States and localities pump more money into community colleges than four-year campuses
State and county officials used to think bachelor’s and graduate degree students deserved more money than those pursuing two-year associate degrees, but during the pandemic they changed their minds.
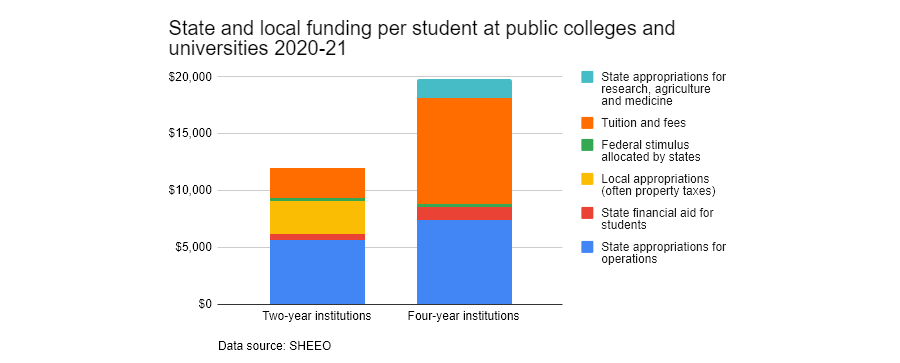
Public two-year community colleges achieved a new budgetary milestone in fiscal year 2021 as they reaped 6% more money per student from state and local governments than public four-year institutions did for their regular operating expenses: $9,347 versus $8,859 for each student. That’s a reversal from 2019 when two-year students received 5% less than four-year students.
These numbers were supplied by an association of officials who oversee public colleges and universities in their states, called the State Higher Education Executive Officers Association, which released a higher education finance report in June. The funding figures exclude additional state and federal money for university research, agricultural projects, medical schools and
“All public institutions need more funding for operations, but community colleges are particularly reliant on state and local funding,” said Sophia Laderman, who leads research and policy analysis at the association. “Community college students are more likely to be low-income and students of color and this can help close equity gaps.”
Even with increased state and local funding, much less is spent on community college students in total. The difference is tuition. Tuition collected from community college students adds up to only about 20% of what community colleges spend on their educational operations. Almost 80% of community college revenues come from state and local funds.
Public four-year colleges, by contrast, charge far higher tuition and ultimately spend more than double their state and local funds on their students. Flagship universities attract big donors and can dip into their endowments. “They can still provide a much better education,” said Laderman.
As an aside, I was struck by how much less we as a nation spend on public higher education than we do public school for younger students. Per pupil funding of kindergarten through high school students averaged $15,711 during the 2019-20 school year, according to the most recent data from the Department of Education. Then again, it makes sense for the government to spend more on children’s education which is mandated by the state. College is optional.
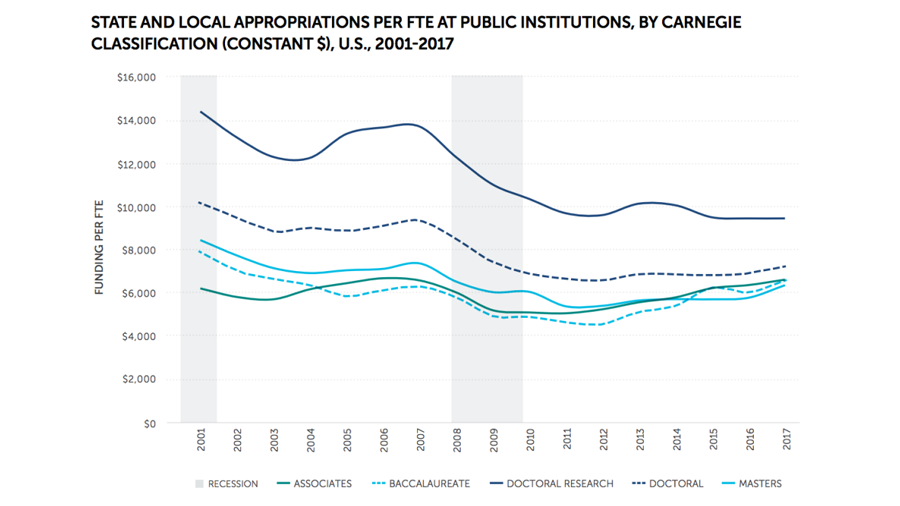
Lawmakers have historically funded public four-year institutions that confer bachelor’s and graduate degrees, such as the University of Texas, more generously than two-year colleges, such as Austin Community College, which award associate degrees and educate more than a third of undergraduate students across the country. When the 2008 recession hit, both community colleges and four-year universities alike were hit with big budget cuts.
As the economy recovered, however, state lawmakers restored funding to community colleges, which positioned themselves as places for blue-collar workforce training. In addition to appropriating more money directly to two-year colleges, lawmakers created many new free community college programs and scholarships, which now operate in hundreds of cities and counties and statewide in almost 30 states. By contrast, a conservative backlash against “liberal” academics tamped enthusiasm for funding increases at more elite four-year universities.
Community colleges also gained from regional real estate booms, which increased property taxes that flow to two-year colleges.
Funding for community colleges, already on the upswing, then surpassed that of four-year universities during the pandemic. State lawmakers had discretion over how to spend a portion of their federal stimulus money and steered a big chunk to community colleges. Some states dug even deeper into their own pockets. Washington, for example, increased its funding of community colleges by 27% in 2021, as it introduced a free community college program. By comparison, the state boosted funding of its four-year colleges by 6.5% that year.
Ironically, some of the increase in per-student funding was also driven by misfortune. Community colleges hemorrhaged 827,000 students during the pandemic as young adults chose work over school. Some government funding is tied to the numbers of enrolled students but some isn’t. With fewer students, there was more of that untied funding to spread among remaining students.
Laderman cautioned, however, that this aspect of the increase was not a boon for community colleges. They still had to cover many of the same bills as they had before the students left, from faculty salaries to custodians and electricity. Many are struggling financially.
Per-student funding would have gone up even without the decline in student enrollment at community colleges. Laderman calculated that state and local education appropriations per community college student would have increased by half as much, or 7%, if enrollment hadn’t declined.
It’s unclear how higher education finance will fare going forward. If a recession hits and unemployed adults return to school, that could increase funds for community colleges. But lawmakers may also be pressured once again to cut funding if tax collections run dry.
This story was produced by The Hechinger Report, a nonprofit, independent news organization focused on inequality and innovation in education.
Enjoy reading ASBMB Today?
Become a member to receive the print edition four times a year and the digital edition monthly.
Learn moreGet the latest from ASBMB Today
Enter your email address, and we’ll send you a weekly email with recent articles, interviews and more.
Latest in Policy
Policy highlights or most popular articles

Women’s health cannot leave rare diseases behind
A physician living with lymphangioleiomyomatosis and a basic scientist explain why patient-driven, trial-ready research is essential to turning momentum into meaningful progress.

Building a stronger future for research funding
Hear from Eric Gascho of the Coalition for Health Funding about federal public health investments, the value of collaboration and how scientists can help shape the future of research funding.

Councilors advocate for science on Capitol Hill
ASBMB Councilors meet with their elected officials to advocate for basic scientific research funding and training the next generation of scientists.

Hope for a cure hangs on research
Amid drastic proposed cuts to biomedical research, rare disease families like Hailey Adkisson’s fight for survival and hope. Without funding, science can’t “catch up” to help the patients who need it most.

Supporting science through advocacy and community building
ASBMB calls on scientists to take action as funding cuts and policy shifts threaten the U.S. research enterprise, emphasizing the power of community advocacy and persistence in protecting the future of science.

Seven steps to advocating in your home state
Find out how to schedule, prepare for and conduct a productive district office meeting to communicate the importance of fundamental scientific research funding to your representatives.


