Ching C. Wang (1936—2017)
Ching C. “C.C.” Wang was a passionate scientist who turned a childhood of suffering into a lifetime crusade against parasitic diseases. He worked tirelessly to build and promote the field of molecular parasitology and was a driving force in creating a community characterized by rigor, creativity and genuine camaraderie. On Aug. 22, at the age of 81, he lost his battle with cancer, and molecular parasitology lost an inspirational leader, mentor and friend. As Ken Stuart of the Center for Infectious Disease Research eloquently wrote, “C.C.’s big smile, enthusiasm for so much, his booming voice and caring for others will be sorely missed. He gave so much of himself to his colleagues, trainees, his research field, friends and family.”
C.C. was born in Beijing in 1936 during the tumult of the Japanese invasion. He contracted many tropical diseases while his family roamed the countryside, and this childhood experience fueled his desire to combat parasitic diseases. His family eventually escaped to Taiwan, where young C.C. thrived and developed his interest in science. An excellent chemistry student, he came to the U.S. and earned his doctorate in microbial biochemistry at the University of California, Berkeley, in 1966. There, C.C. also met his future wife and partner in both life and science, Alice Wang. After his postdoctoral training at Columbia University, he joined the parasitology division at Merck in Rahway, N.J., where he hoped to work on cures for the parasitic diseases that afflicted the world’s poor, including those he had as a child.
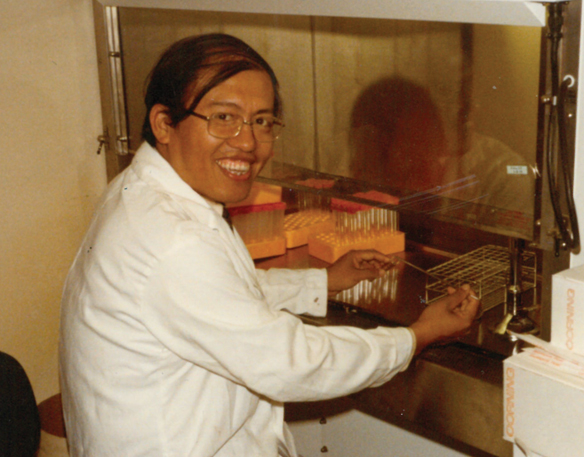 C.C. Wang works in his lab at the University of California, San Fransicso, where he studied parasitic diseases. courtesy of the wang family
C.C. Wang works in his lab at the University of California, San Fransicso, where he studied parasitic diseases. courtesy of the wang family
Merck’s transformative antiparasitic drug ivermectin, now a World Health Organization essential medicine, was discovered in 1975, and CC was assigned to investigate its mechanism of action, which was a priority of Merck’s new president, Roy Vagelos. Target identification is a gnarly task even now, and C.C. had few tools beyond his keen observational skills and biochemical instincts. C.C. noticed that ivermectin paralyzes worms, and eventually he showed that it targets glutamate-gated chloride channels. This tour de force led to a faculty appointment as a tenured professor in the Department of Pharmaceutical Chemistry at the University of California, San Francisco, in 1981, at a time when the transition from industry to academics was virtually unheard of.
Despite the success of ivermectin, C.C. arrived at UCSF disillusioned with the screening methods used to discover antiparasitic drugs and determined to develop rational approaches. Where most parasitology laboratories focused on a single pathogen, C.C. investigated several overlooked protozoa, Giardia lamblia, Trypanosoma brucei, Trichomonas vaginalis and Tritrichomonas foetus. He began to unravel their mysteries with uncanny molecular intuition and a fearless disregard for disciplinary boundaries. His many seminal contributions include mapping nucleotide salvage pathways, characterizing a novel organelle called the glycosome and the discovery, with Alice, of a double-stranded RNA virus in Giardia. He later turned his efforts to protein degradation, translation initiation and cell-cycle regulation. He was always at the forefront, applying new techniques and forging ahead to the next question. A much-lauded lecturer and mentor, he trained many students and postdocs, including both authors, who had the fortune of working with him in the early days of his laboratory (Meg as a Ph.D. student and Liz as a postdoctoral fellow).
 C.C. Wang met his wife, Alice, at the University of California, Berkeley. The couple loved to travel and had many adventures. courtesy of Meg Phillips and Liz Hedstrom
C.C. Wang met his wife, Alice, at the University of California, Berkeley. The couple loved to travel and had many adventures. courtesy of Meg Phillips and Liz Hedstrom
C.C. was devoted to the field of molecular parasitology. He recognized that fellowship was just as important to scientific discovery as rigor and creativity, and he was the nucleus for many forums that enabled the field to thrive. C.C. and his dear friend John Boothroyd at Stanford co-organized the Bay Area Parasitology Club in the 1980s. Alice and C.C. would hold club meetings at their home. Sitting around their living room with the speaker using a home slide projector and screen, we listened to a lecture, discussed the science and snacked on delicious dim sum. These lectures became the hottest tickets in town for budding young parasitologists. Speaking was a special honor for Meg and others who attended during their training.
C.C. felt it was critically important that molecular parasitology be recognized not just for the diseases these organisms cause but also for their fascinating biology. This passion led him to start the journal Eukaryotic Cell as a home for such work. Later, C.C. and Alice worked with the American Society for Biochemistry and Molecular Biology to establish the Alice and C.C. Wang Award in Molecular Parasitology, now in its seventh year. C.C. and Alice created this annual award to highlight groundbreaking discoveries in the field of parasitology. As C.C. hoped, the award provides a platform to introduce parasitology to the wider scientific community, both to increase appreciation for the dedicated and versatile scientists that study these organisms and to recruit new scientists to the field.
C.C. was a true scientist’s scientist, insightful and rigorous and a champion of truth and integrity. He sat in the front row of every seminar and asked the most penetrating questions. He was always ready for a feisty debate and relished stirring the pot. Many a student and postdoc, including the authors, learned not just how to be a good scientist from C.C. but also what it meant to embrace life itself. His moves on the dance floor were notorious, and he was always the last one to leave a party. He treasured good food, often cooked by Alice, and fine wine and liked nothing better than sharing a meal. He especially loved treating his friends to mysterious Chinese delicacies, smiling at their pleasure and then laughing when he revealed exactly what they had eaten.

Giving parasites
their due
C.C. Wang introduced biochemical methods to parasitology, effectively modernizing the field and helping to bring about important antiparasitic drugs. In 2016, Wang shared with ASBMB Today his formative experiences with life-threatening illnesses in southern China and the professional journey that took him from the East to the West and back again.
He was generous and warm-hearted, providing beds for new postdocs and gifting projects to fledgling professors. Mike Ferguson of the University of Dundee, the 2016 Wang awardee, wrote, “C.C. was, at once, a giant in his scientific field and an immensely kind and warm human being. I met him first as a Ph.D. student and last as a grateful recipient of the Alice and C.C. Wang Award — he was as nice and as much fun the first time as the last time, and at all times in between.”
C.C.’s first round with cancer caused him to close his laboratory, yet he remained engaged after his retirement. He continued to attend the Molecular Parasitology Meeting at Woods Hole, Mass., where he loved the free exchange of ideas. He and Alice enjoyed travel and had many adventures as they traipsed across the world, like the time he broke his leg in Ireland or, on their last trip, sampling the best food Japan had to offer. He also greatly enjoyed spending time with his daughter, Charlotte, and the grandkids.
All of us who knew, learned from and loved C.C. will miss him dearly. But C.C. would have agreed with the sentiment of Jay Bangs of the University of Buffalo, who wrote, “I would prefer to celebrate a life well lived … he was and remains forever an inspiration!”
Enjoy reading ASBMB Today?
Become a member to receive the print edition four times a year and the digital edition monthly.
Learn moreGet the latest from ASBMB Today
Enter your email address, and we’ll send you a weekly email with recent articles, interviews and more.
Latest in People
People highlights or most popular articles

In memoriam: Walter A. Shaw
He is the namesake for the Walter A. Shaw Young Investigator Award in Lipid Research and founded Avanti Polar Lipids.

Dorn named assistant professor
She will open her lab at the University of Vermont in fall 2026, and her research will focus on catalysis, synthetic methodology and medicinal chemistry.

The data that did not fit
Brent Stockwell’s perseverance and work on the small molecule erastin led to the identification of ferroptosis, a regulated form of cell death with implications for cancer, neurodegeneration and infection.

Building a career in nutrition across continents
Driven by past women in science, Kazi Sarjana Safain left Bangladesh and pursued a scientific career in the U.S.

Kiessling wins glycobiology award
She was honored by the Society for Glycobiology for her work on protein–glycan interactions.
2026 ASBMB election results
Meet the new Council members and Nominating Committee member.


