A $1 million pledge, a faculty position and a Passano award
Hazelbauer pledges $1 million to high school
Gerald Hazelbauer, a curators’ distinguished professor emeritus of biochemistry at the University of Missouri, plans to donate $1 million to foster innovative science teaching at Lyons Township High School in Illinois.
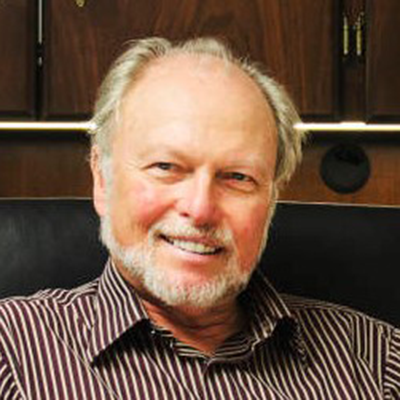

Hazelbauer, a 1962 graduate of the school, is making the bequest in honor of Ruth Wenner, his freshman biology teacher, according to an article in the Riverside/Brookfield Landmark.
Wenner, described by Hazelbauer as an innovative and challenging teacher who treated her students like scientists, arranged for him to accompany her to some laboratory sessions of a summer course for teachers at an Illinois Institute of Technology after his freshman year. The following year she gave him the opportunity to be student leader of a high school research project funded by the National Science Teachers’ Association through the Future Scientists of America Foundation. He went on to earn a bachelor’s degree in biology from Williams College, a master’s degree in biology from Case Western Reserve University and a Ph.D. in genetics from the University of Wisconsin.
Research in the Hazelbauer lab at the MU School of Medicine and the College of Agriculture, Food and Natural Resources focuses on elucidating molecular mechanisms of transmembrane receptors and sensory transduction in bacterial chemotaxis. A number of recent projects have used the emerging technology of nanodiscs to manipulate membrane proteins in a water-soluble state.
Hazelbauer is making an initial $20,000 donation to LTHS this year, which will support creative projects of several of the school’s science teachers. He has pledged to give at least the same amount each year while he and his wife are alive, prior to the $1 million posthumous donation.
A member of the American Society for Biochemistry and Molecular Biology since 1984, Hazelbauer is also a fellow of the American Association for the Advancement of Science and of the American Academy of Microbiology.
McReynolds to join faculty at Penn State
Melanie McReynolds, a postdoctoral fellow at Princeton University, will join the faculty at Pennsylvania State University’s department of biochemistry and molecular biology, taking a named early-career chair, in January of next year.

McReynolds studies the metabolic changes that occur during aging, focusing on NAD+, the essential metabolite converted into NADH during cellular respiration. NAD+ declines with age in both mice and the roundworm Caenorhabditis elegans. When it is missing, glycolysis can slow down. McReynolds’ research explores how the resulting energy deficit might contribute to cellular ageing and whether it can be reversed. She has also published extensively on mentoring and improving the equity of scientific training.
The move is a homecoming of sorts: McReynolds earned her Ph.D. in biochemistry, molecular biology and microbiology at Penn State in 2017. She served as the president of the Black Graduate Student Association during her time in State College. She arrived at Penn State through a Bridges to the Doctorate program with Alcorn State University in Mississippi, where she earned her bachelor’s and master’s degrees. Her awards as a graduate student included the Alfred P. Sloan Foundation’s minority Ph.D. program; as a postdoc, she has received a Howard Hughes Medical Institute Hanna Gray fellowship and the Burroughs Wellcome Fund Postdoctoral Enrichment Program.
Department chair Wendy Hanna–Rose was McReynolds’ dissertation advisor. “Dr. McReynolds is a creative and collaborative researcher of exceptional promise,” she stated in a Penn State news release. “As a graduate student, she was well known and recognized across campus for her activism and leadership.”
Passano Foundation honors Goldberg
Alfred Goldberg, professor of cell biology at Harvard Medical School, won the 2021 Passano Award, which is presented by the Passano Foundation to a researcher who has made an exceptional contribution to the advancement of medical science.

Goldberg was recognized for introducing the proteasome inhibitors (MG132) now very widely used as research tools and initiating the research that led to the development of the inhibitor bortezomib, which is used worldwide in the primary treatment of the blood cancer multiple myeloma.
Goldberg’s major discoveries have concerned the biochemical mechanisms and physiological regulation of protein breakdown in cells and the importance of this process in human disease.
His laboratory first discovered the ATP-dependent system for protein breakdown, now termed the ubiquitin-proteasome pathway. They first demonstrated the involvement of the proteasomes in this process and discovered the ATP-dependent proteases responsible for protein degradation in bacteria and mitochondria.
Also of great impact have been his findings about the mechanisms for the excessive protein degradation and muscle atrophy in many disease states and their elucidation of the role of the proteasome and cellular peptidases in antigen presentation to the immune system. Goldberg’s wide-ranging work has had a major impact on many areas of biology, medicine, and biotechnology.
Enjoy reading ASBMB Today?
Become a member to receive the print edition four times a year and the digital edition monthly.
Learn moreGet the latest from ASBMB Today
Enter your email address, and we’ll send you a weekly email with recent articles, interviews and more.
Latest in People
People highlights or most popular articles

In memoriam: Walter A. Shaw
He is the namesake for the Walter A. Shaw Young Investigator Award in Lipid Research and founded Avanti Polar Lipids.

Dorn named assistant professor
She will open her lab at the University of Vermont in fall 2026, and her research will focus on catalysis, synthetic methodology and medicinal chemistry.

The data that did not fit
Brent Stockwell’s perseverance and work on the small molecule erastin led to the identification of ferroptosis, a regulated form of cell death with implications for cancer, neurodegeneration and infection.

Building a career in nutrition across continents
Driven by past women in science, Kazi Sarjana Safain left Bangladesh and pursued a scientific career in the U.S.

Kiessling wins glycobiology award
She was honored by the Society for Glycobiology for her work on protein–glycan interactions.
2026 ASBMB election results
Meet the new Council members and Nominating Committee member.
