From the journals: JBC
Chain length and malarial infection. Diet supplements and fatty liver disease. Effects of a lesser-known synuclein. Read about recent papers on these topics published in the Journal of Biological Chemistry.
Chain length and malarial infection
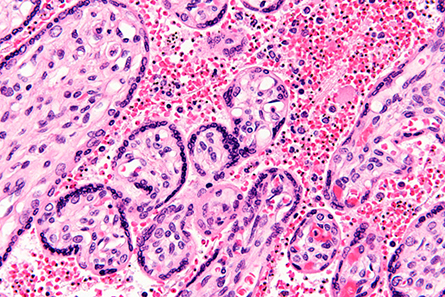
within red blood cells in this stained high-magnification micrograph, that targets
the placenta.
Malaria kills hundreds of thousands of people every year, and most of these deaths are caused by the parasite Plasmodium falciparum,which binds to blood cells, allowing it to remain in the vasculature and escape immune clearance in the spleen. Pregnant women are particularly susceptible to a serologically distinct parasite variant that targets the placenta. Placental malaria is mediated by the protein VAR2CSA interacting with the placental glycosaminoglycan chondroitin sulfate, or CS.
Previously, researchers had identified a shared type of oncofetal chondroitin sulfate, or ofCS, that is common to placenta and tumors, but scientists still lack a clear understanding of its structure and selectivity to VAR2CSA. In a study recently published in the Journal of Biological Chemistry, Charlotte B. Spliid of the University of California, San Diego, and Copenhagen University Hospital, Denmark, and an international teamperformed structural analysis of ofCS and found that both placenta- and tumor-derived ofCS had high N-acetylgalactosamine 4-O-sulfation levels.
The researchers showed that both tissues had more chondroitin sulfate moieties of higher molecular weight than other tissues, concurrent with chondroitin polymerization proteins being upregulated in most cancer types. CRISPR/Cas9 targeting of these proteins showed a reduction in cell-surface chondroitin molecular weight, which reduced the binding to recombinant VAR2, or rVAR2.
Finally, the researchers showed that rVAR2 binding is dependent on the length of the chondroitin sulfate chains. They concluded that the amount and accessibility of CS chains affect rVAR2 binding and, in doing so, malaria infection.
Diet supplements and fatty liver disease
Nonalcoholic fatty liver disease, or NAFLD, is a set of diseases involving fat accumulation and inflammation of the liver that affect almost a quarter of the U.S. population.
Low hepatic nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide, or NAD+, levels previously have been associated with NAFLD. In a recent article in the Journal of Biological Chemistry, Morten Dall, Anna Hassing and a team at the University of Copenhagen describe how they determined that removing hepatic nicotinamide phosphoribosyltransferase, or NAMPT, the enzyme responsible for NAD+ formation, increases susceptibility to liver injury in diet-induced metabolic stress.
Feeding experiments using specific formulations showed that mice genetically altered to lack the Nampt gene, called HNKO mice, had higher liver inflammation, necrosis and fibrosis than unmodified mice. They also presented decreased amounts of mitochondrial proteins involved in oxidoreductase activity, and liver sections showed a negative correlation between fibrosis and NAD+ levels. The researchers used mass spectrometry–based proteomic analysis to determine that supplementation with the NAD+ precursors nicotinamide riboside and nicotinic acid prevented liver injury and rescued hepatic levels of oxidoreductases. Finally, single nucleus RNAseq in HNKO mice liver determined transcriptional changes that were associated with necrosis.
The authors concluded that “HNKO livers have reduced respiratory capacity, decreased abundance of mitochondrial proteins, and are susceptible to fibrosis due to low NAD+ levels.” They suggest that NAD+ precursor supplementation in the diet could prevent liver injury and NAFLD progression.
Effects of a lesser-known synuclein
Synucleins are a family of three proteins highly expressed in neurons involved in Parkinson’s and certain other neurodegenerative diseases. While the role of alpha-synuclein as a modulator of various mechanisms implicated in chemical neurotransmission is well known, researchers know less about the other family members, beta-synuclein and gamma-synuclein.
In research recently published in the Journal of Biological Chemistry, Natalia Ninkina, Steven J. Millership and Owen M. Peters of Cardiff University and a team in the U.K. aimed to decipher the role β-synuclein plays in uptake of the neurotransmitter dopamine. They first showed that the sole presence of this protein improves dopamine uptake in triple-negative striatal vesicles.
The authors also showed that the presence of β-synuclein increased resistance to subchronic administration of the Parkinson’s disease–inducing prodrug 1-methyl-4-phenyl-1,2,3,6-tetrahydropyridine, or MPTP, in dopaminergic neurons of the substantia nigra pars compacta when one or both of the other synucleins are absent. Additional proteomics analyses showed different protein compositions in synuclein-deficient synaptic vesicles versus those containing only β-synuclein.
The authors suggest that the increase in dopamine uptake by β-synuclein may be due to a change in protein architecture of synaptic vesicles, which leads to increased resistance to an MPTP toxic metabolite in dopaminergic neurons.
Enjoy reading ASBMB Today?
Become a member to receive the print edition monthly and the digital edition weekly.
Learn moreGet the latest from ASBMB Today
Enter your email address, and we’ll send you a weekly email with recent articles, interviews and more.
Latest in Science
Science highlights or most popular articles

Genetics studies have a diversity problem that researchers struggle to fix
Researchers in South Carolina are trying to build a DNA database to better understand how genetics affects health risks. But they’re struggling to recruit enough Black participants.
Scientists identify new function of learning and memory gene common to all mammalian brain cells
Findings in mice may steer search for therapies to treat brain developmental disorders in children with SYNGAP1 gene mutations.
From the journals: JBC
Biased agonism of an immune receptor. A profile of missense mutations. Cartilage affects tissue aging. Read about these recent papers.
Cows offer clues to treat human infertility
Decoding the bovine reproductive cycle may help increase the success of human IVF treatments.
Immune cells can adapt to invading pathogens
A team of bioengineers studies how T cells decide whether to fight now or prepare for the next battle.
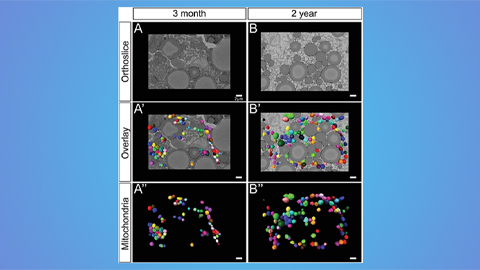
Hinton lab maps structure of mitochondria at different life stages
An international team determines the differences in the 3D morphology of mitochondria and cristae, their inner membrane folds, in brown adipose tissue.

