From the journals: JLR
A new site-specific cholesterol control option and a better way to assess vitamin D status in critical care. Read about papers on these topics recently published in the Journal of Lipid Research.
A new site-specific cholesterol control option
Cholesterol is an essential component of mammalian cell membranes. Its unesterified, or free, form, localized within plasma, controls mechanical properties of the lipid bilayer such as rigidity and permeability. Cholesterol also directly interacts with a wide variety of cellular proteins at the plasma membrane, thus regulating cell signaling.
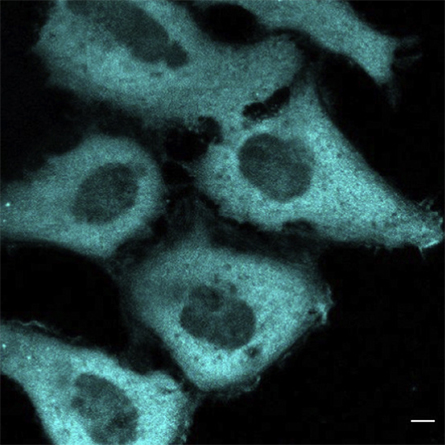
cholesterol oxidase in HeLa cells.
Researchers manipulate cellular cholesterol levels either through chemical extraction and enrichment of cholesterol by methyl-beta-cyclodextrin, or MβCD, and MβCD-cholesterol adducts, respectively; or by inhibition of new cellular cholesterol biosynthesis by statins. These methods are convenient but lack site-specific control of cholesterol levels within cells. Moreover, they can cause nonspecific cholesterol depletion that exerts harmful effects on cells including cell death and nonspecific alteration of cell physiology.
Ha Pham and a team of researchers from the University of Illinois Chicago and the University of Western Australia, Perth, have developed a new system that allows inducible, site-specific cholesterol depletion. They created a genetically encoded bacterial cholesterol oxidase whose membrane binding activity is altered in a way that allows spatiotemporally specific control of its membrane targeting by chemically induced dimerization with a partner protein located in a specific membrane site. The team documented the system and their findings in a recent research paper published in the Journal of Lipid Research.
In combination with quantitative imaging of cholesterol and signaling activity assays, this novel system will allow for unambiguous determination of site-specific functions of cholesterol in diverse cell membranes, including the plasma membrane and the lysosomal membrane.
Assessing vitamin D status in critical care
Vitamin D helps regulate calcium and phosphorus levels, plays a role in maintaining proper bone structure and regulates immune function. Vitamin D deficiency results in bone diseases, such as rickets, as well as cancer and cardiovascular and diseases, and is associated with increased risk for respiratory infections, including COVID-19.
When absorbed by the body, vitamin D is metabolized to 25-hydroxyvitamin D, or 25OH-D, which often is used as a biomarker to measure vitamin D levels in the body. Liquid chromatography–tandem mass spectrometry, or LC-MS/MS, is the gold standard for quantitative 25OH-D determination, and this technique has several advantages over previously used immunoassays, including greater selectivity, lower detection limits and improved precision.
Researchers at McMaster University and the Children’s Hospital of Eastern Ontario Research Institute have developed a high-throughput method for assessing vitamin D status from blood specimens based on direct infusion–MS/MS, or DI-MS/MS, following click derivatization using 2-nitrosopyridine, which is optimized for quicker analysis than LC-MS/MS and greater accuracy than a commercial immunoassay.
In a comparative test study, Erick Helmeczi and a team found that 25OH-D concentrations from reference blood samples measured by DI-MS/MS were less biased than the commercial immunoassay when compared to LC-MS/MS. They found that, compared to DI-MS/MS, the commercial immunoassay, often used for screening in clinical trials, underestimates the prevalence of vitamin D deficiency in critically ill children who might benefit from high-dose vitamin D supplements.
These findings, published in a paper in the Journal of Lipid Research, show that DI-MS/MS can be used to assess vitamin D status rapidly and reliably in clinical trials and large-scale studies. The researchers will focus future efforts on adapting this method for the purpose of reporting clinical values.
Enjoy reading ASBMB Today?
Become a member to receive the print edition four times a year and the digital edition monthly.
Learn moreGet the latest from ASBMB Today
Enter your email address, and we’ll send you a weekly email with recent articles, interviews and more.
Latest in Science
Science highlights or most popular articles

When oncogenes collide in brain development
Researchers at University Medical Center Hamburg, found that elevated oncoprotein levels within the Wnt pathway can disrupt the brain cell extracellular matrix, suggesting a new role for LIN28A in brain development.

The data that did not fit
Brent Stockwell’s perseverance and work on the small molecule erastin led to the identification of ferroptosis, a regulated form of cell death with implications for cancer, neurodegeneration and infection.

Building a career in nutrition across continents
Driven by past women in science, Kazi Sarjana Safain left Bangladesh and pursued a scientific career in the U.S.

Avoiding common figure errors in manuscript submissions
The three figure issues most often flagged during JBC’s data integrity review are background signal errors, image reuse and undeclared splicing errors. Learn how to avoid these and prevent mistakes that could impede publication.

Ragweed compound thwarts aggressive bladder and breast cancers
Scientists from the University of Michigan reveal the mechanism of action of ambrosin, a compound from ragweed, selectively attacks advanced bladder and breast cancer cells in cell-based models, highlighting its potential to treat advanced tumors.

Lipid-lowering therapies could help treat IBD
Genetic evidence shows that drugs that reduce cholesterol or triglyceride levels can either raise or lower inflammatory bowel disease risk by altering gut microbes and immune signaling.

