Decoding a protein’s role in connective tissue disorders
Composed of proteins, fibers, cells and other substances, connective tissues attach, stabilize and reinforce the structure of human bodies. While there are many causes of connective tissue disorders, Ehlers–Danlos syndrome, or EDS, involves the disruption of collagen or collagen-regulating proteins by means of genetic mutations.
EDS, which affects as many as one in 2,500 people, is an inherited disorder that weakens connective tissues, specifically affecting the skin, joints and blood vessels. Researchers recently have found that some EDS-presenting families share mutations in the adipocyte enhancer binding protein 1, or AEBP1, gene, which encodes for the aortic carboxypeptidase-like protein, or ACLP, found in collagen-rich connective tissues including the skin, ligaments, tendons and vasculature. Individuals with AEBP1 mutations develop a subtype of EDS called EDS-classic-like-2, or EDSCLL2, which is characterized by joint hypermobility, abnormal scarring, delayed wound healing and vascular ruptures.
Medical student Neya Vishwanath, then a second-year master’s student in the medical sciences program at the Boston University School of Medicine, and colleagues in Matthew Layne’s lab were interested in investigating mutations in AEBP1 and the processing mechanisms for ACLP. Their goal was to examine mechanisms of protein secretion and collagen fiber stability for these proteins in the context of EDS.
“In all my biology courses, we were always taught how integral connective tissue is to a healthy body,” Vishwanath said. “In the Layne lab, (we) wanted to better understand the importance of ACLP in connective tissue health and figure out how mutations in ACLP could cause human disease.”
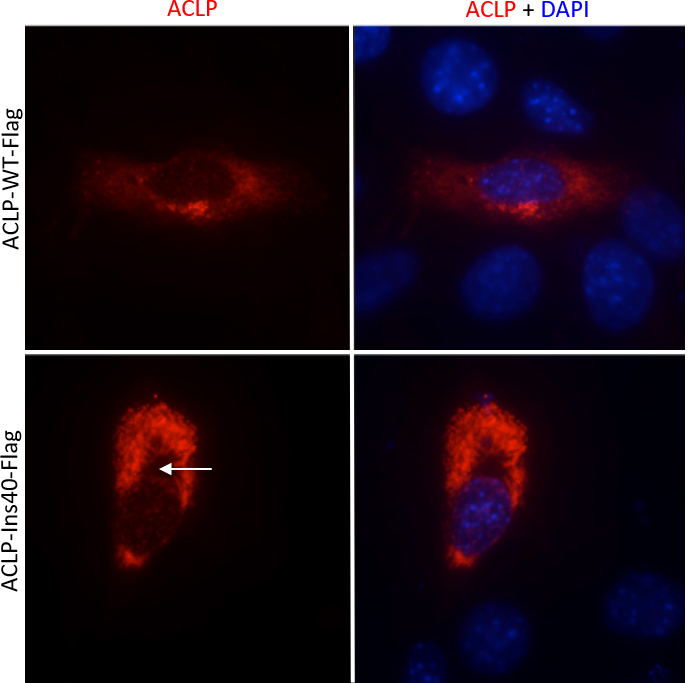
protein leads to an apparent gap around the nucleus, potentially indicating an absence of intracellular trafficking to the Golgi.
In a recent paper in the Journal of Biological Chemistry, Vishwanath and colleagues highlight a specific mutation found in EDS patients called ACLP-Ins40. They found that this mutation, which causes an insertion of 40 amino acids in the collagen-binding region of ACLP, results in the improper exit of ACLP from cells and leads to cellular stress. The researchers also mapped and identified the specific amino acids required for proper ACLP secretion.
The team also identified novel protein processing mechanisms critical in ACLP secretion. Specifically, they demonstrated how glycosylation, or the addition of sugar groups to ACLP, is necessary for the proper cellular exit. When sugar groups are unattached to ACLP, the result is in-cell retention of ACLP and increased cellular stress.
Research with two other labs focused on the potential for ACLP to contribute to collagen fiber mechanics, specifically highlighting ACLP’s role in mechanical strength, Vishwanath said. “Our collaborative studies with Michael Smith and Joyce Wong’s laboratories at Boston University determined that ACLP contributes to the mechanical strength of collagen fibers that make up numerous connective tissues including ligaments, tendons, and cartilage.”
Vishwanath and her colleagues hope insights from this work will contribute to a greater understanding of the mechanisms involved in connective tissue structures and provide scientists with targets for pharmacological interventions to treat connective tissue disorders such as EDS.
Enjoy reading ASBMB Today?
Become a member to receive the print edition four times a year and the digital edition monthly.
Learn moreGet the latest from ASBMB Today
Enter your email address, and we’ll send you a weekly email with recent articles, interviews and more.
Latest in Science
Science highlights or most popular articles

Sizing up cells: How stem cells know when to divide
Stanford University researchers find that stem cells control their size early in cell division across living multicellular systems.

When oncogenes collide in brain development
Researchers at University Medical Center Hamburg, found that elevated oncoprotein levels within the Wnt pathway can disrupt the brain cell extracellular matrix, suggesting a new role for LIN28A in brain development.

The data that did not fit
Brent Stockwell’s perseverance and work on the small molecule erastin led to the identification of ferroptosis, a regulated form of cell death with implications for cancer, neurodegeneration and infection.

Building a career in nutrition across continents
Driven by past women in science, Kazi Sarjana Safain left Bangladesh and pursued a scientific career in the U.S.

Avoiding common figure errors in manuscript submissions
The three figure issues most often flagged during JBC’s data integrity review are background signal errors, image reuse and undeclared splicing errors. Learn how to avoid these and prevent mistakes that could impede publication.

Ragweed compound thwarts aggressive bladder and breast cancers
Scientists from the University of Michigan reveal the mechanism of action of ambrosin, a compound from ragweed, selectively attacks advanced bladder and breast cancer cells in cell-based models, highlighting its potential to treat advanced tumors.

