
Roos’ career pivot to maximize impact
Shortly before the pandemic, David S. Roos closed the doors to his research lab. Unlike most lab closings, however, this has increased his group’s impact on science, as he has transitioned from studying parasitology to managing database resources full time.
Roos now leads a team of more than 50 staff, who work together like a well-oiled machine to keep multiple genomic databases up to date. For his body of work, Roos was named the winner of the American Society for Biochemistry and Molecular Biology’s 2024 Alice and C.C. Wang Award in Molecular Parasitology.
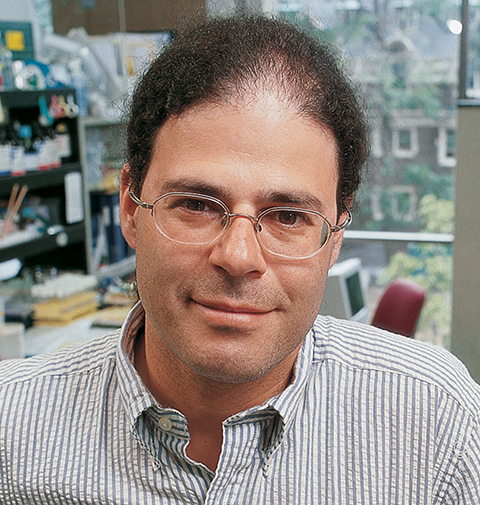

Roos’ group pioneered integrated databases resources, including the Eukaryotic Pathogen, Host & Vector Bioinformatics Resource Center VEuPathDB.org, the Orthology Database OrthoMCL.org and the Clinical & Epidemiology Resource ClinEpiDB.org. These tools help to make large-scale data sets findable and accessible for thousands of investigators worldwide, Roos said.
“I've been a scientist for a long time,” Roos said, “training scores of students and postdocs and publishing hundreds of papers — including some that have been cited thousands of times. However, our database resources are used by 50,000 unique users per month. I will never in my career publish a paper that is cited 50,000 times, let alone 50,000 times every month, year in and year out. It is particularly gratifying to see that these resources are equally useful to students and researchers all around the world.”
Though he’s had a wide impact on the parasitology field, Roos did not begin his scientific career studying parasites. “I think of myself as an evolutionary cell biologist,” he said.
Hoping to apply his skills to develop molecular tools enabling the genetic dissection of host–pathogen interactions, Roos became interested in molecular parasitology and was inspired by the enthusiastic support of C.C. Wang.
The Bay Area Parasitology meetings, often held in the Wang home, inspired Roos to establish his laboratory at the University of Pennsylvania in 1989 to work on parasites, despite never having previously published in this field.
“C.C. was somebody who not only provided great encouragement to me but also highlighted that it was possible to do something new,” Roos said.
A ‘crazy’ organelle
In 1997, David Roos saw his work, earlier published in Science, prominently featured in a New York Times article about a newly discovered organelle in parasites that may lead to life-saving drugs against malaria and toxoplasmosis.
Roos and collaborators had identified the apicoplast, a vestigial plastid surrounded by four membranes with essential metabolic functions that evolved via secondary endosymbiosis in certain parasites.
“Imagine the ancestor of plants and algae eating a cyanobacterium, which gave rise to the chloroplast, surrounded by a double membrane,” Roos said. “Now imagine that an ancestral parasite eats this alga and retains the algal plastid. This concept of secondary endosymbiosis sounds crazy, but it predicts that the organelle should be surrounded by four membranes, exactly as we see.”
Roos also defined the motifs responsible for protein traffic to the new organelle and a complete metabolic pathway map, including numerous therapeutic targets.
“Computational integration of diverse datasets is increasingly the driver for experimentally testable hypotheses,” Roos said. “And the tools we developed to ask our crazy questions — ‘find plant genes in malaria parasites’ — have proved to be readily generalizable to support other questions as well, yielding the database resources we now provide to the global community.”
2024 ASBMB award winners
Phillips turns parasite’s metabolic weakness into hope for human health
Herbert Tabor Research Award: Margaret Phillips
Ando's pioneering journey: From physics to structural enzymology
Mildred Cohn Young Investigator Award: Nozomi Ando
Stoddard changes mentoring practices in academia
Ruth Kirschstein Diversity in Science Award: Shana Stoddard
For Wolfson, every classroom is a laboratory
ASBMB Sustained Leadership Award: Adele Wolfson
Kennelly considers his fortune of three careers
William C. Rose Award for Exemplary Contributions to Education: Peter Kennelly
Balla leaves no phosphoinositide unturned
Avanti Award in Lipids: Tamas Balla
From virology to immunology, Wu focuses on structure
Bert & Natalie Vallee Award in Biomedical Science: Hao Wu
Stillman charts the path of genome replication
Earl And Thressa Stadtman Distinguished Scientist Award: Bruce Stillman
In failure, Simcox finds a way to learn
Walter A. Shaw Young Investigator in Lipid Research Award: Judith Simcox
Enjoy reading ASBMB Today?
Become a member to receive the print edition four times a year and the digital edition monthly.
Learn moreGet the latest from ASBMB Today
Enter your email address, and we’ll send you a weekly email with recent articles, interviews and more.
Latest in People
People highlights or most popular articles
2026 ASBMB election results
Meet the new Council members and Nominating Committee member.

Simcox wins SACNAS mentorship award
She was recognized for her sustained excellence in mentorship and was honored at SACNAS’ 2025 National Conference.

From humble beginnings to unlocking lysosomal secrets
Monther Abu–Remaileh will receive the ASBMB’s 2026 Walter A. Shaw Young Investigator Award in Lipid Research at the ASBMB Annual Meeting, March 7-10 in Washington, D.C.

Chemistry meets biology to thwart parasites
Margaret Phillips will receive the Alice and C. C. Wang Award in Molecular Parasitology at the ASBMB Annual Meeting, March 7-10 in Washington, D.C.

ASBMB announces 2026 JBC/Tabor awardees
The seven awardees are first authors of outstanding papers published in 2025 in the Journal of Biological Chemistry.

Decoding how bacteria flip host’s molecular switches
Kim Orth will receive the Earl and Thressa Stadtman Distinguished Scientists Award at the ASBMB Annual Meeting, March 7–10, just outside of Washington, D.C.

