Do sperm offer the uterus a secret handshake?
Why does it take 200 million sperm to fertilize a single egg?
One reason: When sperm arrive in the uterus, they are bombarded by the immune system. Perhaps, molecular anthropologist Pascal Gagneux says, many are needed so some will survive. On the other hand, the female may benefit by culling so many sperm.
“I’m a lonely zoologist in a medical school,” Gagneux said. “My elevator spiel is that all of life is one big compromise. (For an egg), being too easy to fertilize is bad; being too difficult to fertilize is also bad.”
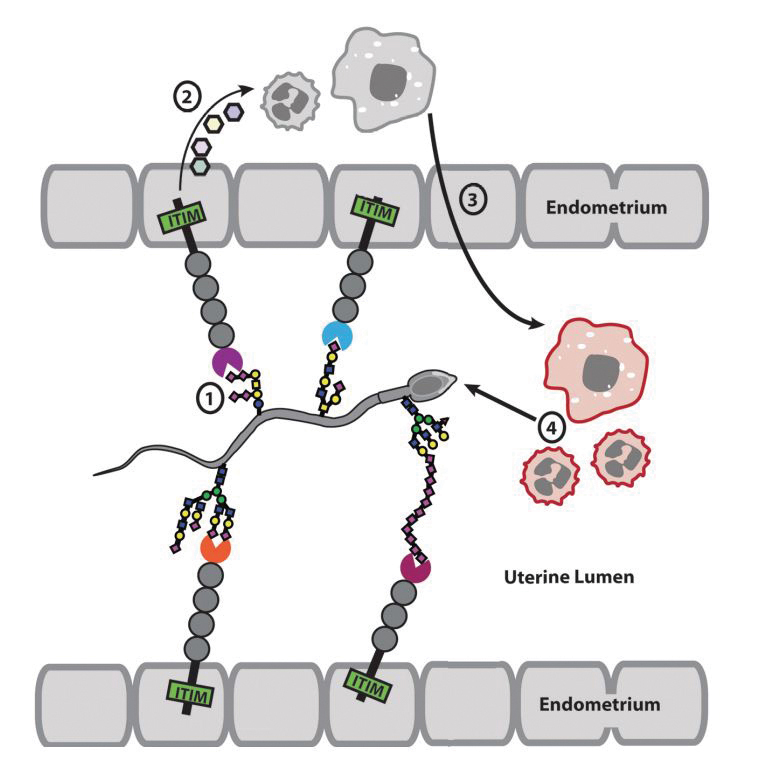
Gagneux’s lab at the University of California, San Diego, has discovered the makings of something that might be compared to a secret handshake between sperm and the cells lining the uterus in mice and, perhaps, humans. Uterine cells, they report in the Journal of Biological Chemistry, express a receptor that recognizes a glycan molecule on the surface of sperm cells. This interaction might adjust the female’s immune response and help sperm make it through the leukocytic reaction.
.jpg)
The leukocytic reaction is not well understood. What we do know, Gagneux said, is that “after crossing the cervix, millions of sperm — a U.S. population worth of sperm — that arrive in the uterus are faced by a barrage of macrophages and neutrophils.”
This attack by the innate immune system kills most of the sperm cells in semen, winnowing hundreds of millions down to just a few hundred that enter the fallopian tubes. The defensive response may help prevent polyspermy, when an egg is fertilized by more than one sperm and cannot develop.
Sperm are coated in sialic acid–rich glycans, and the innate immune system uses sialic acid to differentiate human cells from invaders, so Gagneux and his lab expected that the glycan might interact with innate immune cells called neutrophils. But human neutrophils they tested were activated to a similar degree by sperm with and without sialic acid.
Meanwhile, the team noticed sialic acid–binding receptors called siglecs on endometrial cells. In solution, these endometrial receptors can bind to whole sperm. According to Gagneux, the binding interaction might help the sperm run the gantlet of the leukocytic response — for example, by dampening the immune response. Alternatively, it may be a way for uterine cells to weed out faulty sperm. In the immune system, siglecs help cells to recognize sialic acid molecules as markers of the body’s own cells, and in that context they can turn inflammation either up or down.
“It’s somewhat embarrassing how little we can say about what this (interaction) means,” Gagneux said. To understand its physiological significance, researchers first must look for direct interaction between sperm and intact uterine tissue — this paper looked at only sperm interacting with purified proteins and isolated cells.
It’s humbling to work in such a poorly understood area, Gagneux said. Reproduction “is a very, very delicate tug-of-war at many levels. The fact that there is (also) this immune game going on is completely fascinating.”
Enjoy reading ASBMB Today?
Become a member to receive the print edition four times a year and the digital edition monthly.
Learn moreGet the latest from ASBMB Today
Enter your email address, and we’ll send you a weekly email with recent articles, interviews and more.
Latest in Science
Science highlights or most popular articles

Sizing up cells: How stem cells know when to divide
Stanford University researchers find that stem cells control their size early in cell division across living multicellular systems.

When oncogenes collide in brain development
Researchers at University Medical Center Hamburg, found that elevated oncoprotein levels within the Wnt pathway can disrupt the brain cell extracellular matrix, suggesting a new role for LIN28A in brain development.

The data that did not fit
Brent Stockwell’s perseverance and work on the small molecule erastin led to the identification of ferroptosis, a regulated form of cell death with implications for cancer, neurodegeneration and infection.

Building a career in nutrition across continents
Driven by past women in science, Kazi Sarjana Safain left Bangladesh and pursued a scientific career in the U.S.

Avoiding common figure errors in manuscript submissions
The three figure issues most often flagged during JBC’s data integrity review are background signal errors, image reuse and undeclared splicing errors. Learn how to avoid these and prevent mistakes that could impede publication.

Ragweed compound thwarts aggressive bladder and breast cancers
Scientists from the University of Michigan reveal the mechanism of action of ambrosin, a compound from ragweed, selectively attacks advanced bladder and breast cancer cells in cell-based models, highlighting its potential to treat advanced tumors.

