The researcher and the roaches
“Cockroaches are more advantageous than you would think.”
So said Jingwei Li, an undergraduate student at Case Western Reserve University, who has been studying cockroaches to learn about Parkinson’s disease.
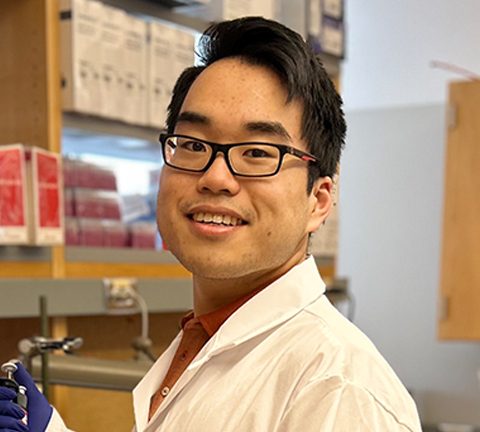

“So many of my friends were in labs that use mice,” he said. After plenty of pipetting in his past lab rotations, a hands-on project with the American cockroach, or Periplaneta americana, sounded appealing. “Sure, I’ll try,” he said.
Roaches have a few genes in the brain that are similar to humans’, including genes for Parkin and D2-like dopamine receptors. And because they have a longer lifespan than fruit flies — staples of scientific study — scientists can study longitudinal changes more easily.
With fruit flies, you only have 40 days. With cockroaches, you can have a year or two.
Model student, model organism
Ryan Arvidson, Li’s supervisor and an assistant professor of biochemistry at Case Western, said Li began with only “some pilot data and a few replicates,” and yet, “he seemed to succeed almost immediately.” (That never happens.)
“He wasn’t there to check a box,” Arvidson said of his student.
Li was tenacious, documenting the molecular shopping list of a huge bunch of nerves called the cephalic ganglia. This shopping list is called a transcriptome, and it will give insight into a roach’s brain on Parkinson’s.
Li’s research also involved measuring how cockroaches with genetically induced Parkinson’s disease walked. “Cockroach locomotion,” it’s called.
The cockroaches with Parkinson’s moved spontaneously: Instead of making laps around a container’s perimeter, their movement was jerky and unpredictable — think Michael Jackson’s “Thriller.” They also had less grip strength. To determine this, Li tied one end of a string around a cockroach’s thorax. He lifted the cockroach slowly and noted how high the tension gauge reading got before the cockroach let go.
And the cockroaches’ movements became smaller and fewer over time. “Hypokinesia,” it’s called, and it’s from diminished dopamine, not diminished muscle. The body begins to move with less oomph.
From pest to Parkinson’s
Cockroaches have played a role in scientific research for over a century, including for what robotics researchers describe as the “elegant” transition they can make from horizontal walking to vertical climbing, but neuroscience tools rarely have been applied to them until now.
One day, scientists hope to use the lifespan of cockroaches, and new genetic tools, to test FDA-approved drugs and the impact of diet on Parkinson’s symptoms.
After a long day of studying cockroach locomotion, Li likes to impair his own with the environmental stimuli of a good gym session. “To destroy my muscles,” he said.
In Arvidson’s lab, Li said, “I felt like a bigger part of the picture. I wasn’t just there to grow some cells and that was it.”
Li will graduate this semester and, heading for medical school, hopes to keep returning to research.
And the cockroaches? The cockroaches were lifted from their status as pests. Li said they became a lot more like pets.
Enjoy reading ASBMB Today?
Become a member to receive the print edition four times a year and the digital edition monthly.
Learn moreGet the latest from ASBMB Today
Enter your email address, and we’ll send you a weekly email with recent articles, interviews and more.
Latest in People
People highlights or most popular articles

The data that did not fit
Brent Stockwell’s perseverance and work on the small molecule erastin led to the identification of ferroptosis, a regulated form of cell death with implications for cancer, neurodegeneration and infection.

Building a career in nutrition across continents
Driven by past women in science, Kazi Sarjana Safain left Bangladesh and pursued a scientific career in the U.S.

Kiessling wins glycobiology award
She was honored by the Society for Glycobiology for her work on protein–glycan interactions.
2026 ASBMB election results
Meet the new Council members and Nominating Committee member.

Simcox wins SACNAS mentorship award
She was recognized for her sustained excellence in mentorship and was honored at SACNAS’ 2025 National Conference.

From humble beginnings to unlocking lysosomal secrets
Monther Abu–Remaileh will receive the ASBMB’s 2026 Walter A. Shaw Young Investigator Award in Lipid Research at the ASBMB Annual Meeting, March 7-10 in Washington, D.C.

