From the journals: MCP
We summarize a selection of papers recently published in the journal Molecular & Cellular Proteomics.
New therapeutic targets for hyperactive mTOR
Overactive signaling of the protein kinase mammalian target of rapamycin, or mTOR, which leads to increased cell size and proliferation, is found in many cancers and other pathologies. While drugs exist that target mTOR, the authors of a new study in the journal Molecular & Cellular Proteomics point out that none of these drugs are effective in the long term, because cells adapt to the inhibition of mTOR.
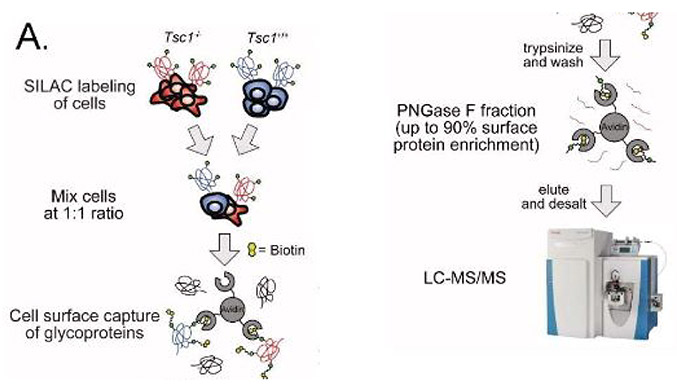
Authors Junnian Wei, Kevin Leung and their colleagues at the University of California, San Francisco, addressed this clinical issue by finding other proteins to target in cases of upregulated mTOR activity. They used two cell lines — one with and one without tuberous sclerosis complex 1, or TSC1 — as their model, since cells without an active TSC1/2 complex have overactive mTOR signaling. The authors compared these two cell lines using stable isotope labeling by amino acids in cell culture; they labeled either the TSC1+/+ or TSC1-/- cells with heavy carbon and nitrogen, performed mass spectrometry on samples enriched for surface proteins, and looked for surface proteins whose expression changed between the strains. A number of proteins changed, and the researchers validated the top upregulated hits using flow cytometry. The metalloproteinases neprilysin, or NEP/CD10, and aminopeptidase N, or APN/CD13, were discovered to be the most highly upregulated in TSC-/- cells.
The researchers confirmed this increase in mouse cell lines and diverse human cell lines with upregulated mTOR, indicating that these proteins may be promising conserved targets. They also found that when they downregulated either of these two proteins in cancer cell lines with upregulated mTOR, the cell proliferation decreased. Similarly, the loss of TSC1 or 2 and the resulting overactive mTOR sensitized cells to the inhibition of NEP and APN. These two new targets may be useful in the future treatment of diseases with hyperactive mTOR.
— Elizabeth Stivison
A SPEEDy way to prepare mass spec samples
To prepare samples for mass spectrometry analysis, researchers typically rely on detergents or chaotropic reagents. These methods present problems in sample digestion or extraction and require many steps, and the results can be biased. Joerg Doellinger and colleagues at the Centre for Biological Threats and Special Pathogens in Germany have reimagined how to prepare samples for mass spec, and they report on their new method in the journal Molecular & Cellular Proteomics.
The researchers call their method SPEED, short for sample prep by easy extraction and digestion, and it relies on acidification instead of detergents. In SPEED, pure trifluoroacetic acid is used to dissolve cells and tissues, the advantage being that the acid doesn’t disrupt peptide bonds and doesn’t modify amino acids. The dissolved sample then is neutralized, and the neutralized sample can be digested easily. When compared to other methods of preparation for liquid chromatography–mass spectrometry, SPEED consistently had the least variation batch to batch, indicating better reproducibility. In difficult to lyse samples such as mouse lung tissue and Bacillus cereus cells, it identified up to 41% more proteins than other methods.
A new program to detect citrullination
Citrullination is the replacement of the imine group in the amino acid arginine with an oxygen, which converts arginine to citrulline. Recent studies have tied citrullination to autoimmune diseases such as rheumatoid arthritis and have highlighted the role that citrullination of proteins by the pathogenic bacterium Porphyromonas gingivalis may play in the development of that disorder. To understand exactly what citrullination and citrullinated proteins are doing in biology and pathology, an accurate way of identifying citrullinated proteins is required. Mass spectrometry is the most reliable method but presents problems, including misinterpretation of data.
Daniel Nyberg Larsen and colleagues at the University of Southern Denmark have developed a new computer program, Citrullia, to identify and validate citrullinated peptides. The program displays all relevant information in a single window and allows potential citrullinated residues to be evaluated on primary mass spectrum specificity, fragment ions, fragmentation pattern and retention time behavior, producing reliable results that can be validated in a straightforward manner. This study was published in the journal Molecular & Cellular Proteomics.
Enjoy reading ASBMB Today?
Become a member to receive the print edition four times a year and the digital edition monthly.
Learn moreGet the latest from ASBMB Today
Enter your email address, and we’ll send you a weekly email with recent articles, interviews and more.
Latest in Science
Science highlights or most popular articles

The data that did not fit
Brent Stockwell’s perseverance and work on the small molecule erastin led to the identification of ferroptosis, a regulated form of cell death with implications for cancer, neurodegeneration and infection.

Building a career in nutrition across continents
Driven by past women in science, Kazi Sarjana Safain left Bangladesh and pursued a scientific career in the U.S.

Avoiding common figure errors in manuscript submissions
The three figure issues most often flagged during JBC’s data integrity review are background signal errors, image reuse and undeclared splicing errors. Learn how to avoid these and prevent mistakes that could impede publication.

Ragweed compound thwarts aggressive bladder and breast cancers
Scientists from the University of Michigan reveal the mechanism of action of ambrosin, a compound from ragweed, selectively attacks advanced bladder and breast cancer cells in cell-based models, highlighting its potential to treat advanced tumors.

Lipid-lowering therapies could help treat IBD
Genetic evidence shows that drugs that reduce cholesterol or triglyceride levels can either raise or lower inflammatory bowel disease risk by altering gut microbes and immune signaling.

Key regulator of cholesterol protects against Alzheimer’s disease
A new study identifies oxysterol-binding protein-related protein 6 as a central controller of brain cholesterol balance, with protective effects against Alzheimer’s-related neurodegeneration.

