JBC: Zinc homeostasis and autophagy: beyond protein recycling
Zinc is a metal essential for life. In cells, zinc normally is bound to proteins, where it serves as a cofactor, which is essentially a “helper molecule” that aids proper protein function. Absence of zinc can have severe cellular consequences and has been implicated in disease. Recently, a study in the Journal of Biological Chemistry by the lab of Nobel laureate Yoshinori Ohsumi of the Tokyo Institute of Technology revealed that the cellular-degradation system known as autophagy is another consequence of zinc starvation.
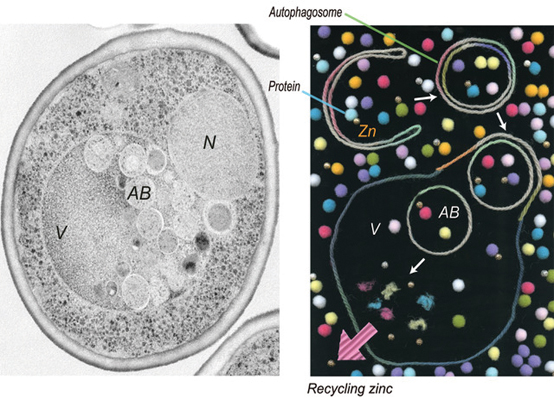 A yeast cell undergoing zinc deprivation-induced autophagy.Image courtesy of the Ohsumi lab
A yeast cell undergoing zinc deprivation-induced autophagy.Image courtesy of the Ohsumi lab
Autophagy is an intracellular degradation process that can function as a recycling system inside the cell. Autophagy occurs at low levels in healthy cells, serving as a quality-control mechanism. Autophagy ramps up when cells are starved for nutrients. The breakdown of intracellular products then provides building blocks for other essential cellular processes.
“Autophagy is often described as a recycling system for proteins,” explains Tomoko Kawamata, lead author of the study, “but we recently uncovered that autophagy also functions as a recycling system for metal, such as zinc.”
Previous genetic analysis of zinc-starved cells had revealed that genes related to autophagy are important during zinc starvation. However, the exact role that autophagy plays in zinc starvation remained unknown. “To understand the rules for the induction of autophagy, we tried to dissect how the lack of key nutrients affected growth rate between wild-type and autophagy-deficient cells,” explains Kawamata.
Kawamata’s team grew normal yeast cells and mutant versions deficient in autophagy in a media lacking zinc. The mutant cells’ growth in zinc-free media was impaired significantly compared with normal cells’, suggesting autophagy is important for cellular growth in zinc-depleted conditions.
They also observed that zinc depletion induces autophagy and compared this to what they know about nitrogen starvation, which is thought of as the classical inducer of autophagy. “Compared to autophagy by nitrogen starvation, autophagy by zinc starvation is characterized by a delay in induction,” says Kawamata. “The reason may be that intracellular zinc pools can suppress autophagy for some period of time.” In other words, when starved of zinc, the cells may access their internal stores of the metal to carry on, so autophagy doesn’t kick in right away.
Kawamata then wanted to determine if the zinc starvation-induced autophagy specifically targets the degradation of zinc-containing proteins. She fluorescently tagged a high-abundance protein called Adh1 known to contain zinc, and she tagged two proteins that don’t contain zinc. Then she tracked protein degradation induced by zinc starvation using the fluorescent signals. She found the proteins were degraded on a similar timescale, suggesting autophagy is not selectively going after proteins with zinc.
There’s a lot to learn about the links between external nutrient levels, internal nutrient levels and autophagy. “Our data suggest that induction of autophagy by some forms of nutrient starvation could be closely linked to internal nutrient availability, like the case for zinc starvation,” says Kawamata. This data expands on their recent findings that autophagy plays a role in iron recycling as well.
Furthermore, the research helps us better understand the role of a crucial nutrient in our cells. Zinc deficiency can lead to irregularities in a variety of organ systems, as zinc-containing proteins are involved with a number of biochemical pathways. “Abnormal zinc homeostatsis causes problems, including disease,” says Kawamata. “We hope our research is useful for understanding diseases linked to this deficiency.”
Enjoy reading ASBMB Today?
Become a member to receive the print edition four times a year and the digital edition monthly.
Learn moreGet the latest from ASBMB Today
Enter your email address, and we’ll send you a weekly email with recent articles, interviews and more.
Latest in Science
Science highlights or most popular articles

Avoiding common figure errors in manuscript submissions
The three figure issues most often flagged during JBC’s data integrity review are background signal errors, image reuse and undeclared splicing errors. Learn how to avoid these and prevent mistakes that could impede publication.

Ragweed compound thwarts aggressive bladder and breast cancers
Scientists from the University of Michigan reveal the mechanism of action of ambrosin, a compound from ragweed, selectively attacks advanced bladder and breast cancer cells in cell-based models, highlighting its potential to treat advanced tumors.

Lipid-lowering therapies could help treat IBD
Genetic evidence shows that drugs that reduce cholesterol or triglyceride levels can either raise or lower inflammatory bowel disease risk by altering gut microbes and immune signaling.

Key regulator of cholesterol protects against Alzheimer’s disease
A new study identifies oxysterol-binding protein-related protein 6 as a central controller of brain cholesterol balance, with protective effects against Alzheimer’s-related neurodegeneration.

From humble beginnings to unlocking lysosomal secrets
Monther Abu–Remaileh will receive the ASBMB’s 2026 Walter A. Shaw Young Investigator Award in Lipid Research at the ASBMB Annual Meeting, March 7-10 in Washington, D.C.

Chemistry meets biology to thwart parasites
Margaret Phillips will receive the Alice and C. C. Wang Award in Molecular Parasitology at the ASBMB Annual Meeting, March 7-10 in Washington, D.C.