.
The group blocked SUMOylation in hiPSCs using an inhibitor called ML792 and found that key pluripotency markers were lost. They next engineered cells to express modified versions of two enzymes, SUMO1 and SUMO2, to identify which proteins were modified and where.
They identified 427 SUMO-modified proteins and 976 SUMO sites in hiPSCs and used bioinformatic tools to identify networks of proteins that were SUMOylated. They found that the majority of the protein targets were involved in regulating transcription and chromatin structure, both of which influence gene expression.
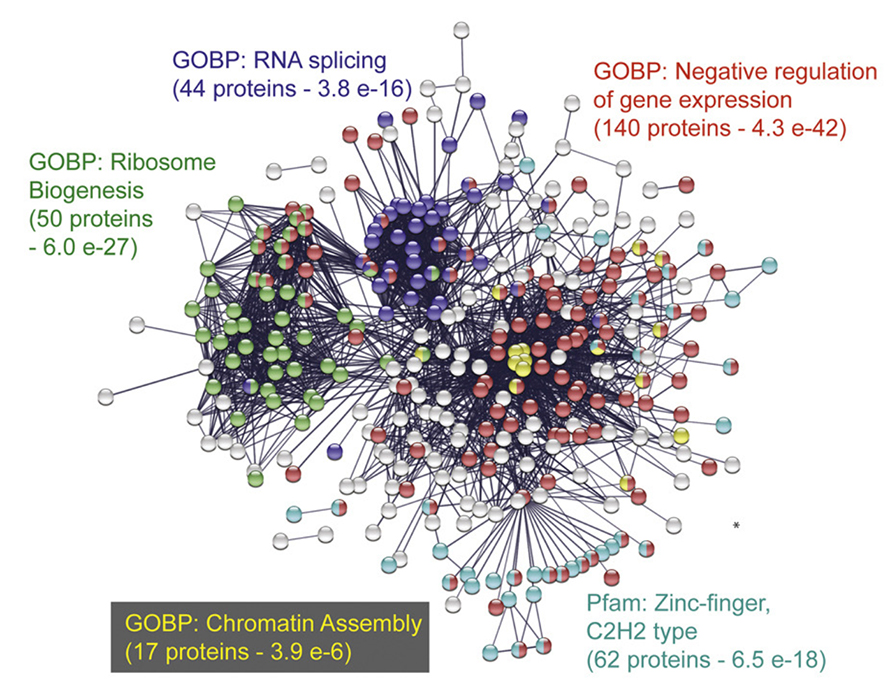
“Delicate balance of SUMO modification might be the key to maintenance of pluripotent state and control of various differentiation processes,” Mojsa said.
The team’s technique also allowed them to differentiate between SUMO1 and SUMO2 targets.
“We didn’t expect to observe such a big difference between SUMO1 and SUMO2 targets,” Mojsa said. “It was previously suggested that these two proteins are rather redundant in their functions.”
This research has impacts beyond understanding what forces control the pluripotent state. The ML792 inhibitor recently entered clinical trials for cancer treatment —understanding its broader effect is informative. Furthermore, hiPSCs can be used to generate almost any human cell type and therefore could have therapeutic uses. However, the process to differentiate the cells can be lengthy.
“If what we think is true and SUMOylation acts as a brake to cell differentiation, we could imagine using SUMOylation inhibitors to increase the efficiency or shorten the time required for differentiation, which would be a great advantage for regenerative medicine,” Mojsa said.
In the future, the group is interested in understanding how SUMOylation affects differentiation pathways.
Enjoy reading ASBMB Today?
Become a member to receive the print edition four times a year and the digital edition monthly.
Learn moreGet the latest from ASBMB Today
Enter your email address, and we’ll send you a weekly email with recent articles, interviews and more.
Latest in Science
Science highlights or most popular articles

Building a career in nutrition across continents
Driven by past women in science, Kazi Sarjana Safain left Bangladesh and pursued a scientific career in the U.S.

Avoiding common figure errors in manuscript submissions
The three figure issues most often flagged during JBC’s data integrity review are background signal errors, image reuse and undeclared splicing errors. Learn how to avoid these and prevent mistakes that could impede publication.

Ragweed compound thwarts aggressive bladder and breast cancers
Scientists from the University of Michigan reveal the mechanism of action of ambrosin, a compound from ragweed, selectively attacks advanced bladder and breast cancer cells in cell-based models, highlighting its potential to treat advanced tumors.

Lipid-lowering therapies could help treat IBD
Genetic evidence shows that drugs that reduce cholesterol or triglyceride levels can either raise or lower inflammatory bowel disease risk by altering gut microbes and immune signaling.

Key regulator of cholesterol protects against Alzheimer’s disease
A new study identifies oxysterol-binding protein-related protein 6 as a central controller of brain cholesterol balance, with protective effects against Alzheimer’s-related neurodegeneration.

From humble beginnings to unlocking lysosomal secrets
Monther Abu–Remaileh will receive the ASBMB’s 2026 Walter A. Shaw Young Investigator Award in Lipid Research at the ASBMB Annual Meeting, March 7-10 in Washington, D.C.