In memoriam: Sadaaki Iwanaga
Sadaaki Iwanaga, an honorary member of the American Society for Biochemistry and Molecular Biology since 1989 and a pioneer in the study of blood clotting, died June 21, 2020, the ASBMB learned recently.
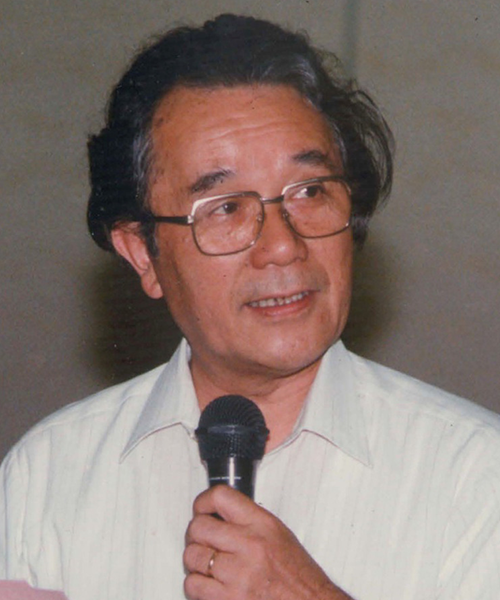

Born in Tokyo on Jan. 5, 1933, Iwanaga was a high school baseball player before turning his attention to science. He earned a Ph.D. in pharmaceutical sciences in 1960.
In the 1960s and ‘70s, Iwanaga held positions at Kyoto and Osaka universities and the Institute for Protein Research in Japan, and spent several years with Birger Blombäck at the Karolinska Institute studying the chemical structure of fibrinogen, a protein that helps blood clots to form. He came to Kyushu University as a professor of biology in 1978 and stayed until his retirement in 1996.
Blood clotting and coagulation are relevant to human health, and this focus allowed Iwanaga to explore exotic biofluids such as snake venom and horseshoe crab hemolymph.
In horseshoe crabs, hemolymph coagulates in response to bacterial lipopolysaccharides or foreign polysaccharides and triggers a defensive response. (This response has been used historically to test the sterility of pharmaceutical products.) Iwanaga's lab investigated the protease cascade that kicks off hemolymph coagulation: One protease cleaves another from its inactive to an active form, and that protease then activates a third enzyme. The cascade includes four proteases and a clotting protein. The lab also investigated protease inhibitors called serpins, which prevent runaway coagulation, along with LPS-binding proteins and antimicrobial peptides.
Iwanaga also studied clotting in human blood, which, as in horseshoe crabs, is activated through a cascading system of proteases. He developed protease substrates that fluoresce when cleaved, which can be used to monitor protease activity. He studied kallikrein, a protease that affects blood pressure by cleaving and activating peptide hormones called kinins. He also studied snake venom, interested in how its proteins prevent clotting.
“He was a hard-working scientist,” several of Iwanaga’s mentees wrote in a memorial article in the Journal of Thrombosis and Haemostasis. “He made it a custom to come to work before everyone else and go home after everyone else, even over the weekends and during holidays. He was a sharp observer of the field and this helped him to be ahead of the curve.”
Iwanaga and his wife, Mihiko, loved to travel. He was also a fan of sumo wrestling, according to the article, and would bring visiting scientists to the Kyushu Grand Sumo Tournament “where Mihiko would book large box seats for the group.”
Enjoy reading ASBMB Today?
Become a member to receive the print edition four times a year and the digital edition monthly.
Learn moreGet the latest from ASBMB Today
Enter your email address, and we’ll send you a weekly email with recent articles, interviews and more.
Latest in People
People highlights or most popular articles

Kiessling wins glycobiology award
She was honored by the Society for Glycobiology for her work on protein–glycan interactions.
2026 ASBMB election results
Meet the new Council members and Nominating Committee member.

Simcox wins SACNAS mentorship award
She was recognized for her sustained excellence in mentorship and was honored at SACNAS’ 2025 National Conference.

From humble beginnings to unlocking lysosomal secrets
Monther Abu–Remaileh will receive the ASBMB’s 2026 Walter A. Shaw Young Investigator Award in Lipid Research at the ASBMB Annual Meeting, March 7-10 in Washington, D.C.

Chemistry meets biology to thwart parasites
Margaret Phillips will receive the Alice and C. C. Wang Award in Molecular Parasitology at the ASBMB Annual Meeting, March 7-10 in Washington, D.C.

ASBMB announces 2026 JBC/Tabor awardees
The seven awardees are first authors of outstanding papers published in 2025 in the Journal of Biological Chemistry.
