Bananapocalypse – the tricky genetics of a devastating fungus
Did you know that the bananas you eat today are not the same type as the ones people were eating a few generations ago? The banana you might have had with your breakfast today is a variety called the Cavendish banana, while the one that was in grocery stores up to the 1950s was a variety called Gros Michel, which was wiped out by a disease called Fusarium wilt of banana, or FWB.
FWB of Gros Michel was caused by Fusarium oxysporum race 1, a fungal pathogen that affects bananas. This fungal infection kills a plant by occupying its vascular system, blocking water and mineral transportation.
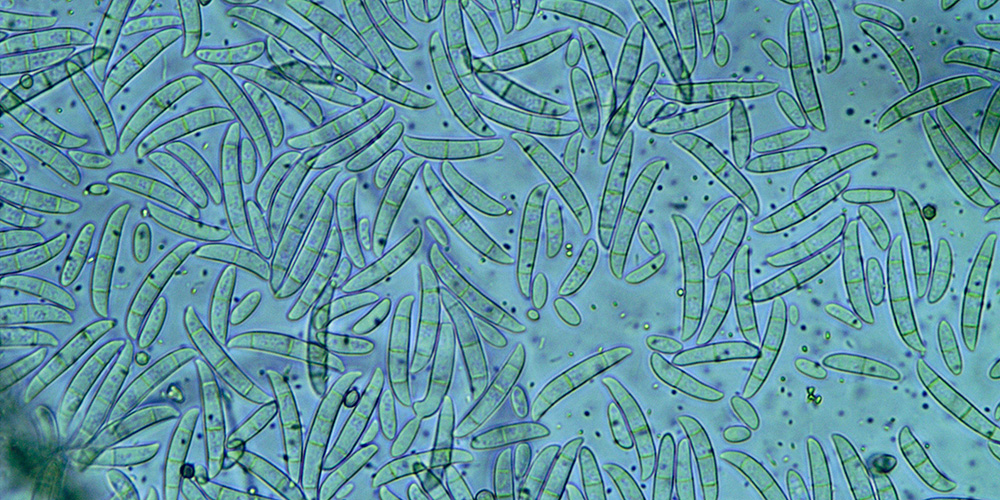
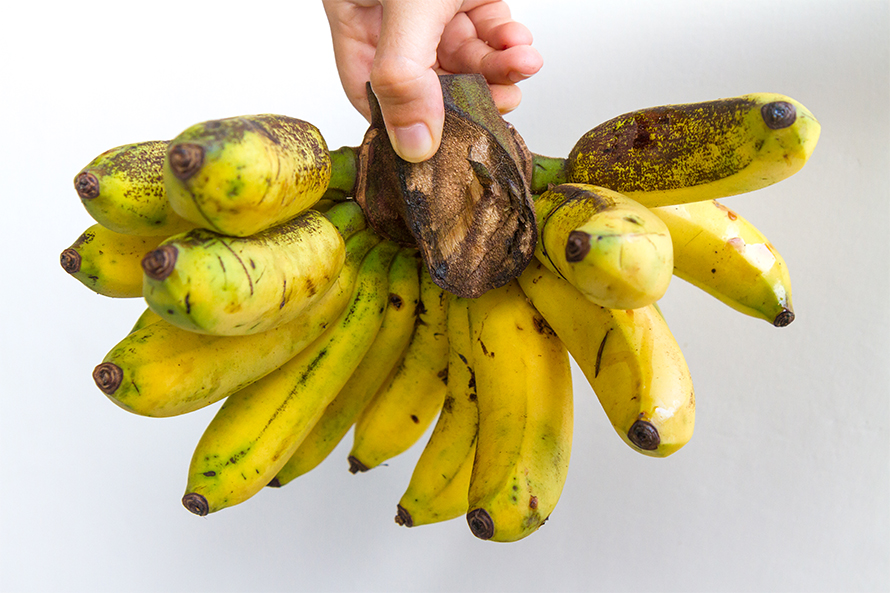
Plant biologists developed the Fusarium-resistant Cavendish variety to replace the Gros Michel. Yet, over the past few decades, a resurgence of FWB caused by a different strain of the same fungus called tropical race 4, or TR4, is once again threatening global banana production.
How did Fusarium oxysporum gain the ability to overcome resistance and infect so many different plants?

The two-part genome of F. oxysporum
I am a genomicist who has spent the past decade studying the genetic evolution of Fusarium oxysporum. As a species complex, F. oxysporum can cause wilt and root rot diseases in over 120 plant species. Certain strains can also infect people.
In 2010, my lab discovered that each F. oxysporum genome can be divided into two parts: a core genome shared among all strains that codes for essential housekeeping functions, and an accessory genome varying from strain to strain that codes for specialized functions like the ability to infect a specific plant host.
Each species of plant has a sophisticated immune response to defend against microbial invasion. So to establish an infection, each F. oxysporum strain uses its accessory genome to suppress a plant’s unique defense system. This functional compartmentalization allows F. oxysporum to greatly increase its host range.
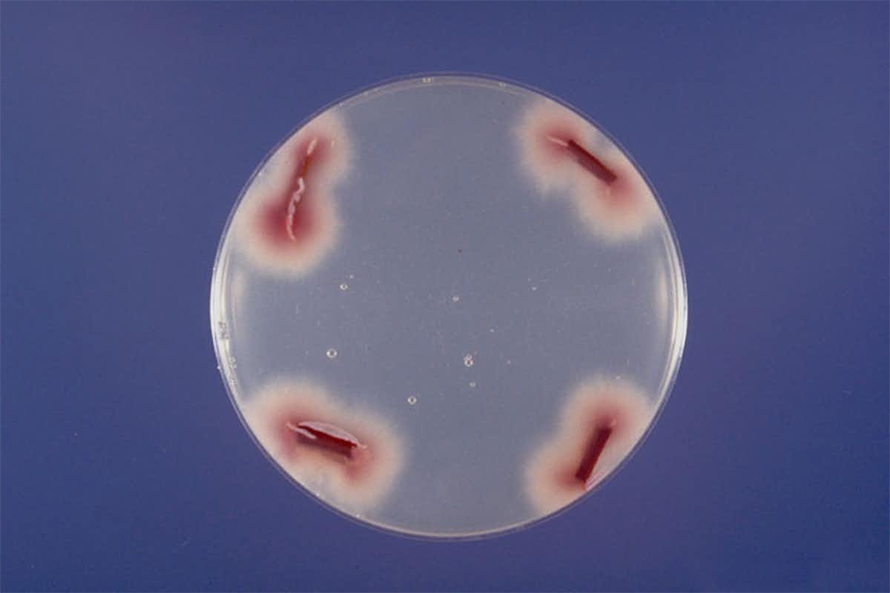
In our newly published research, my team and colleagues in China and South Africa found that the TR4 strain that kills Cavendish bananas has a different evolutionary origin and different sequences in its accessory genome compared with the strain that killed Gros Michel bananas.
Looking at the interface of where the TR4 strain is battling with its Cavendish banana host, we found that some of its activated accessory genes release nitric oxide, a gas harmful to the Cavendish banana. This sudden burst of toxic gases facilitates infection by disarming the plant’s defense system. At the same time, the fungus protects itself by increasing production of chemicals that detoxify nitric oxide.
Increasing banana diversity
In tracing the global spread of this new version of Fusarium oxysporum, we realized that a major cause for the recent resurgence of this fungal infection is the domination of the international banana industry by a single clone of banana.
Growing different varieties of bananas can make agriculture more sustainable and reduce disease pressure on a single crop. Farmers and researchers can control Fusarium wilt of banana by identifying or developing banana varieties that are tolerant or resistant to TR4. Our findings suggest that another way to protect Cavendish bananas would be to design effective nitric oxide scavengers to reduce the toxic pressure of the gas burst.
It can be hard to imagine how a consumer who simply enjoys eating bananas could participate in the battle against the disease devastating banana crops. However, consumers determine the market, and farmers are forced to grow what the market demands.
You can help increase banana diversity in your supermarket by intentionally trying one or more of the other hundreds of other existing banana varieties when they show up there. You can also buy local varieties of other fruits and agricultural products to help preserve plant diversity and support local growers.
Collaboration among scientists, farmers, industry and consumers around the world can help avoid future shortages of bananas and other crops.
This article is republished from The Conversation under a Creative Commons license. Read the original article.
![]()
Enjoy reading ASBMB Today?
Become a member to receive the print edition four times a year and the digital edition monthly.
Learn moreGet the latest from ASBMB Today
Enter your email address, and we’ll send you a weekly email with recent articles, interviews and more.
Latest in Science
Science highlights or most popular articles

Sizing up cells: How stem cells know when to divide
Stanford University researchers find that stem cells control their size early in cell division across living multicellular systems.

When oncogenes collide in brain development
Researchers at University Medical Center Hamburg, found that elevated oncoprotein levels within the Wnt pathway can disrupt the brain cell extracellular matrix, suggesting a new role for LIN28A in brain development.

The data that did not fit
Brent Stockwell’s perseverance and work on the small molecule erastin led to the identification of ferroptosis, a regulated form of cell death with implications for cancer, neurodegeneration and infection.

Building a career in nutrition across continents
Driven by past women in science, Kazi Sarjana Safain left Bangladesh and pursued a scientific career in the U.S.

Avoiding common figure errors in manuscript submissions
The three figure issues most often flagged during JBC’s data integrity review are background signal errors, image reuse and undeclared splicing errors. Learn how to avoid these and prevent mistakes that could impede publication.

Ragweed compound thwarts aggressive bladder and breast cancers
Scientists from the University of Michigan reveal the mechanism of action of ambrosin, a compound from ragweed, selectively attacks advanced bladder and breast cancer cells in cell-based models, highlighting its potential to treat advanced tumors.

