Receptor regulation clues may scratch an itch
Whether you’ve been stung by an insect or suffer from allergies, most people have experienced itchy skin, which usually can be relieved with time or simple remedies. However, for certain patients with liver disease, an intense itching sensation, known as cholestatic pruritis — the medical term for itch — often does not respond to standard treatments.
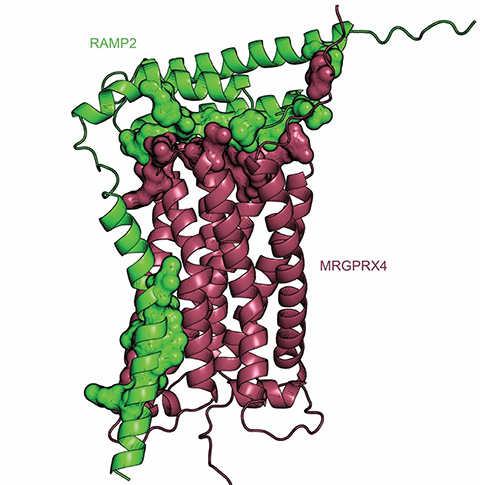
Thomas Sakmar’s lab at the Rockefeller University uses biochemical and biophysical methods to study transmembrane signal transduction by G protein-coupled receptors. GPCRs play an important role in human physiology; they make up the largest family of membrane proteins and mediate many signaling pathways. Therefore, these receptors are frequent drug targets for a wide variety of diseases and disorders such as cancer, depression, hypertension and more.
In a recent paper in the Journal of Biological Chemistry, Sakmar and his team write about their work on the regulation of a particular GPCR through receptor activity–modifying protein 2, or RAMP2. This receptor, mas-related GPCR subtype X4, or MRGPRX4, is associated with cholestatic itch and is present in the sensory neurons of the skin.
“Our research is unique in that it illustrates a role for RAMPs in MRGPRX4 biology,” Sakmar said. “Since GPCRs represent the molecular targets of approximately one-third of current Food and Drug Administration-approved drugs, a better understanding of GPCR regulation can lead to the development of more potent and selective drugs for a large range of diseases.”
The Sakmar lab had already collaborated to create a multiplexed screening platform to better understand and explore how commonly expressed GPCRs interact with RAMPs. With this technology they identified, for the first time, MRGPRX4 interacting with RAMP2, which they further characterized using pharmacological and computational methods.
In addition to characterizing the MRGPRX4–RAMP2 complex, Sakmar’s team studied how bile acids can activate the receptor. The slowing or stopping of the flow of bile from the liver, known as cholestasis, is believed to cause intense itching in patients with cholestatic disorders. Bile acids are elevated in patients with liver disease, so, taken together with the newly discovered MRGPRX4–RAMP2 interaction, this research improves a broader understanding of the role MRGPRX4 plays in cholestatic itch.
Researchers need to understand the regulation of GPCRs to elucidate how therapies act on these receptors, Sakmar said. “Our discovery that many GPCRs, including MRGPRX4, are regulated by RAMPs might improve drug discovery paradigms, and it is possible that our work might lead to new drugs to treat cholestatic itch or minimize the chance that a drug candidate might cause itch as a side effect.”
The lab plans to take their findings to the next level by increasing the depth and breadth of their work, Sakmar said. “We plan to study the MRGPRX4–RAMP2 interaction in primary skin cells to gain a better understanding of how this protein–protein interaction affects the pharmacology of MRGPRX4 in a highly physiologically relevant environment.”
Enjoy reading ASBMB Today?
Become a member to receive the print edition monthly and the digital edition weekly.
Learn moreGet the latest from ASBMB Today
Enter your email address, and we’ll send you a weekly email with recent articles, interviews and more.
Latest in Science
Science highlights or most popular articles
New class of antimicrobials discovered in soil bacteria
Scientists have mined Streptomyces for antibiotics for nearly a century, but the newly identified umbrella toxin escaped notice.
New study finds potential targets at chromosome ends for degenerative disease prevention
UC Santa Cruz inventors of nanopore sequencing hail innovative use of their revolutionary genetic-reading technique.
From the journals: JLR
How lipogenesis works in liver steatosis. Removing protein aggregates from stressed cells. Linking plasma lipid profiles to cardiovascular health. Read about recent papers on these topics.
Small protein plays a big role in viral battles
Nef, an HIV accessory protein, manipulates protein expression in extracellular vesicles, leading to improved understanding of HIV-1 pathogenesis.

Genetics studies have a diversity problem that researchers struggle to fix
Researchers in South Carolina are trying to build a DNA database to better understand how genetics affects health risks. But they’re struggling to recruit enough Black participants.
Scientists identify new function of learning and memory gene common to all mammalian brain cells
Findings in mice may steer search for therapies to treat brain developmental disorders in children with SYNGAP1 gene mutations.

