From the journals: MCP
We offer a selection of papers on a variety of topics recently published in the journal Molecular & Cellular Proteomics.
A fast new way to ID bacteria in infections
When a patient with an infection needs treatment, doctors often take a sample of urine or blood to analyze and prescribe broad-spectrum antibiotics for a few days until the bacterial culture results come back from the lab. However, treating with broad-spectrum antibiotics is not very effective for some infections and has many unintended results, including contributing to antibiotic resistance. Using more species-specific antibiotics is the best route, because it lessens the number of bacteria unnecessarily exposed to antibiotics; however, current methods of determining what bacteria are present take a few days. Speeding this up would give the patient accurate, effective treatment more quickly.
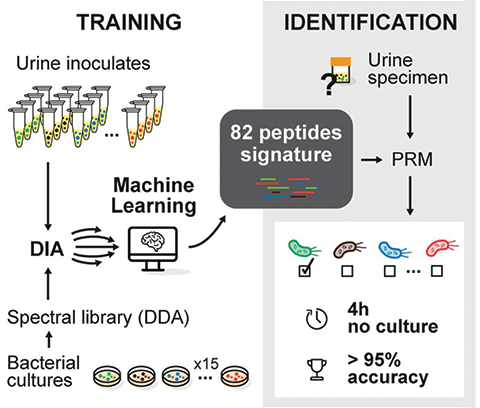
Florence Roux–Dalvai and colleagues at the Université Laval Research Center in Quebec aim to address this problem by creating a new method to identify bacterial species in patient samples in under four hours. They recently published a paper on their work in the journal Molecular & Cellular Proteomics.
The researchers used liquid chromatography tandem mass spectrometry, or LC–MS/MS, of bacterial peptides and machine learning to identify peptide fingerprints of each bacterial strain. First, they grew pure bacterial cultures of 15 species commonly found in urinary tract infections and digested the proteins to create many short peptides. Then they analyzed the peptides by LC-MS/MS to create a library of thousands. Next, they inoculated healthy urine with bacteria and tested 190 samples to create lists of peptides, using the libraries created from the pure cultures as a reference. They then submitted those lists of peptides to the machine-learning program to determine peptide signatures for each strain. This resulted in a signature of between five and 26 peptides for each bacterial species. They then validated this algorithm by testing patient urine and successfully identifying the pathogens. This work holds real promise for improving the treatment of UTIs and many other infections.
How deadly bacteria survive and multiply
Francisella tularensis is extremely infectious; just 10 of the bacteria can cause tularemia, a life-threatening infection. The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention has classified F. tularensis as a bioterrorism agent, and scientists now are getting a grasp on how this bacteria lives.
After being engulfed by white blood cells, F. tularensis is able to escape the phagosome inside the cell by using its type VI secretion system, or T6SS, to secrete its own proteins into the cell. This allows the bacteria to proliferate in the cytosol, causing the eventual death of the blood cell. Understanding this process can help us find ways to prevent it.
Jason Ziveri and colleagues at the Université Paris Descartes published a paper in the journal Molecular & Cellular Proteomics analyzing the change in the proteome and phosphoproteome during the assembly of a central component of the T6SS, the sheath. While the proteome remained unchanged, the team found one component of the sheath to be phosphorylated, the first evidence of phosphorylation in Francisella. More importantly, they found that when they mutated the phosphorylated residue to a nonphosphorylatable residue, the bacteria no longer could assemble the T6SS and escape the phagosome to grow in the cell, indicating that this phosphorylation event is essential to the bacteria’s survival.
Golgi protein plays key role in virus maturation
Pathogenic phleboviruses can cause a range of diseases from mild to fatal. To find treatments for those infected, researchers must understand the virus lifecycle. One critical step that remains poorly understood is how these viruses bud and exit host cells. Zina M. Uckeley, Rebecca Moeller and a research team from Germany and Sweden published a paper in the journal Molecular & Cellular Proteomics on work that took a proteomics approach to elucidating this step.
The researchers examined the Uukuniemi virus of the phlebovirus family as it infected human cells. They performed a pull-down of the virus and used mass spectrometry to determine what host cell proteins came out with it. They found 39 cellular protein partners, picked the 12 candidates with the best likelihood of having a role in the virus lifecycle and knocked each down with siRNA.
One gene, GBF1, decreased infection by 50% when knocked down, indicating that it plays an essential role. GBF1 resides in the Golgi and participates in the secretory pathway of cells, which viruses hijack. The researchers then examined other viruses that rely on the secretory pathway, finding that GBF1 plays a key role in the lifecycles of the Flaviviridae, Coronaviridae, Rhabdoviridae and Togaviridae familes as well. GBF1 may be a promising antiviral target for many viruses that replicate in the cytoplasm of cells.
Enjoy reading ASBMB Today?
Become a member to receive the print edition four times a year and the digital edition monthly.
Learn moreGet the latest from ASBMB Today
Enter your email address, and we’ll send you a weekly email with recent articles, interviews and more.
Latest in Science
Science highlights or most popular articles

Building a career in nutrition across continents
Driven by past women in science, Kazi Sarjana Safain left Bangladesh and pursued a scientific career in the U.S.

Avoiding common figure errors in manuscript submissions
The three figure issues most often flagged during JBC’s data integrity review are background signal errors, image reuse and undeclared splicing errors. Learn how to avoid these and prevent mistakes that could impede publication.

Ragweed compound thwarts aggressive bladder and breast cancers
Scientists from the University of Michigan reveal the mechanism of action of ambrosin, a compound from ragweed, selectively attacks advanced bladder and breast cancer cells in cell-based models, highlighting its potential to treat advanced tumors.

Lipid-lowering therapies could help treat IBD
Genetic evidence shows that drugs that reduce cholesterol or triglyceride levels can either raise or lower inflammatory bowel disease risk by altering gut microbes and immune signaling.

Key regulator of cholesterol protects against Alzheimer’s disease
A new study identifies oxysterol-binding protein-related protein 6 as a central controller of brain cholesterol balance, with protective effects against Alzheimer’s-related neurodegeneration.

From humble beginnings to unlocking lysosomal secrets
Monther Abu–Remaileh will receive the ASBMB’s 2026 Walter A. Shaw Young Investigator Award in Lipid Research at the ASBMB Annual Meeting, March 7-10 in Washington, D.C.

