From the journals: JBC
We offer a selection of papers recently published in the Journal of Biological Chemistry. Topics include misfolded tau proteins in Alzheimer’s disease, how enzymes trim peptides and how a parasite hijacks the immunity of its host.
Untangling Alzheimer’s and the spread of misfolded proteins
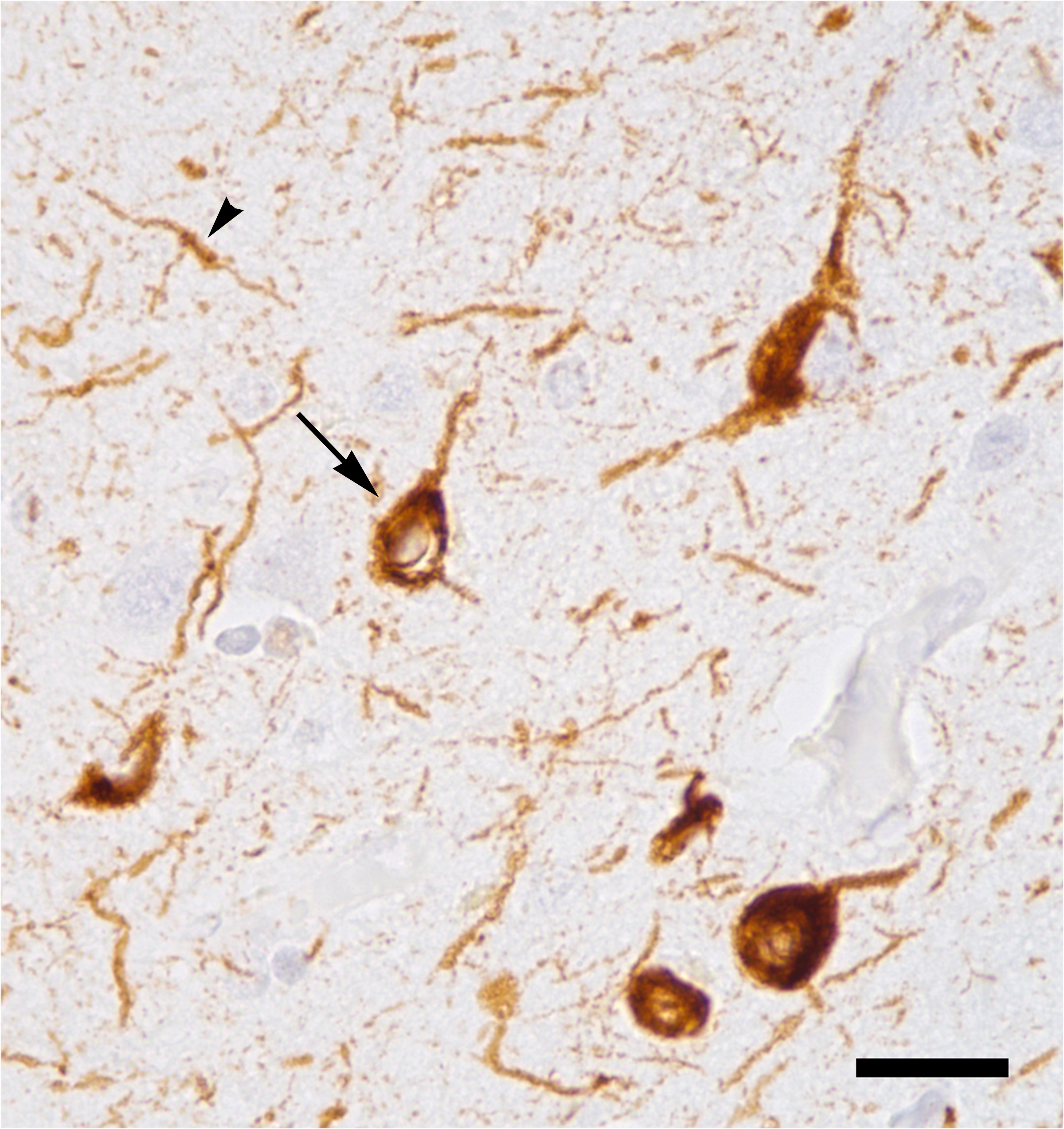
In 1906, seeking to understand the symptoms of a deceased patient who had been plagued by confusion, mood swings and disturbed sleep, Alois Alzheimer arranged for a brain autopsy. He found alterations to proteins in her brain cells, later called amyloid plaques and tau tangles. These are the hallmarks of what we now call Alzheimer’s disease, which affects more that 5 million Americans aged 65 years or older. It remains incurable, with only symptomatic relief available.
In the last decade, Alzheimer’s drug development largely has focused on the elimination of amyloid plaques, with little success. Recently, tau, a protein that modulates cellular support elements called microtubules, has emerged as a therapeutic target. Researchers now believe the buildup and tangling of the protein tau may be at the heart of disease severity. Mounting evidence suggests that tau aggregates spread via prionlike propagation.
To understand how misfolded tau spreads across brain cells, researchers from the University of California, San Francisco, used CRISPR interference, a genetic tool that allows specific genes to be turned off, to identify cellular components involved in the spread of pathological tau.
In a paper published in the Journal of Biological Chemistry, John Chen and colleagues reported that knocking down components of the endosomal sorting complexes required for transport, or ESCRT, machinery using CRISPR interference accelerated the spread of tau buildup in cells. Specifically, the researchers discovered that the individual knockdown of charged multivesicular body protein 6, known as CHMP6, or co-knockdown of CHMP2A and CHMP2B (a gene associated with familial frontotemporal dementia) caused the ESCRT pathway to become leaky and accelerated tau buildup. These results increase our understanding of how pathological tau spreads across brain cells and identify potential therapeutic targets.
Trimming peptides down to size
An important step for the activation of the immune system in response to potential threats is the processing and presentation of peptides by major histocompatibility complex, or MHC, molecules. To accomplish this, a mechanism for handling peptides of various lengths is necessary. The processes underpinning these alterations are not fully understood.
Answers might lie in studying endoplasmic reticulum aminopeptidases, or ERAPs, enzymes essential for the presentation of peptides by MHC I molecules. In a paper published in the Journal of Biological Chemistry, Lenong Li and colleagues at the University of Illinois shed new light on how peptide trimming by ERAP1 shapes the MHC I immunopeptidome and provide detailed structural and biochemical evidence demonstrating how peptides of noncanonical lengths interact with MHC I. Their results provide new fundamental knowledge about the processing and presentation of unconventional peptides by MHC I.
Mollusk proteins that modulate the immune system
Hemocyanins are respiratory proteins responsible for transporting oxygen in a variety of arthropods and mollusks. Mollusk hemocyanins are used widely as carriers, adjuvants and nonspecific immunostimulants in cancer treatments due to their ability to promote Th1 immunity. In a collaborative study published in the Journal of Biological Chemistry, Michelle L. Salazar and researchers in Chile sought to reveal how mollusk hemocyanins — specifically from Concholepas concholepas, Fissurella latimarginata and Megathura crenulata — modulate the immune system. Using an enzyme to remove sugar entities from hemocyanins, the researchers found that sugar residues are important both for their structure and for their immunogenic effects. Furthermore, the changes to glycan content altered the interaction of hemocyanins with immune cells. Their findings elucidate key aspects of hemocyanin immunological activities and have significant implications for the biomedical application of these proteins.
A link between enzyme mutation and cerebellar ataxia
Spinocerebellar autosomal recessive type 16, known as SCAR16, is a fatal neurodegenerative disease characterized by difficulties with swallowing, eye movement, speech and coordinated voluntary movements. SCAR16 is a monogenetic disorder dependent upon coding mutations in a single gene called STUB1, which encodes the versatile enzyme C terminus of HSC70-interacting protein, or CHIP. In a study published in the Journal of Biological Chemistry, Sabrina Madrigal and colleagues at the University of North Carolina School of Medicine examined the relationships between clinical phenotypes of SCAR16 patients and the biophysical, biochemical and functional properties of CHIP variants. The researchers provide linear models that suggest that inhibition of mutant CHIP lessens disease severity, a finding that may be useful for clinical therapies.
Enjoy reading ASBMB Today?
Become a member to receive the print edition four times a year and the digital edition monthly.
Learn moreGet the latest from ASBMB Today
Enter your email address, and we’ll send you a weekly email with recent articles, interviews and more.
Latest in Science
Science highlights or most popular articles

Sizing up cells: How stem cells know when to divide
Stanford University researchers find that stem cells control their size early in cell division across living multicellular systems.

When oncogenes collide in brain development
Researchers at University Medical Center Hamburg, found that elevated oncoprotein levels within the Wnt pathway can disrupt the brain cell extracellular matrix, suggesting a new role for LIN28A in brain development.

The data that did not fit
Brent Stockwell’s perseverance and work on the small molecule erastin led to the identification of ferroptosis, a regulated form of cell death with implications for cancer, neurodegeneration and infection.

Building a career in nutrition across continents
Driven by past women in science, Kazi Sarjana Safain left Bangladesh and pursued a scientific career in the U.S.

Avoiding common figure errors in manuscript submissions
The three figure issues most often flagged during JBC’s data integrity review are background signal errors, image reuse and undeclared splicing errors. Learn how to avoid these and prevent mistakes that could impede publication.

Ragweed compound thwarts aggressive bladder and breast cancers
Scientists from the University of Michigan reveal the mechanism of action of ambrosin, a compound from ragweed, selectively attacks advanced bladder and breast cancer cells in cell-based models, highlighting its potential to treat advanced tumors.

