JBC: How do protein tangles get so long?
Long before Alzheimer’s disease patients notice any symptoms, neurofibrillary tangles composed of tau protein filaments begin to form in their brain cells. How toxic these aggregates are and how well they spread depend on their size — that is, the number of tau monomers they contain. However, scientists studying tangle formation have not been able to explain why different sizes of tau aggregates appear in disease.
But now researchers have discovered that instead of adding just one protein at a time, fibrils of various lengths can join end-to-end to create one larger filament. The finding, published in the Journal of Biological Chemistry, helps explain how fibrils can grow to hundreds of nanometers. It also could help researchers understand mechanisms of an emerging group of drug candidates designed to inhibit tau aggregation.
A common simple model of tau aggregation and fibril formation includes two steps. First, two tau proteins bind slowly; additional tau molecules latch on quickly.
Carol Huseby, then a graduate student in Jeff Kuret’s lab at THE Ohio State University, worked with Ralf Bundschuh to expand this mathematical model to include other known ways that tau fibrils behave. Scientists have observed, for example, that sometimes one fibril fragments into two. Or a new fibril can nucleate in the middle of an existing fibril.
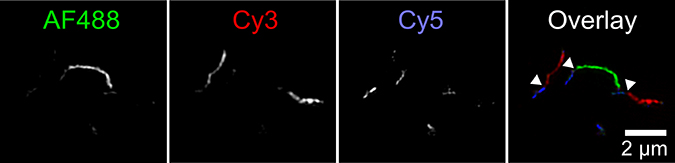 Tau proteins labeled with three fluorescent dyes were allowed to aggregate in separate test tubes, shown in the three images at left. The different colored fibrils were mixed in a fourth test tube, at right, resulting in long fibrils with short sections of each color. Carol Huseby/The Ohio State University
Tau proteins labeled with three fluorescent dyes were allowed to aggregate in separate test tubes, shown in the three images at left. The different colored fibrils were mixed in a fourth test tube, at right, resulting in long fibrils with short sections of each color. Carol Huseby/The Ohio State University
The simple model predicted many short fibrils. But Huseby knew that, under a microscope, aggregated tau appears as a smaller number of long fibrils. That discrepancy suggested that something was happening in the real world that hadn’t been accounted for in the model. They hypothesized that short fibrils could attach end-to-end to get longer.
To test the hypothesis, Huseby labeled tau proteins with three fluorescent colors and allowed them to aggregate in separate test tubes. Then she mixed the different colored fibrils in a fourth test tube.
Images taken with a super-resolution fluorescence microscope showed long fibrils with short sections of each color, indicating that fibrils from the original test tubes had joined ends to form longer fibrils. Control experiments established that this can’t be explained by labeled molecules’ preference for like labels.
After Huseby incorporated this new mechanism into the model, it produced a better description of what purified tau proteins were doing as they formed aggregates. This study is the first to show that the fibrils can elongate by more than a single tau protein at a time.
Alzheimer’s disease researchers still are trying to discern whether tau fibrils are a cause or simply an effect of the disease. Transmission of fibrils from one cell to another may contribute to the spread of disease in the brain. A very long fibril, according to Kuret, is unlikely to spread in this way. “But once it’s broken up into little pieces, those can diffuse,” he said, “facilitating their movement from cell to cell.”
This study used just one type of tau. Six isoforms are known, and phosphorylation and other changes increase the protein’s complexity. The researchers plan to incorporate these variables in future work and to use the model to understand how tau inhibitors change the protein aggregates’ behavior.
Enjoy reading ASBMB Today?
Become a member to receive the print edition four times a year and the digital edition monthly.
Learn moreGet the latest from ASBMB Today
Enter your email address, and we’ll send you a weekly email with recent articles, interviews and more.
Latest in Science
Science highlights or most popular articles

The data that did not fit
Brent Stockwell’s perseverance and work on the small molecule erastin led to the identification of ferroptosis, a regulated form of cell death with implications for cancer, neurodegeneration and infection.

Building a career in nutrition across continents
Driven by past women in science, Kazi Sarjana Safain left Bangladesh and pursued a scientific career in the U.S.

Avoiding common figure errors in manuscript submissions
The three figure issues most often flagged during JBC’s data integrity review are background signal errors, image reuse and undeclared splicing errors. Learn how to avoid these and prevent mistakes that could impede publication.

Ragweed compound thwarts aggressive bladder and breast cancers
Scientists from the University of Michigan reveal the mechanism of action of ambrosin, a compound from ragweed, selectively attacks advanced bladder and breast cancer cells in cell-based models, highlighting its potential to treat advanced tumors.

Lipid-lowering therapies could help treat IBD
Genetic evidence shows that drugs that reduce cholesterol or triglyceride levels can either raise or lower inflammatory bowel disease risk by altering gut microbes and immune signaling.

Key regulator of cholesterol protects against Alzheimer’s disease
A new study identifies oxysterol-binding protein-related protein 6 as a central controller of brain cholesterol balance, with protective effects against Alzheimer’s-related neurodegeneration.

